CRAM User Guide
Overview
Cyber Risk Assessment Management
To proceedinitiate on Onboardingthe Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM), youonboarding process, the client should pressclick the “Get StartedStarted” button.
Figure 2. Cyber Security Risk Management - Asset Identification
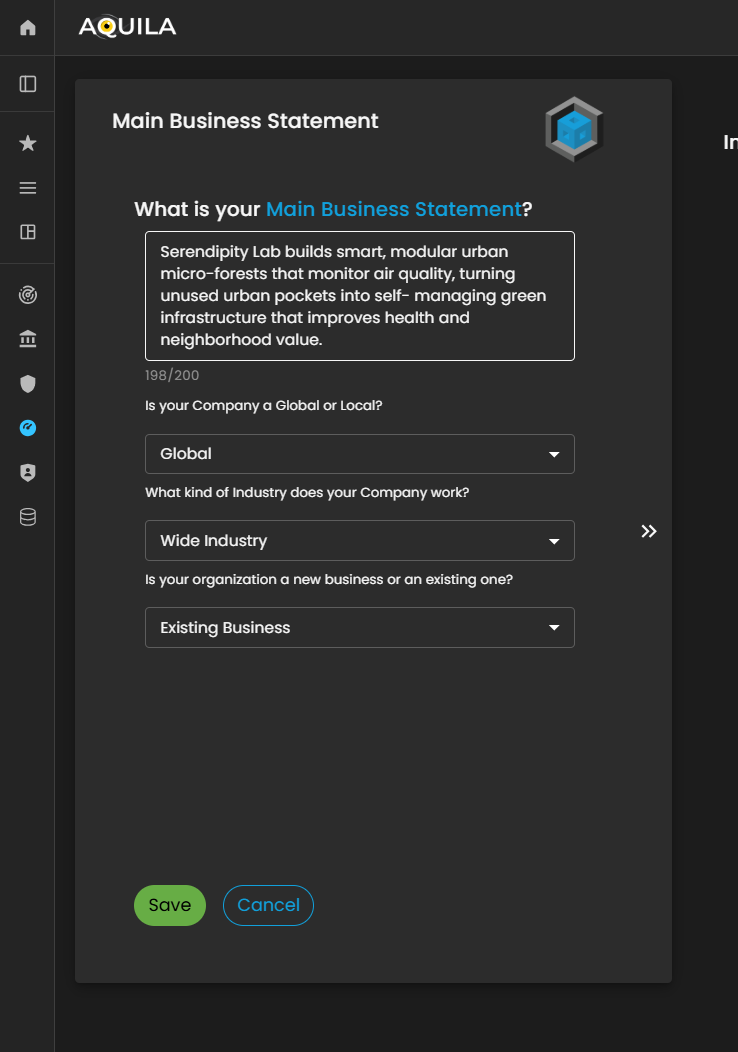
After pressingclicking the get“Get startedStarted” button, you will be directed to thisthe partnext section of the Onboarding.onboarding process. This section requires the client to provide information pertaining to their Main Business Statement.
Disclaimer: This is a simulated company created solely for client guidance and demonstration purposes. The information provided is intended to assist clients in understanding the required inputs and does not represent a real organization.
Main Business Statement
The Main Business Statement defines the organization’s core purpose, primary activities, and overall mission. It requirescaptures information regarding onwhat the clientsorganization does, the products or services it offers, and its strategic focus within the market.
The Main Business Statement.
Disclaimer:serves Thisas isthe notfoundational areference realfor companythe organization’s operations and onlydecision-making. madeIt ensures that all subsequent risk assessments, critical business processes, and functions within the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) framework are aligned with the organization’s mission and objectives, providing context for client'sevaluating guidancevulnerabilities, ondependencies, whatand tocyber input.risk impacts.
Figure 3. Cyber Security Risk Management - Main Business Statement
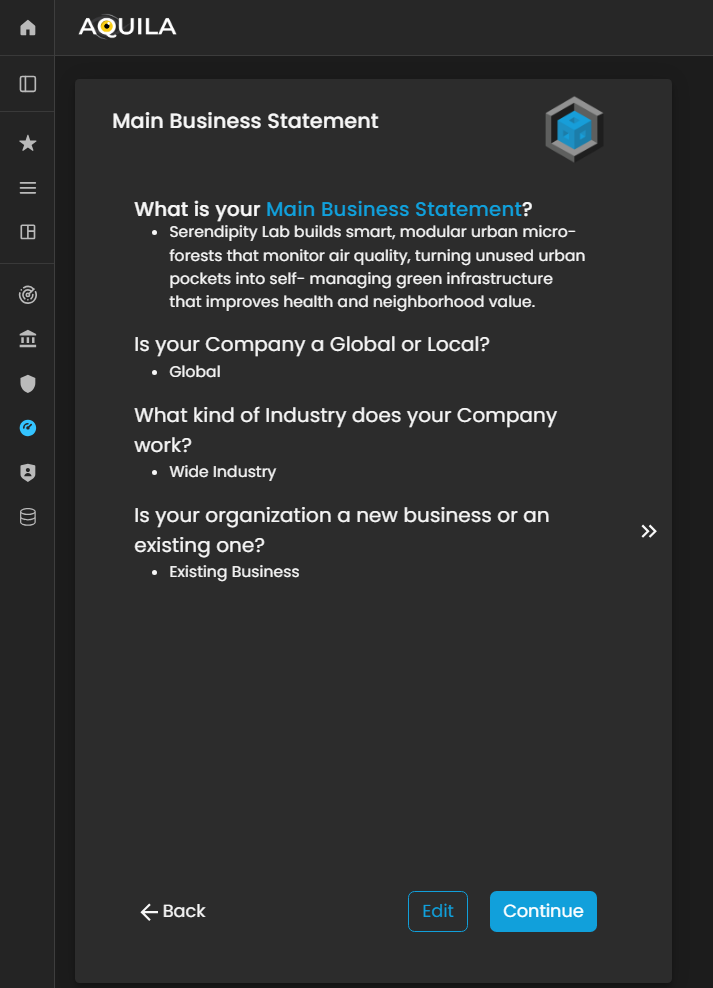
AfterThe addingclient can edit their Main Business Statement through the necessaryEdit section. The Edit button is located below, next to the Continue button, allowing the client to update or refine their organization’s core purpose, activities, and strategic focus as needed.
Figure 3.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Main Business Statement / Edit Section
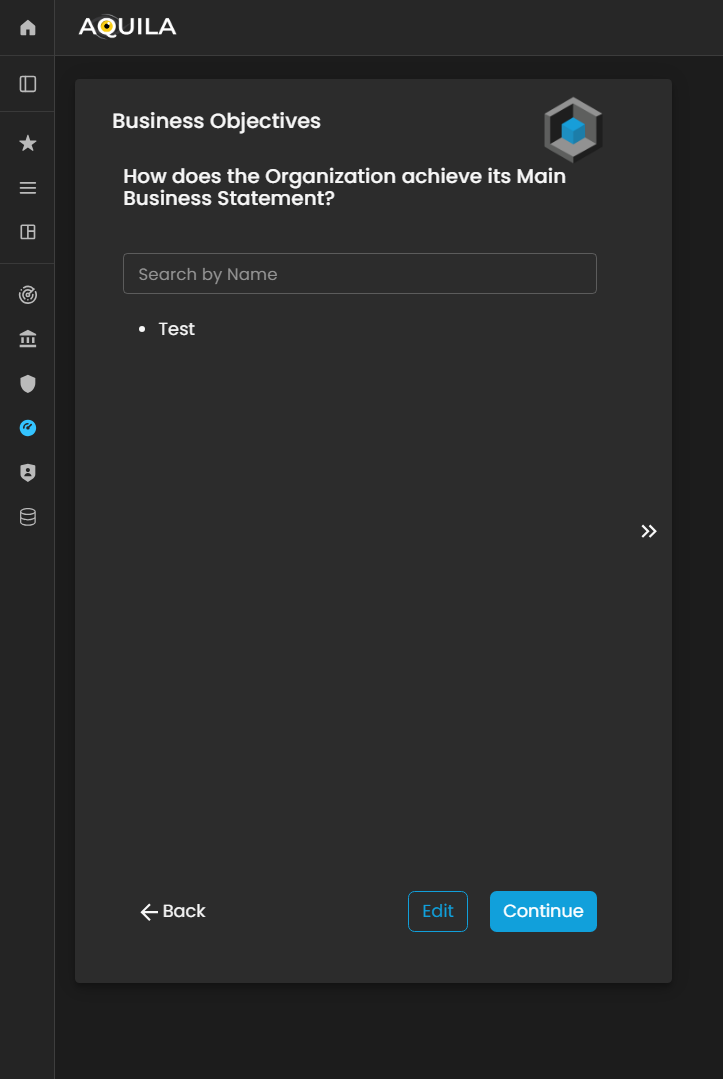
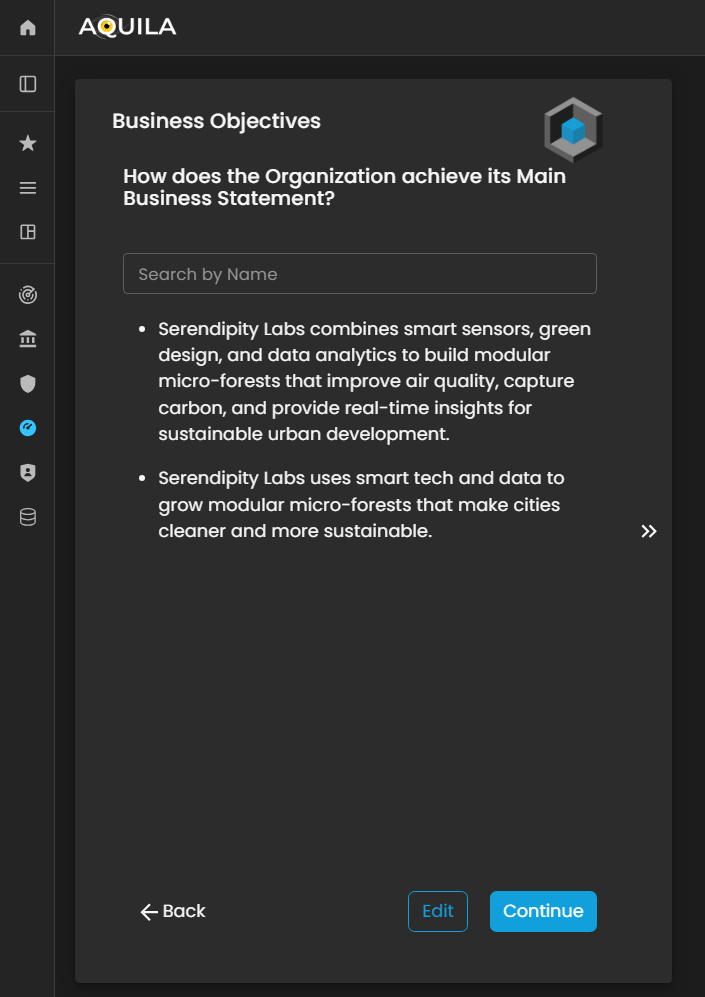
Business Objectives
After entering the required information and pressingclicking save,“Save,” ityou will redirectbe youredirected to this page. The client can editmodify the informationprovided heredetails by pressingselecting the edit“Edit” option to update or add their businessBusiness objectives.Objectives.
Figure 3.4. Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Objectives
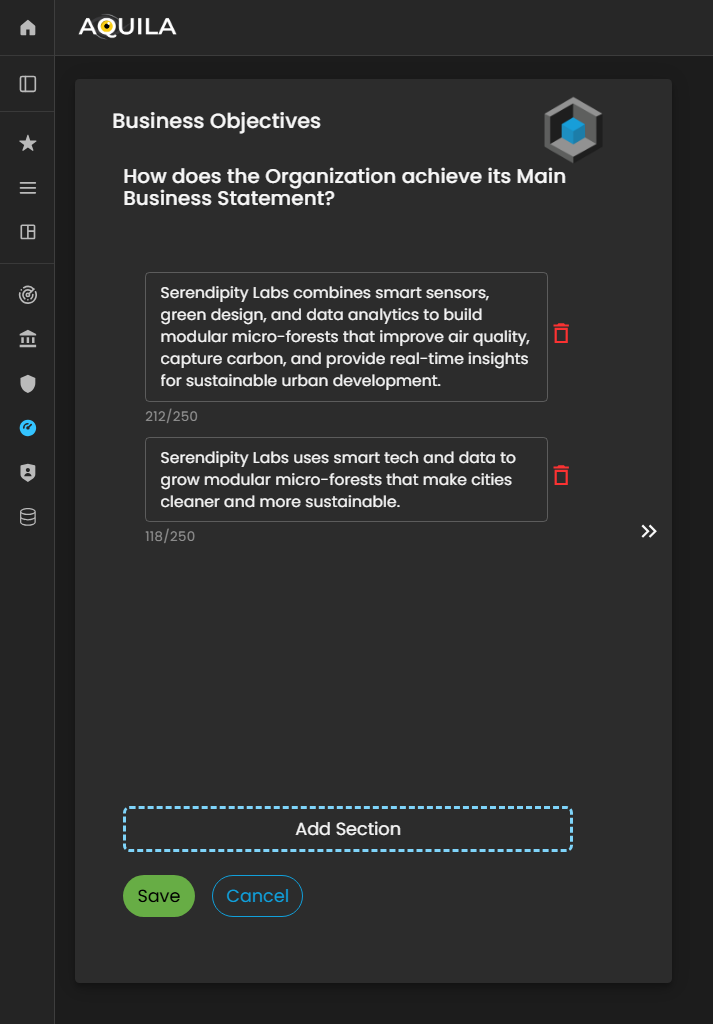
Here'sThis is the editEdit sectionBusiness ofObjectives the business objective,section, where the client can addinput, modify, or update their businessBusiness objectives.Objectives as required.
Figure 4.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Objective / Edit Section
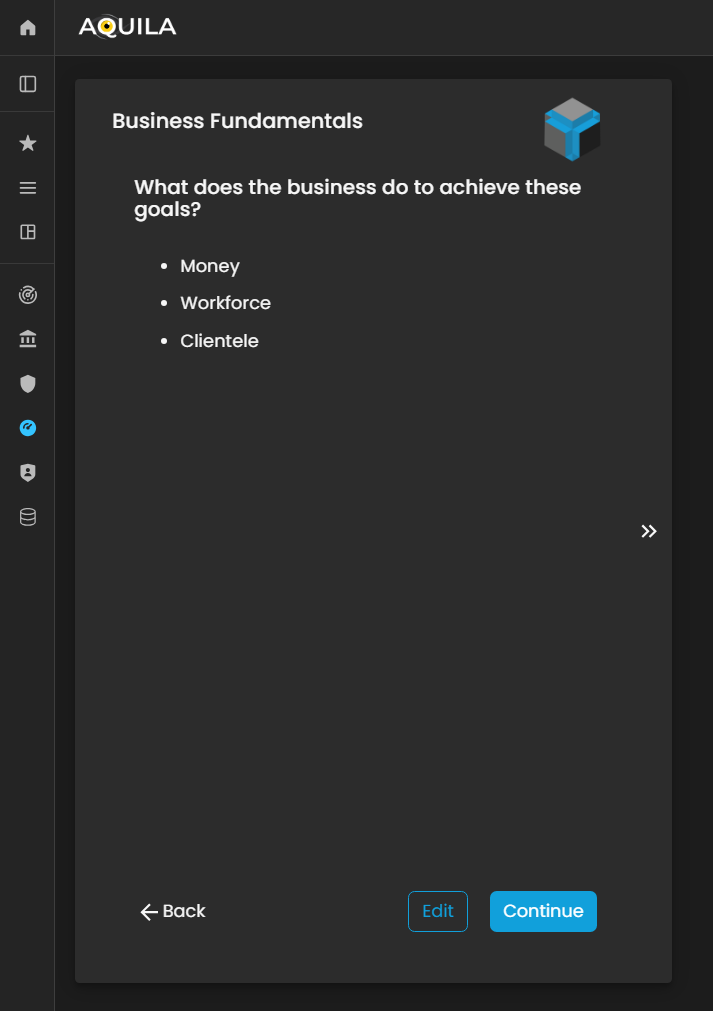
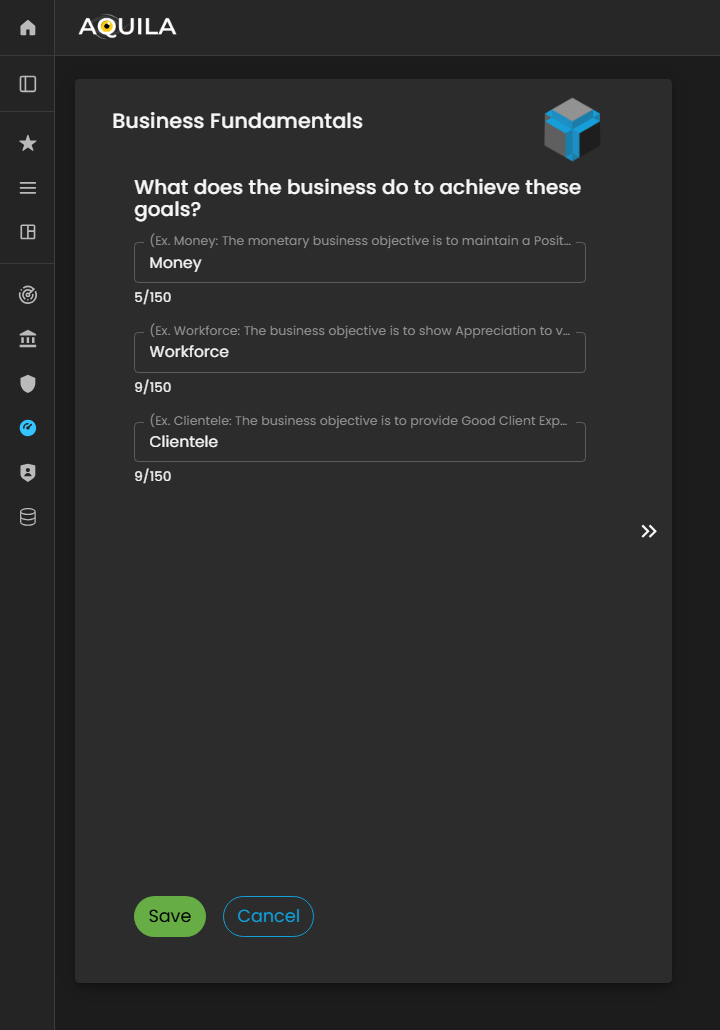
Business Fundamentals
After pressingclicking the save“Save” buttonbutton, ityou will thenbe redirect youredirected to the Business Fundamentals page. On this pagepage, about business fundamentals. Thethe client can alsoreview and edit their businessBusiness fundamentalsFundamentals, andadding addor whatmodifying alignsentries to ensure alignment with their ownorganization’s fundamentals.core principles.
Figure 5. Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Fundamentals
Here'sThis is the editEdit sectionBusiness Fundamentals section, where the client can configure and refine the foundational elements of businesstheir fundamentals.organization’s operational and strategic framework. Within this interface, users can update, modify, or expand their Business Fundamentals to ensure alignment with corporate governance standards, risk management protocols, and organizational objectives.
Figure 5.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Fundamentals / Edit Section
After adding and pressing save it will redirect you to
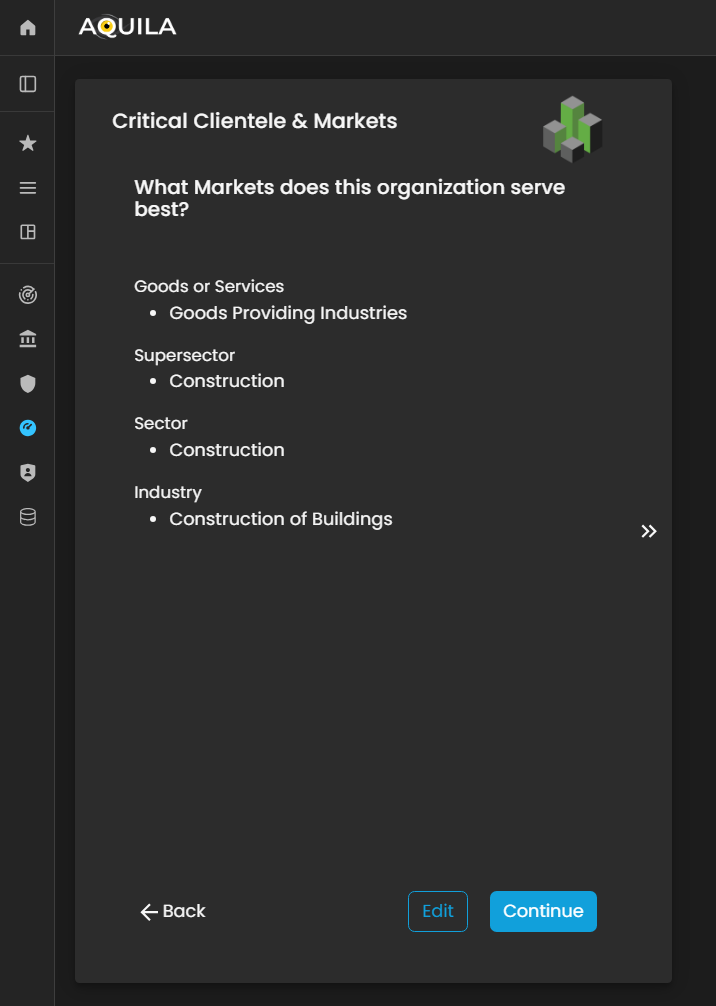
Critical Clientele & Markets.Markets
After entering the required details and clicking the “Save” button, you will be redirected to the Critical Clientele & Markets section. In this module, the client is required to identify and document key customer segments, target markets, and critical business relationships that significantly influence the organization’s operational continuity and strategic objectives.
Figure 5.6. Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Clientele & Markets
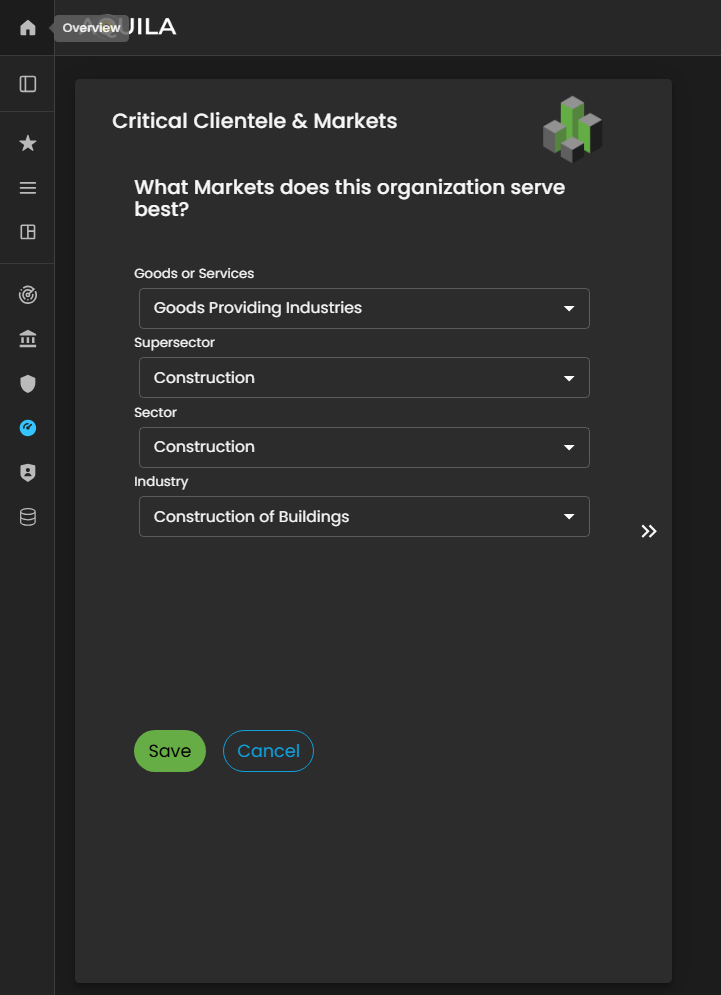
HereThis is the edit section of theEdit Critical Clientele & Markets section, where the client can update or modify essential information related to change any necessary information about their goods or services,services, supersector,supersector, sector,sector, and industry.industry classifications.
Figure 5.6.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Clientele & Markets / Edit Section
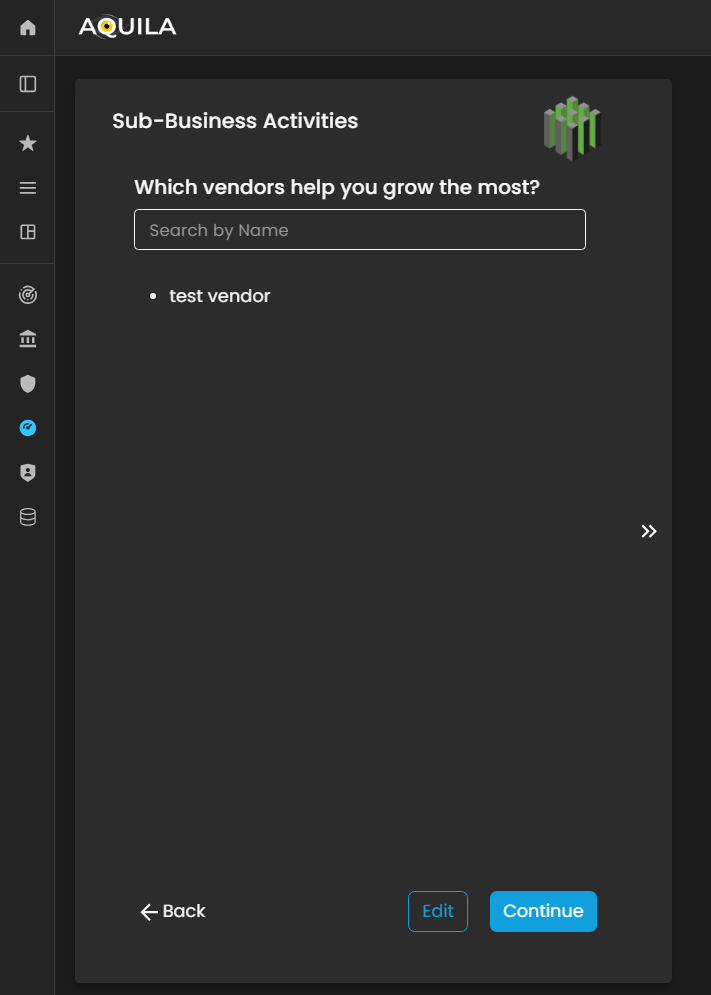
Sub-Business Activities
In this section, the client is prompted to identify the vendors and third-party service providers that contribute most significantly to the organization’s growth and operational efficiency.
By specifying key vendors, the client helps establish a clear understanding of external dependencies and supply chain relationships that are critical to business performance.
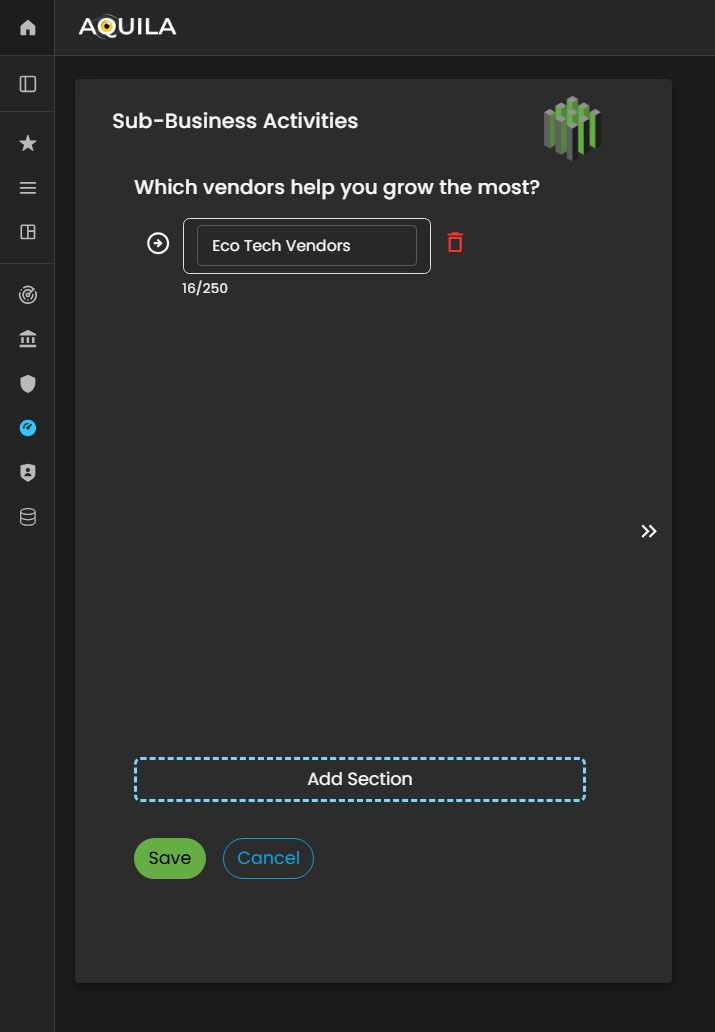
Figure 5.7. Cyber Security Risk Management - Sub-Business Activities
Here'sThis is the edit section of theEdit Sub-Business Activities section, where youthe client can addadd, modify, or remove vendors and third-party partners that helpplay a significant role in the client'organization’s growth and operational success.
Within this interface, users can input detailed information about each vendor, including their business grow.function, service category, and strategic contribution to the client’s operations. Maintaining accurate and comprehensive vendor data in this section is essential, as it allows the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to evaluate third-party dependencies, identify potential supply chain vulnerabilities, and incorporate vendor-related risks into the organization’s overall cyber risk profile.
Figure 5.7.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Sub-Business Activities / Edit Section
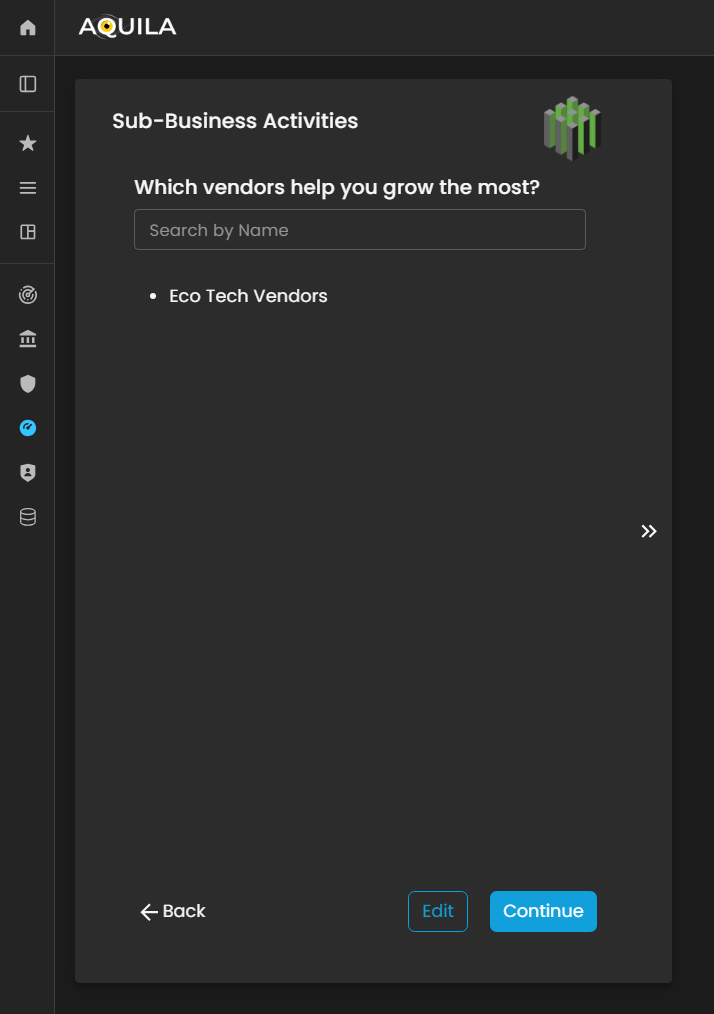
Then afterAfter saving the edit, it will bringedits, the client will be redirected back to the sub-businessSub-Business activitiesActivities page, where theyall newly added vendors and associated details will be displayed. This allows the client to review and verify the entered vendor information for accuracy and completeness.
Once the review is complete, the client can seeclick theirthe added“Continue” vendors. Then Press continuebutton to proceed Onboardingwith the business.next stage of the Business Onboarding process within the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform. This ensures that all vendor-related data is properly integrated into the organization’s profile, supporting a more comprehensive assessment of operational dependencies and cyber risk exposure.
Figure 5.7.2 Cyber Security Risk Management - Sub-Business Activities / Edit Section
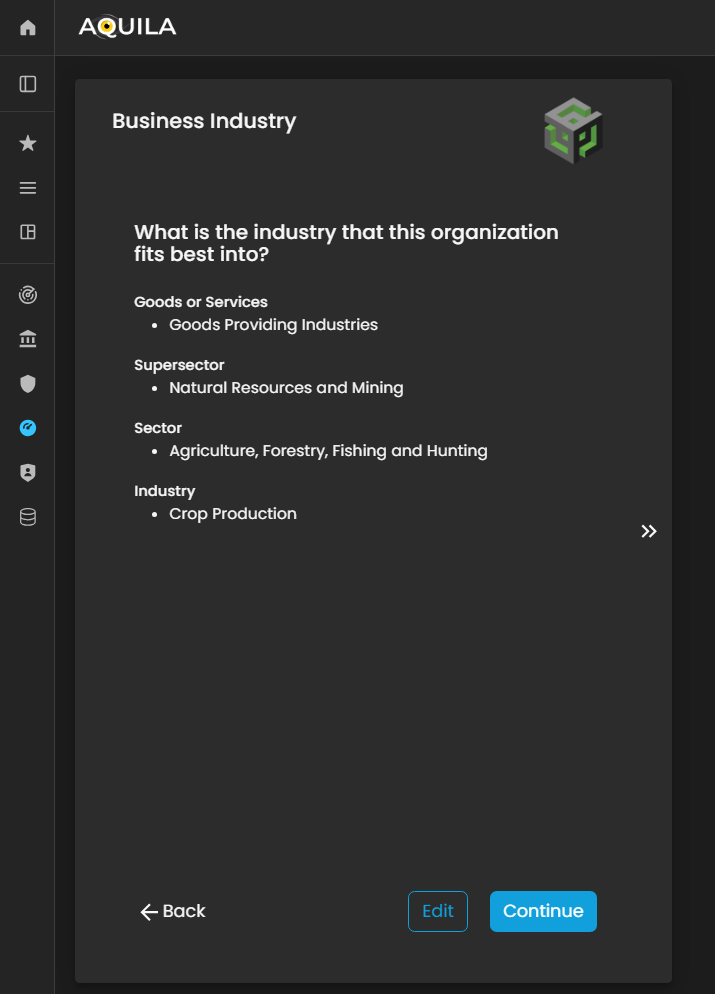
Business Industry.Industry
In this part,section, the client canis putrequired theirto specify the industry classification that best represents the organization’s core operations and market positioning. This information onhelps what isalign the organization bestwithin fitthe into.appropriate industry, supersector, and sector categories, ensuring accurate benchmarking and risk profiling.
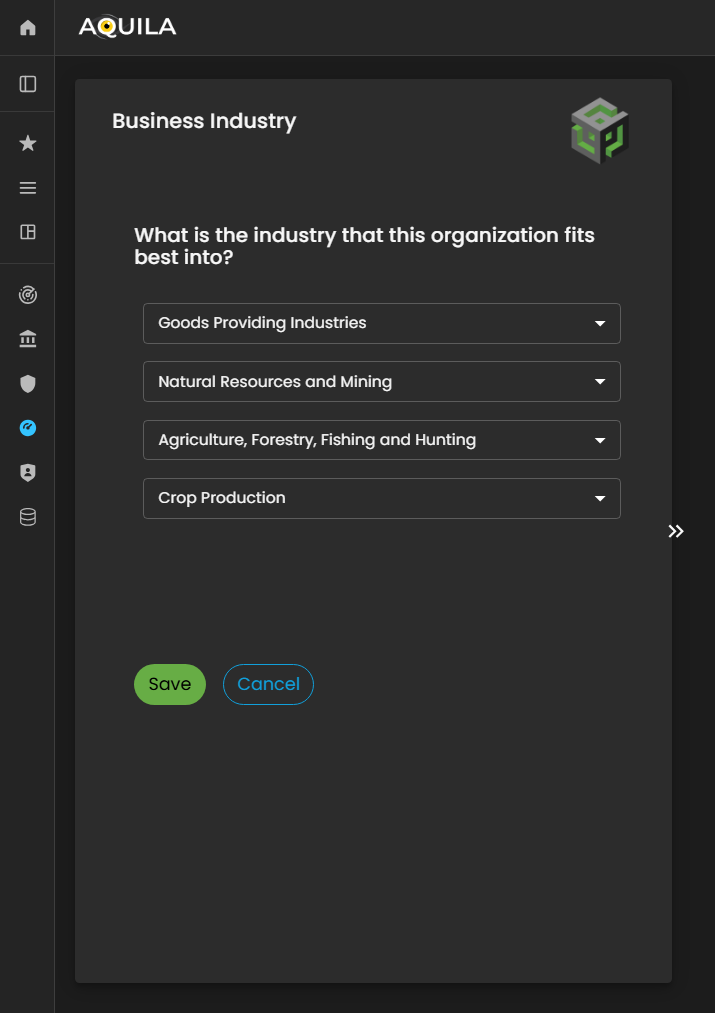
The client can also edituse the Edit function to update or add any necessaryrelevant informationdetails aboutpertaining to their businessBusiness industry.Industry, such as industry-specific activities, regulatory environments, or emerging market segments. Maintaining precise and current industry data enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to generate more accurate risk analyses, identify industry-specific threat patterns, and tailor recommendations based on the organization’s operational landscape.
Figure 5.8. Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Industry
HereThis is the editEdit sectionBusiness ofIndustry the business industrysection, where the client can changemodify anyor necessaryupdate key information regardingrelated onto their business.organization’s industry classification and operational scope.
Within this interface, the client can adjust details such as industry type, market segment, and business category to ensure alignment with the organization’s current structure and strategic direction. Accurate and up-to-date information in this section is essential, as it directly influences how the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform contextualizes the organization within its industry landscape.
Figure 5:9.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Industry / Edit Section
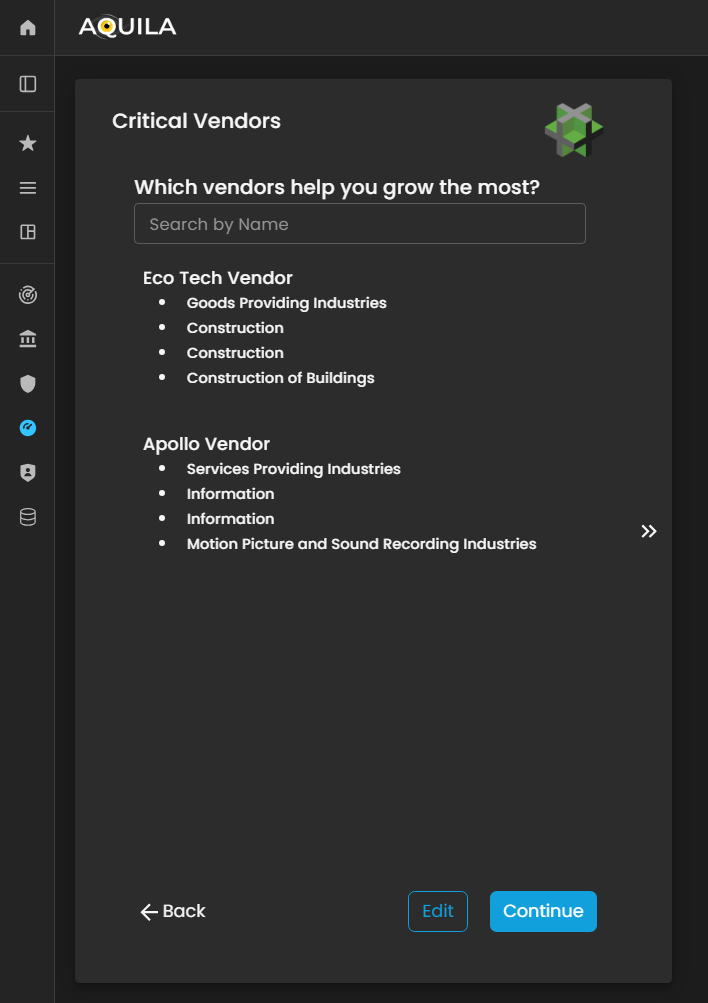
Critical Vendors
After saving the information forunder Business Industry,Industry, thenthe itclient will redirectbe youredirected to the Critical Vendors.Vendors Theresection. In this stage, the client is prompted to identify and document the key vendors and third-party entities that play a vital role in supporting the organization’s operations, service delivery, and business continuity.
An Edit function is also anavailable, editallowing functionthe hereclient to addadd, update, or refine any necessary information regardingrelated onto thetheir clientcritical business.vendors. This includes details such as vendor name, service category, criticality level, and dependency type.
Figure 5:10. Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Vendors
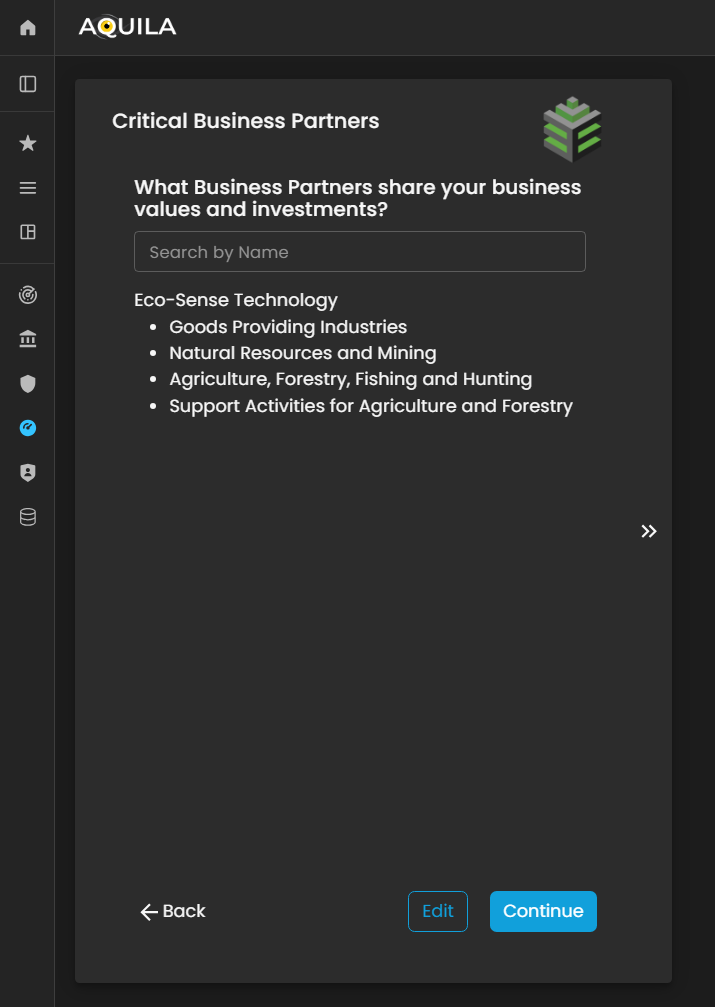
Critical Business Partners
After proceedingcompleting tothe Critical Vendors,Vendors it will then redirectsection, the client will be redirected to the Critical Business Partners. Critical Business Partners ismodule. forThis yoursection focuses on identifying and documenting strategic business partners—organizations or entities that sharesshare mutual values, goals, and investments with the sameclient’s valuesbusiness.
These partnerships often play a key role in driving growth, innovation, and investments.long-term Thesustainability. Through the Edit function, the client can add or update information about their critical business partnerspartners, throughincluding thepartner editnames, button.collaboration scope, strategic alignment, and shared initiatives.
Figure 5:11. Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Partners
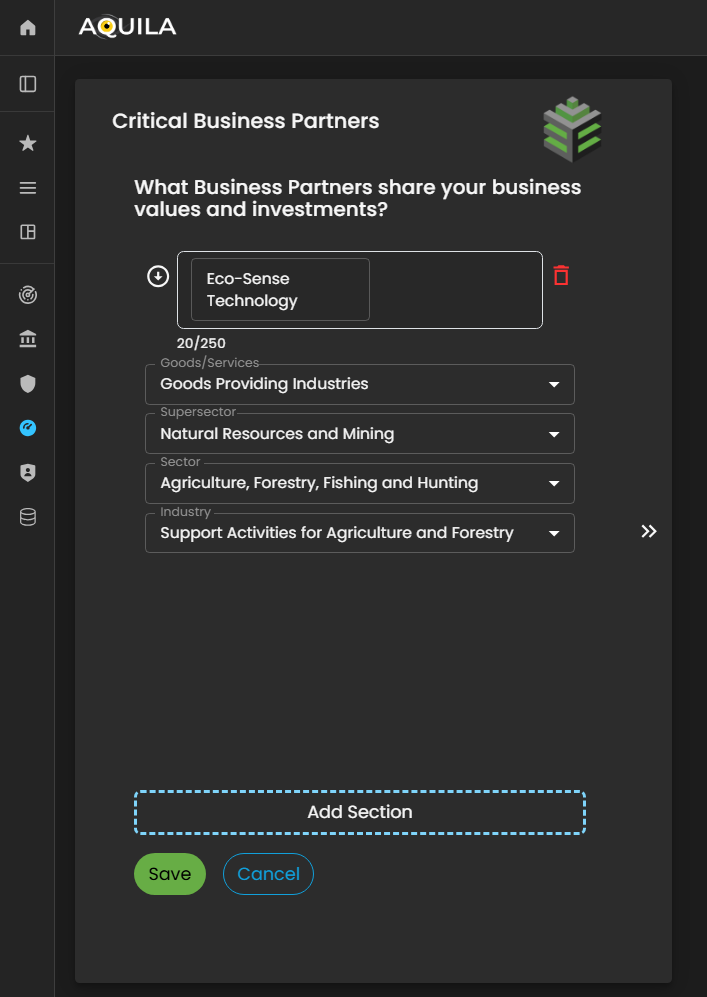
Figure 5:11.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Partners / Edit Section
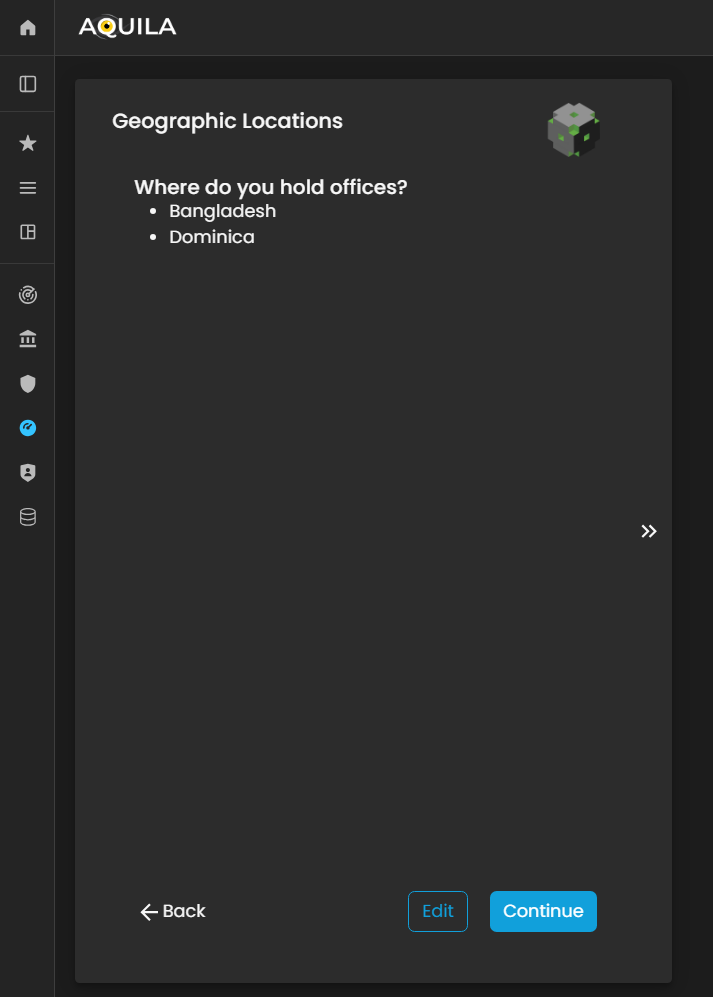
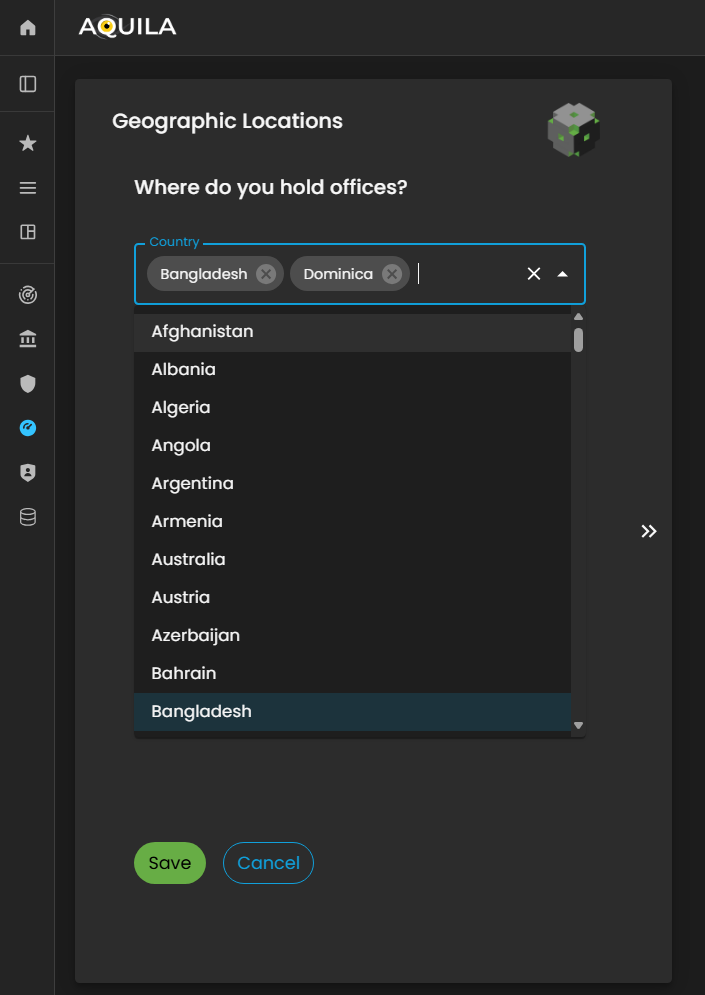
Geographic Locations
After adding and saving the details of your criticalCritical businessBusiness partnersPartners, thenthe itsystem will automatically redirect you to proceedthe in Geographic Locations.Locations Geographicsection. LocationThis section is designed to capture and document the physical locations where the client’s organization operates, including headquarters, regional offices, branch sites, and other operational facilities.
By providing accurate geographic information, the client holdsenables theirthe offices.Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess location-based risks, such as regional threat exposure, regulatory variations, and environmental or geopolitical factors that may influence the organization’s cyber risk posture.
The client can also use the Edit function within this section to add, update, or remove office locations as necessary, ensuring that all operational sites are accurately represented for a comprehensive risk assessment and business continuity evaluation.
Figure 5:12. Cyber Security Risk Management - Geographic Location
TheIn the Edit Geographic Locations section, the client can add or update their geographicorganization’s locationoperational onsites by clicking the editarrow sectionicon byto pressingexpand the arrowinput key.fields. This interface enables the client to specify the countries where their organization is located or conducts business operations.
Figure 5:12.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Geographic Location / Edit Section
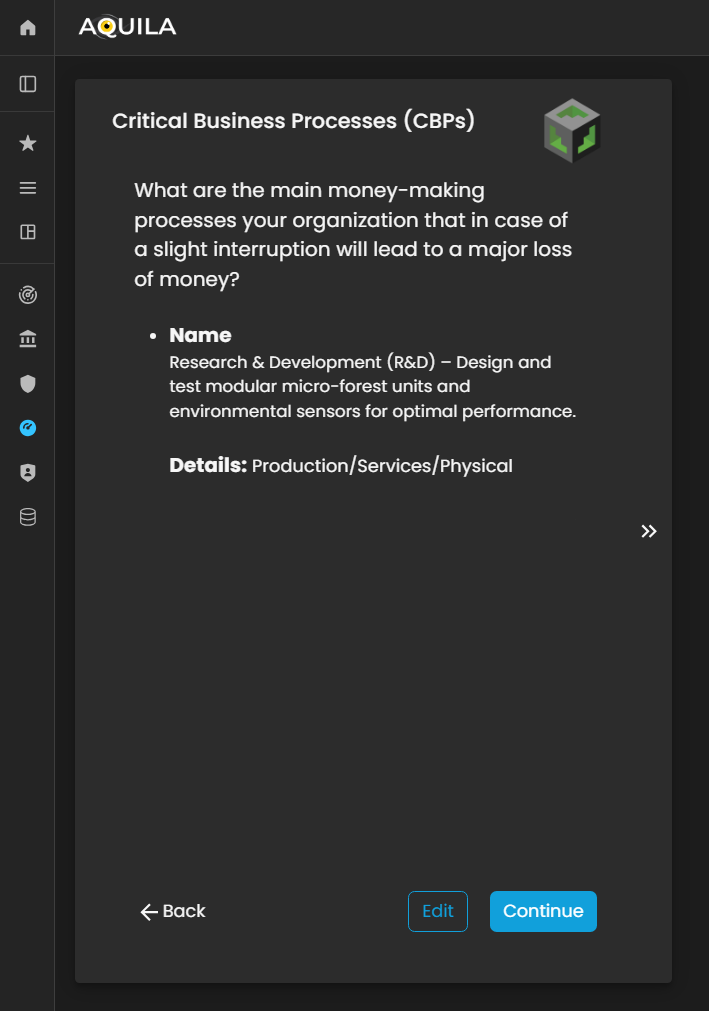
Critical Business Processes (CBP's)
After saving the Geographic Location of the officesdetails and pressingclicking continue“Continue,” the client will be redirected to thisthe Critical Business Processes (CBP's).CBPs) Criticalsection. BusinessThis Processessection isfocuses on identifying and documenting the clients'organization’s money-makingcore processes.revenue-generating Theactivities—the clientessential canprocesses alsothat adddirectly theircontribute money-makingto processbusiness throughprofitability edit.
and operational sustainability.
Figure 5:13. Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Processes (CBP's)
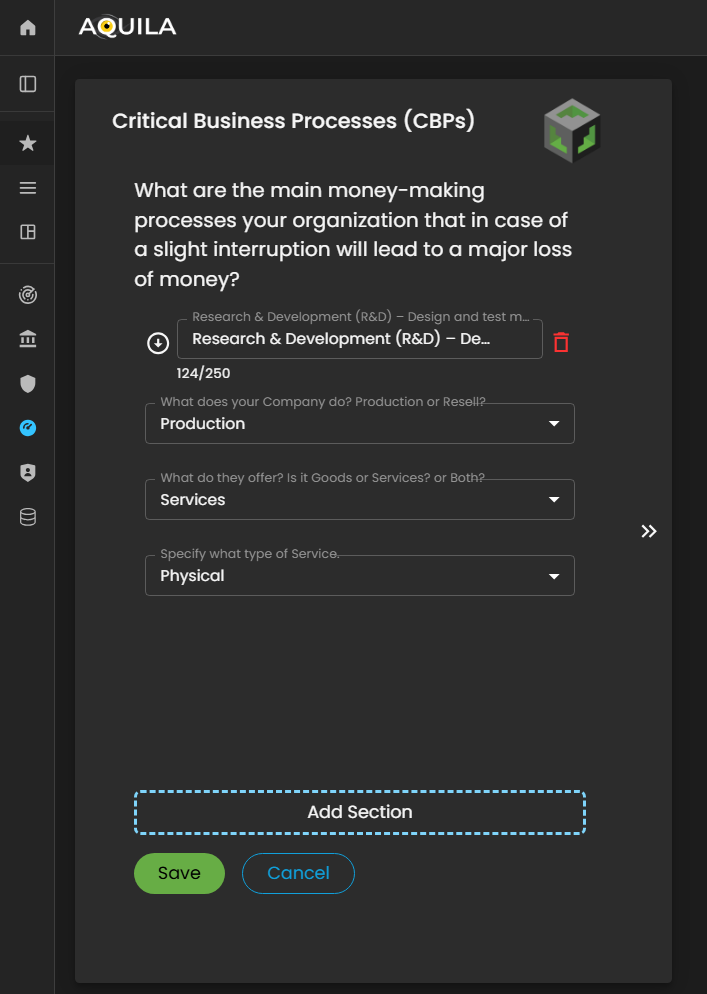
Here inIn the edit section ofEdit Critical Business Processes (CBP's)CBPs) section, the client can addinput detailed information about their informationorganization’s regarding on their money-makingrevenue-generating processes. TheThis clientincludes can also addspecifying what theirthe company do,does, whatthe theyproducts offeror services it offers, and whatthe type of servicebusiness theyactivities do.that contribute directly to its financial performance.
Figure 5:13.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Processes (CBP's) / Edit Section
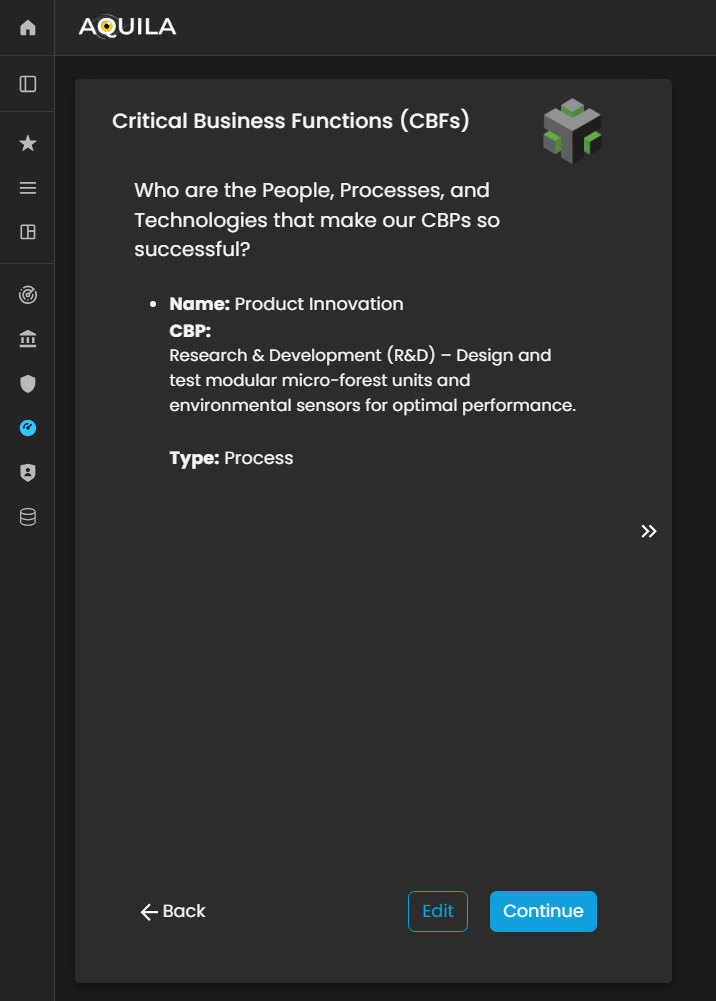
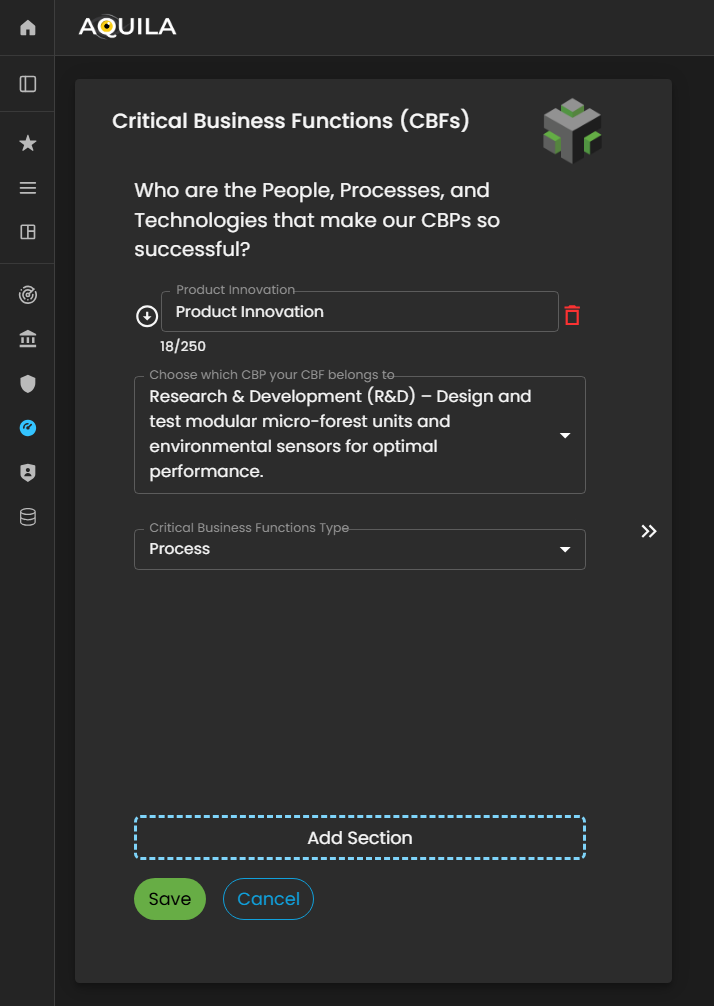
Critical Business Functions (CBF's)
After saving and addingentering the correctrequired inputinformation for CBP'sthe Critical Business Processes (CBPs), the client will be redirected to the Critical Business Functions (CBF's)CBFs) section. This section whereis theydesigned canto addcapture informationand on who aredocument the people, processes, and technologies that makesenable and support the clientssuccess CBP'of the organization’s soCBPs.
Within this module, the client can identify the key roles, operational functions, systems, and technological components that are essential for maintaining business continuity and ensuring the effective execution of their core processes.
The client can adduse the Edit button to add, modify, or update their CBF'sCritical throughBusiness theFunctions, editensuring button.that all dependencies and enablers of their business operations are accurately reflected.
Figure 5:14. Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Functions (CBF's)
HereThis is the editEdit sectionCritical ofBusiness theFunctions CBF's(CBFs) section, where the client can addinput theirdetailed information about what are the people, processes, orand technologies that keepscontribute to the continued success and stability of their business successful.operations.
In afterthis interface, the client can specify key personnel roles, essential operational workflows, and supporting technological systems that directly enable their Critical Business Processes (CBPs). Accurately identifying these elements ensures that all business enablers are clearly defined and properly aligned with the organization’s strategic and operational goals.
After entering and saving the required information, itthe system will thenautomatically redirect the client back to the Critical Business FunctionFunctions (CBF's)CBFs) topage. see if they have put their correct input regarding on their CBF's then after thatHere, the client can pressreview continueand verify that all inputs have been correctly recorded. Once confirmed, the client can click “Continue” to proceed.proceed to the next stage of the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) onboarding process.
Figure 5:14.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Critical Business Function (CBF's) / Edit Section
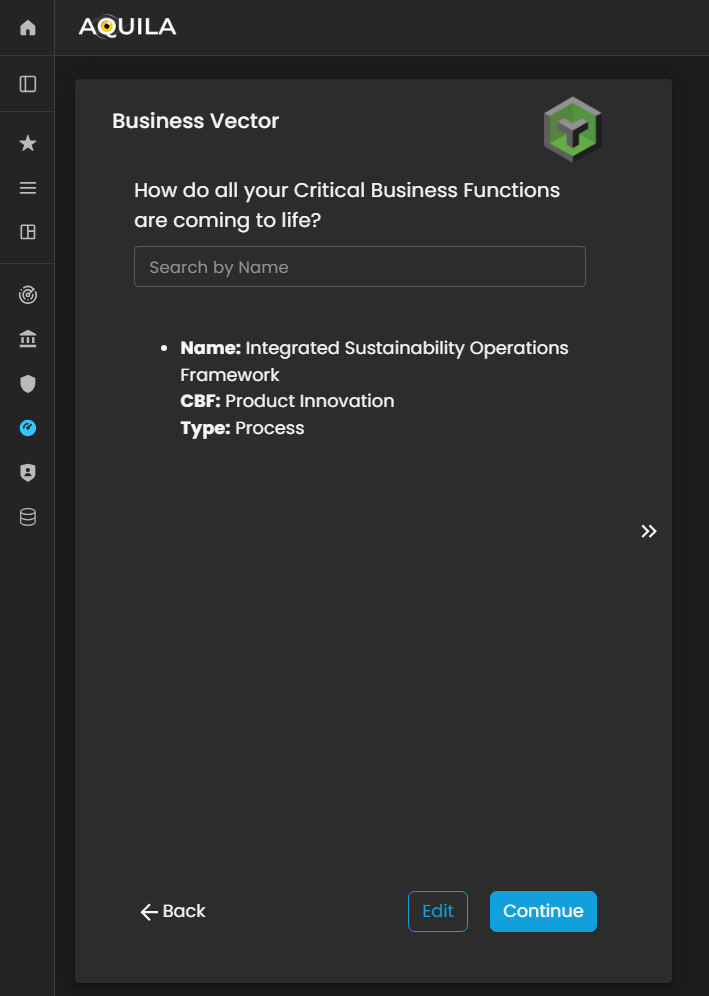
Business Vector
Business Vector is aboutrepresents how the clientsclient’s Critical Business Functions (CBF's)CBFs) are comingexecuted and brought to life.
life within the organization. This section focuses on illustrating the operational dynamics—how people, processes, and technologies interact to deliver business outcomes and sustain critical operations.
Through the Business Vector, the client can define how their organizational capabilities translate into functional performance, including workflows, process integrations, and system interactions that support the execution of Critical Business Processes (CBPs).
Figure 5:15. Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Vector
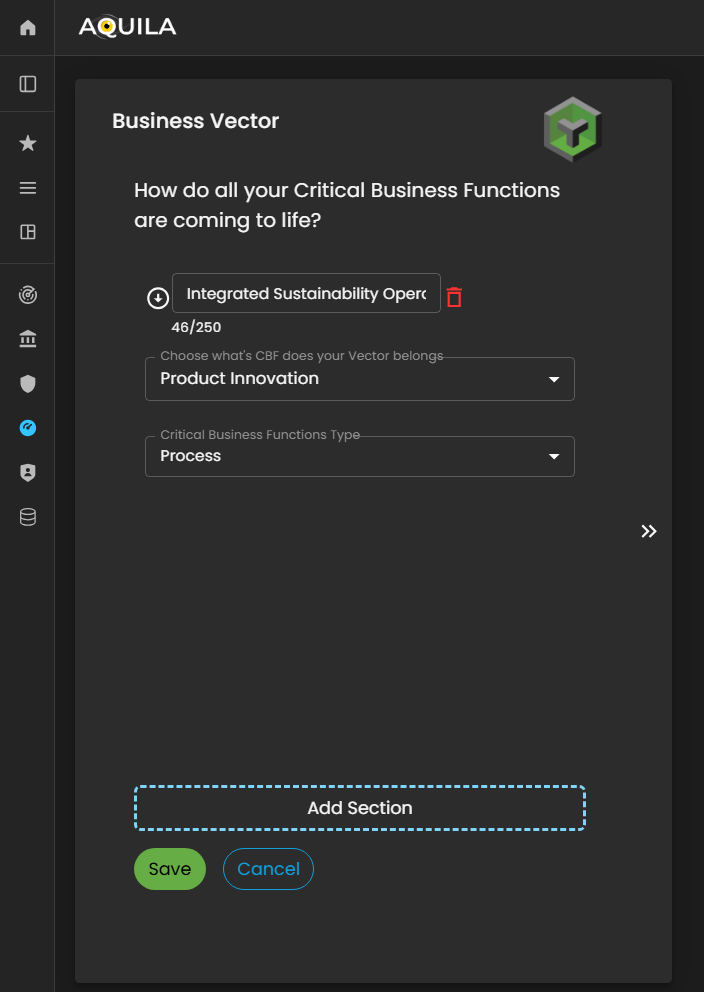
In the Edit Business Vector edit section wheresection, the client can the namedefine and whatmanage key details related to their organization’s operational dynamics. This includes specifying the clientname CBF'sof doesthe yourBusiness Vector and identifying the Critical Business Function (CBF) to which the vector belongs.is associated.
Figure 5:15.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Vector / Edit Section
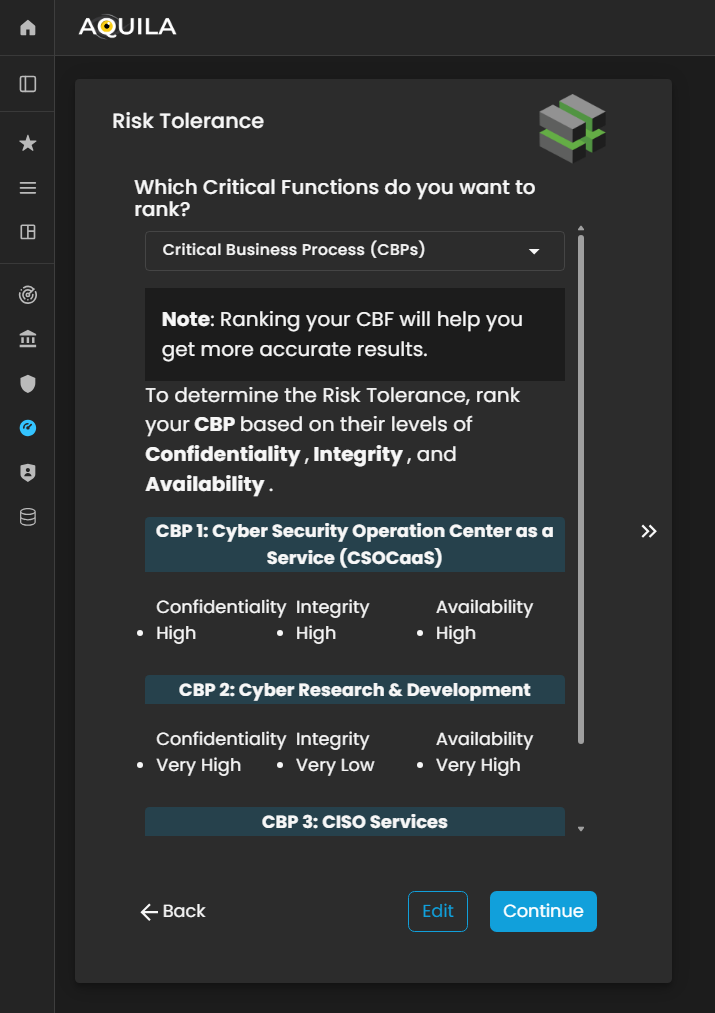
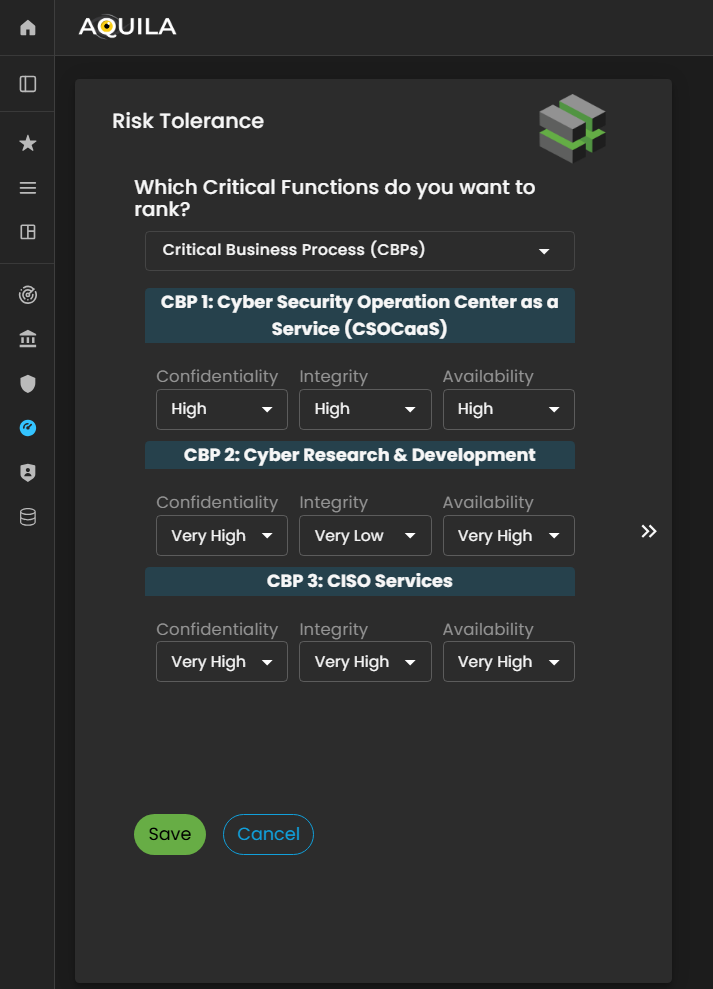
Risk Tolerance
In this sectionsection, the client can seeview and rank their Critical Functions based on importance, impact, or priority within the organization. This ranking helps determine which Criticalfunctions Functionare canmost bevital rank.to Thesustaining business continuity and achieving strategic objectives.
Additionally, the client can alsotoggle switchbetween toviewing Critical Business FunctionFunctions (CBF's)CBFs) orand Critical Business ProcessProcesses (CBP's)CBPs) to analyze how each contributes to the organization’s overall operational framework.
Figure 5:16. Cyber Security Risk Management - Risk Tolerance
Here'sThis is the Risk Tolerance edit sectionsection, where the client can changeadjust their confidentiality,organization’s integrity,levels of Confidentiality, Integrity, and availability.Availability. RankingEach category can be ranked from Very high -High to Very Low.Low, reflecting the organization’s tolerance toward potential risks in these areas.
By setting the appropriate levels, the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform can align its analysis with the client’s defined risk preferences and ensure that subsequent assessments accurately represent the organization’s overall security posture.
Figure 5:16.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Risk Tolerance / Edit Section
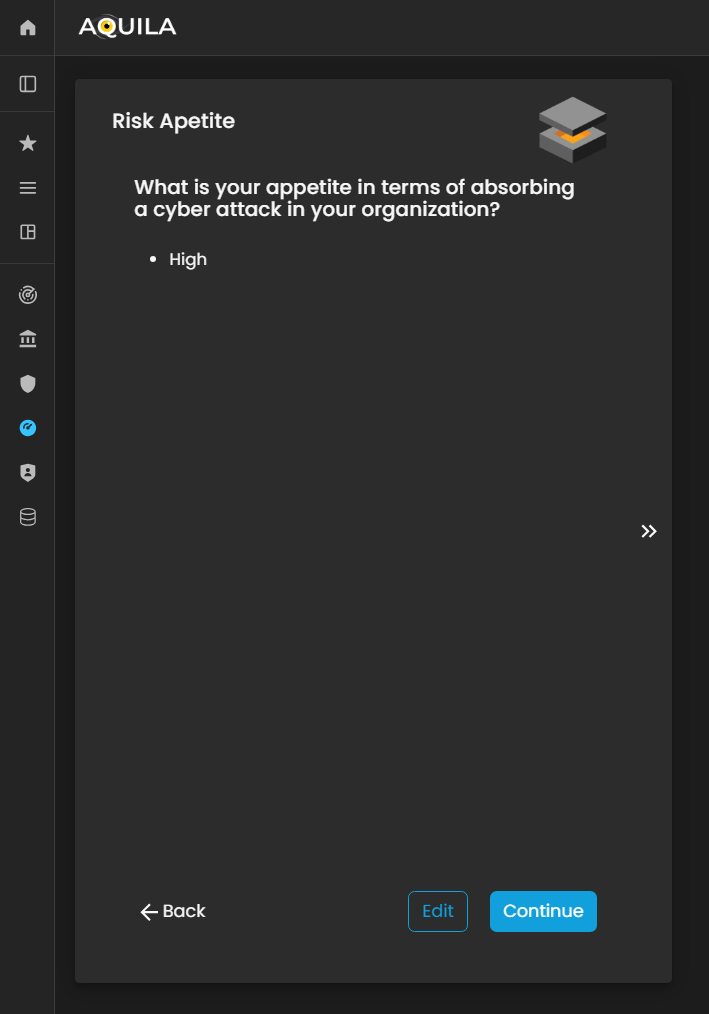
Risk Appetite
In this sectionsection, after proceedingcompleting the Risk Tolerance stage, the client will proceed to Riskthe Tolerance, Risk Appetite issection. knowingRisk Appetite represents how well yourthe organization can absorb or withstand a cyber-attackcyberattack bywithout rankingsignificant Veryimpact highon toits Veryoperations, Low.finances, or reputation.
The client can also changerank their riskorganization’s appetiteRisk throughAppetite on a scale from Very High to Very Low, depending on their capacity and willingness to manage potential cyber risks.
Through the editEdit section.section, the client can update or modify their selected level at any time to reflect changes in the organization’s risk management strategy, operational resilience, or security posture. This helps the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform provide more accurate insights and align cyber risk assessments with the organization’s current risk-bearing capability.
Figure 5:17. Cyber Security Risk Management - Risk Tolerance
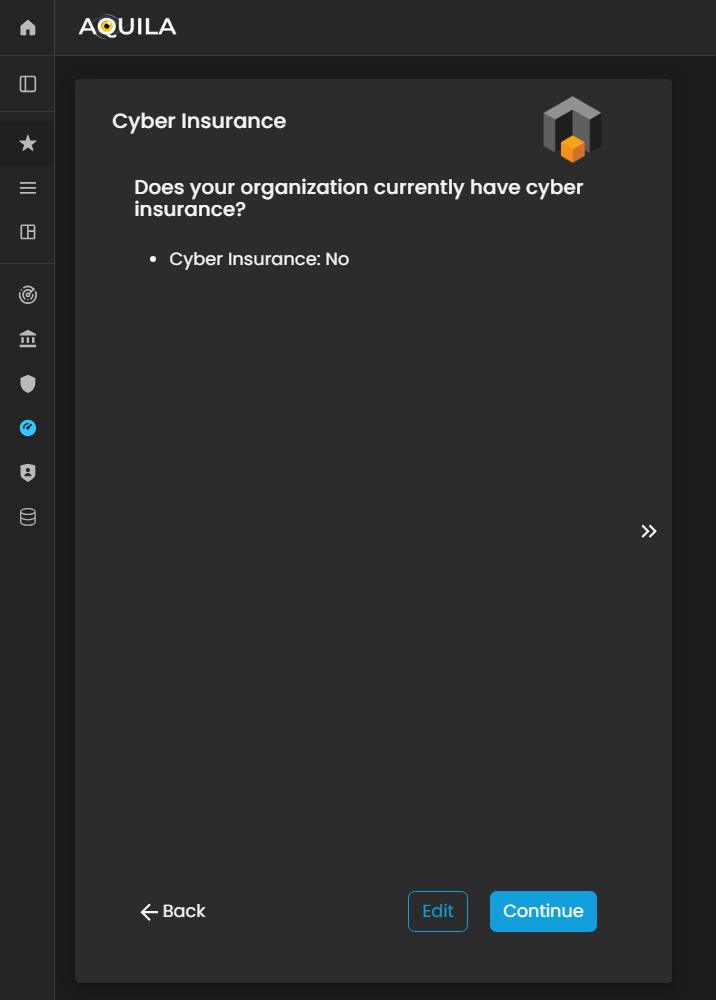
Cyber Insurance
After proceedingcompleting tothe Risk Appetite,Appetite section, the client will be directed to the Cyber Insurance,Insurance askingmodule. ifThis doessection yourasks whether the organization havecurrently holds cyber insurance?insurance Thecoverage.
Using the Edit button, the client can pickselect ifeither its Yes or No throughto indicate their organization’s status. Providing this information helps the editCyber button.Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform evaluate the organization’s risk transfer mechanisms and incorporate insurance coverage into the overall cyber risk assessment and mitigation strategy.
Figure 5:18 Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Insurance
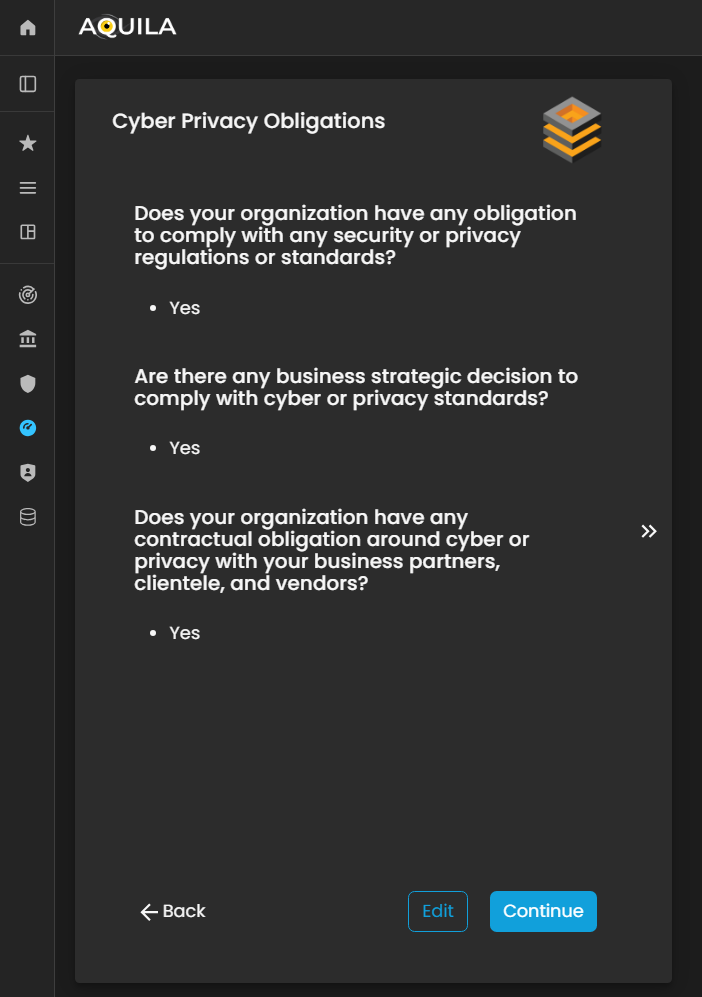
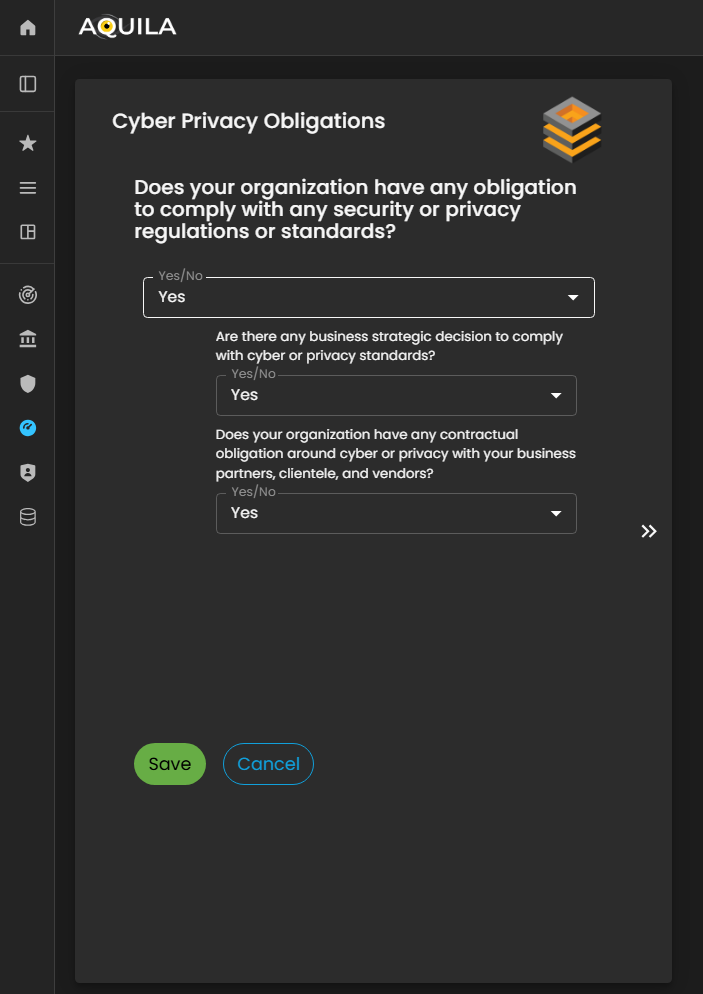
Cyber Privacy Obligation
In this section for Onboardingof the client'sBusiness business,Onboarding youprocess, the client will be asked 3three questions regardingrelated onto thetheir organization’s Cyber Privacy Obligations.
These questions are designed to assess how the organization manages, protects, and complies with data privacy requirements, including regulatory obligations, internal policies, and best practices for handling sensitive or personal information. Accurate responses help the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform evaluate the organization’s privacy posture and identify potential gaps or areas for improvement in its cyber risk framework.
Figure 5:19. Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Privacy Obligations
The client can editmodify their responseresponses toin the edit section of Cyber Privacy ObligationObligations section by pressingclicking the editEdit button below.located below the questions.
This allows the client to update, correct, or refine their answers to ensure that the information accurately reflects the organization’s data privacy practices, compliance measures, and regulatory adherence.
Figure 5:19.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Privacy Obligations / Edit Section
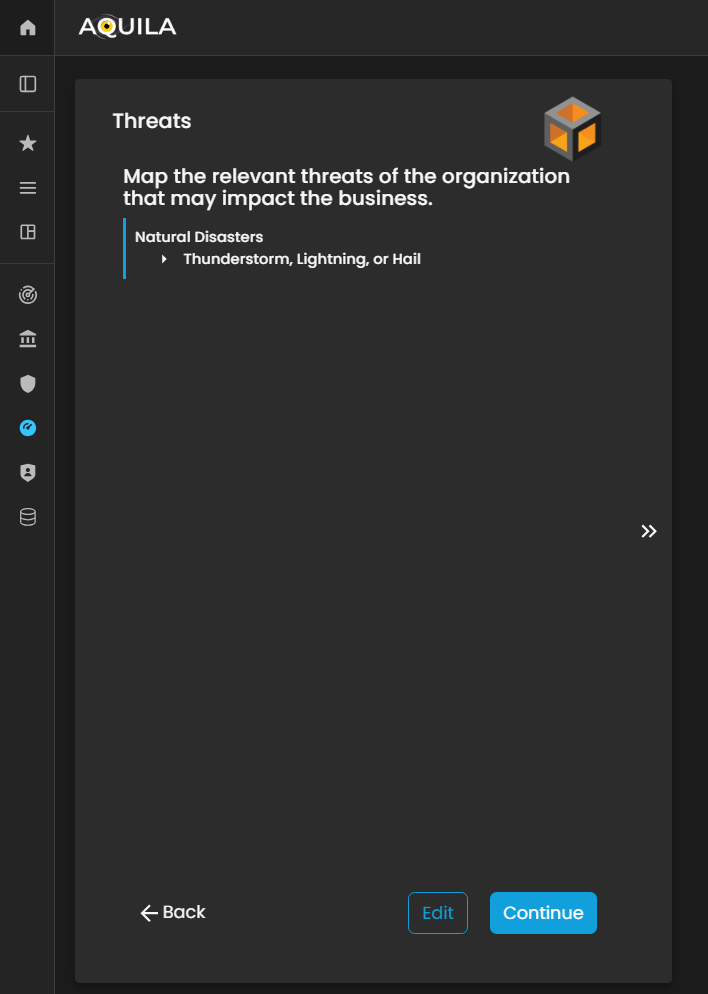
Threats
This section maps any relevant threats of the organization that maycould potentially impact the business.organization’s operations, assets, or overall business continuity.
The client can addadd, themodify, or update these threats through the editEdit section by clicking the editEdit button below. Accurately documenting organizational threats enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess risk exposure, prioritize mitigation strategies, and provide insights tailored to the organization’s specific threat landscape.
Figure 5:20 Cyber Security Risk Management - Threats
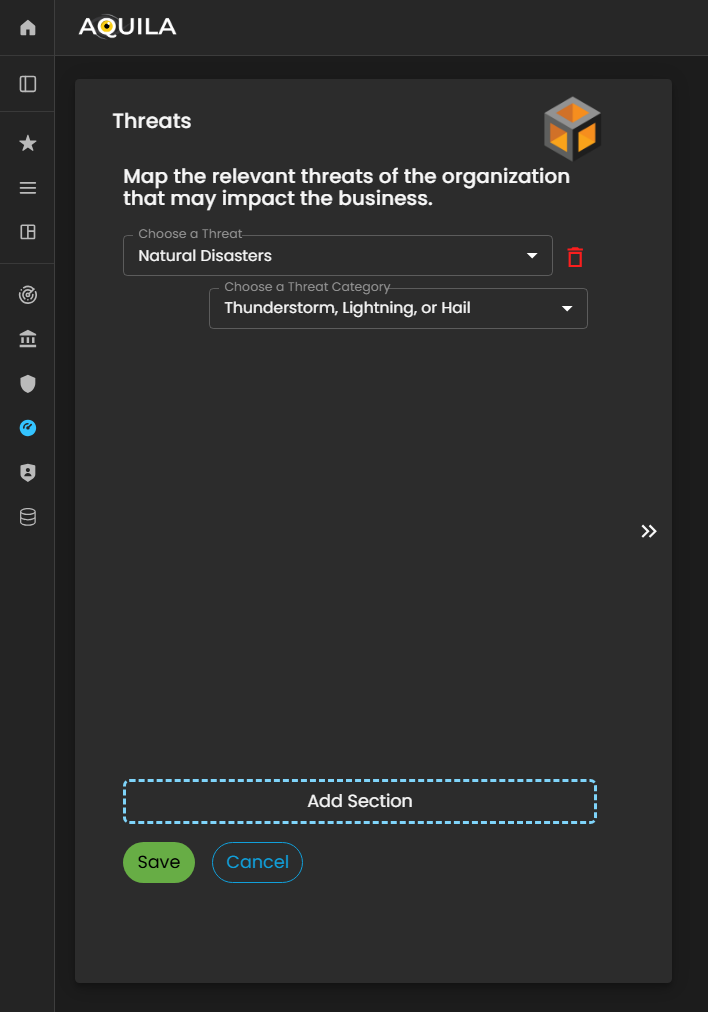
In this Edit Threats section, the client can input potential risks that may impact their organization. These threats can include natural disasters (such as earthquakes, floods, or storms) as well as man-made threats (such as cyberattacks, operational failures, or security breaches).
By accurately identifying and documenting these threats, the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform can evaluate the organization’s vulnerability, potential impact, and risk exposure, enabling more effective planning and mitigation strategies.
Figure 5:20.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Threats / Edit Section
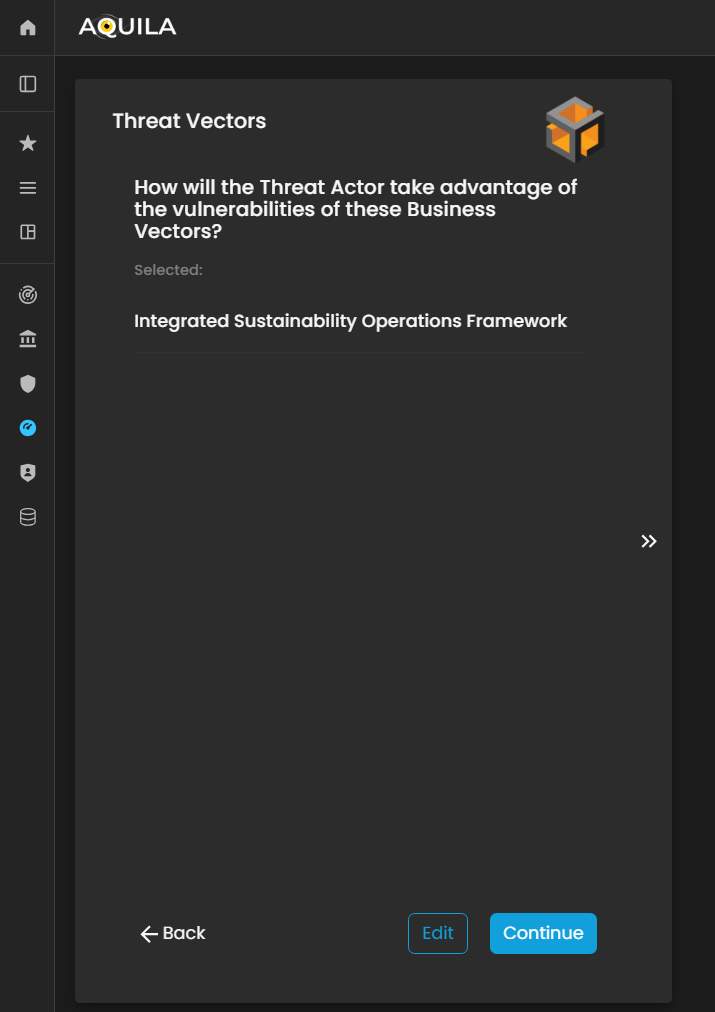
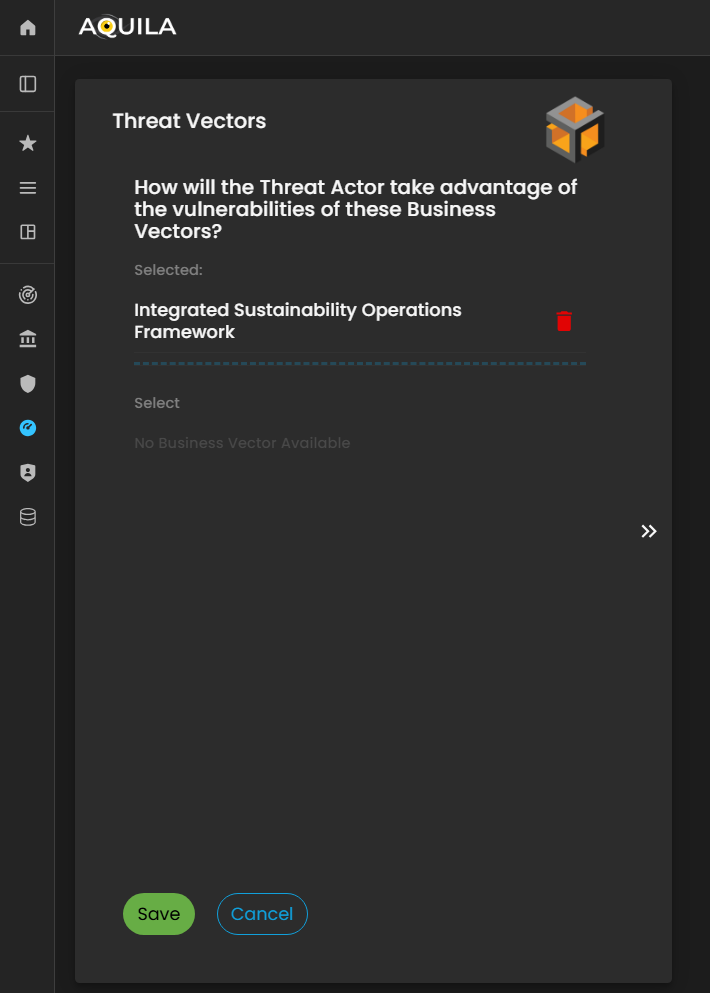
Threat Vectors
After saving the information in the Threats section, the client will proceed to the Threat Vectors module. Threat Vectors describe how an attacker or risk actor could exploit the organization’s vulnerabilities to compromise systems, processes, or data.
This section allows the client to identify potential attack methods, pathways, or techniques that could be used against the organization. By providing accurate information, the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform can analyze the relationship between threats and vulnerabilities, assess potential impact, and support the development of effective risk mitigation and defense strategies.
Figure 21 Cyber Security Risk Management - Threat Vectors
The client can specify their Threat Vectors in the Edit section by clicking the Edit button.
This allows the client to identify and document the specific methods or pathways through which vulnerabilities could be exploited, helping the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform evaluate potential risks and recommend targeted mitigation strategies.
Figure 21.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Threat Vectors / Edit Section
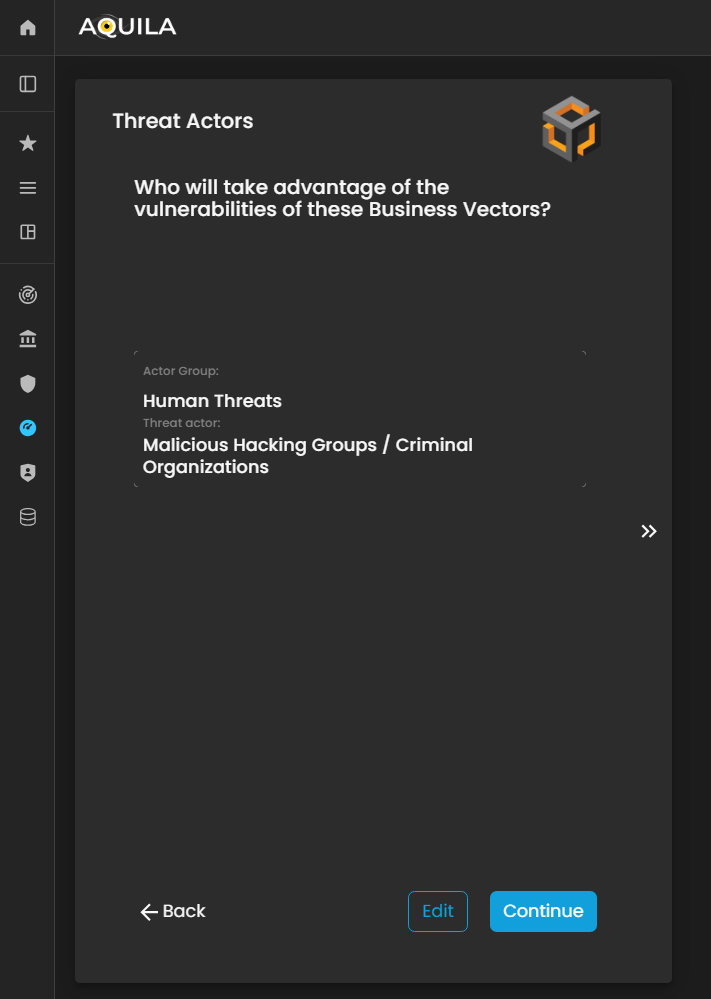
Threat Actors
In this section, Threat Actors are defined as individuals, groups, or entities that could potentially exploit vulnerabilities within the Business Vectors.
The client can add, modify, or update their identified threat actors through the Edit section by pressing the Edit button below. Accurately documenting threat actors enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess who poses a risk, how they might act, and the potential impact on the organization, supporting more effective risk management and mitigation planning.
Figure 22. Cyber Security Risk Management - Threat Actors
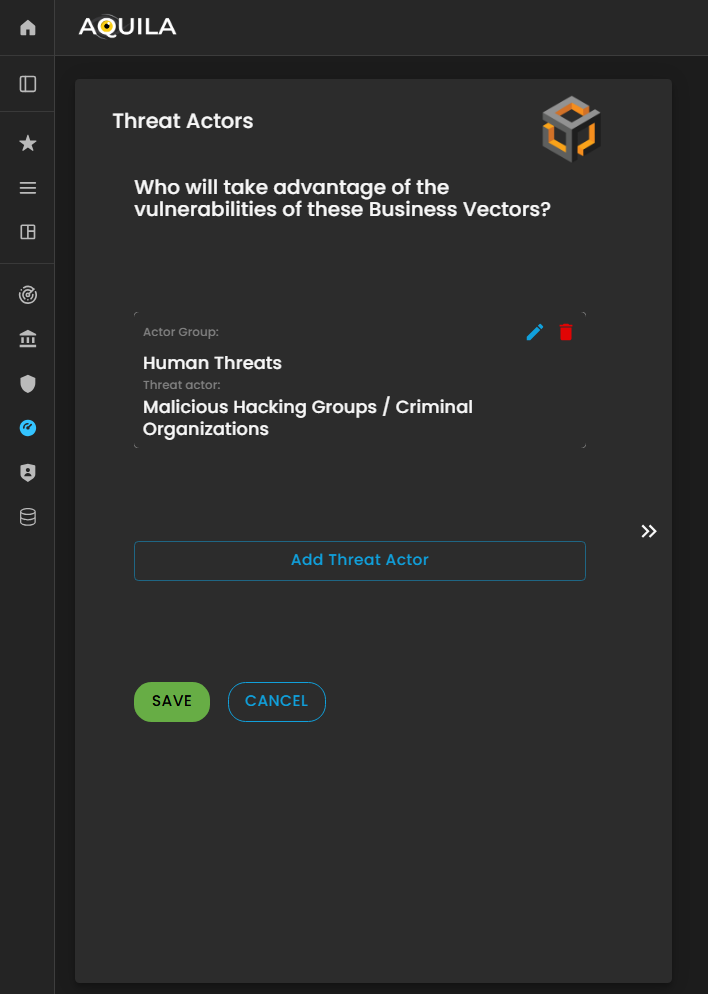
In this part of the Threat Actors section, the client can add, update, or modify information about potential Threat Actors through the Edit section.
This allows the client to specify individuals, groups, or entities that may target the organization’s Business Vectors or exploit existing vulnerabilities. Accurately documenting threat actors helps the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform evaluate risk sources, anticipate potential attacks, and support informed mitigation strategies.
Figure 22.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Threat Actors / Edit Section
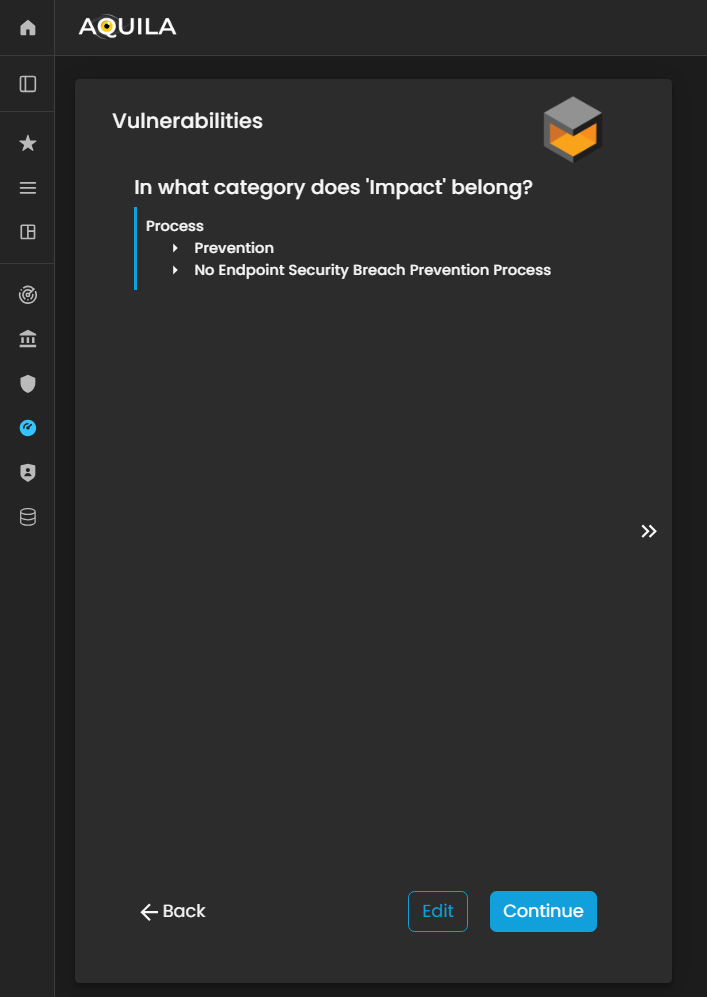
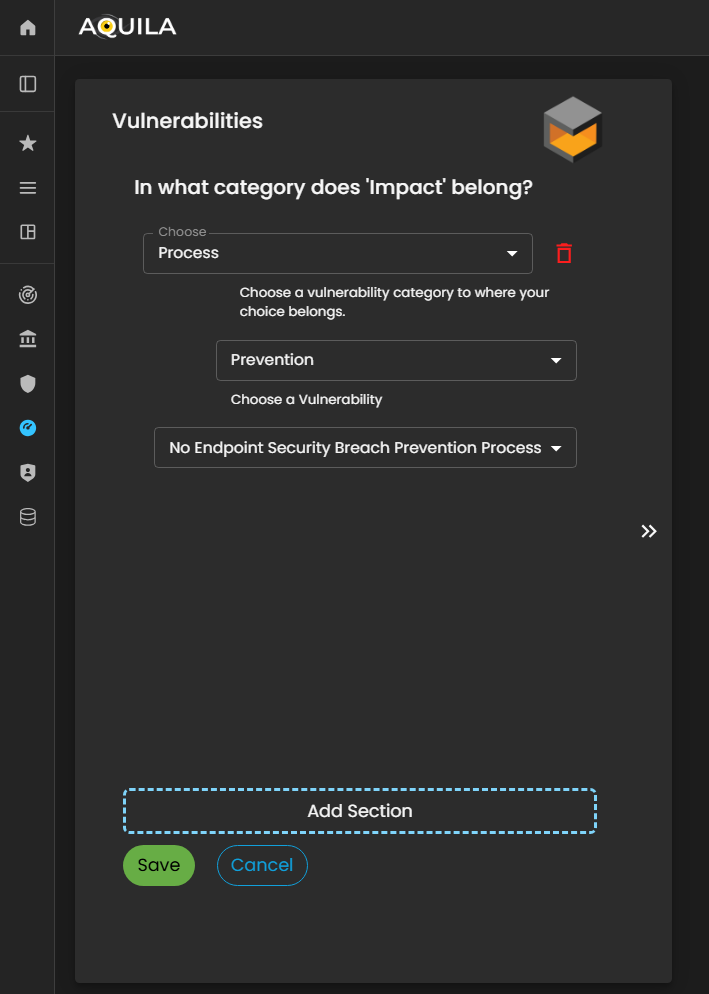
Vulnerabilities
In this section, the client is asked, “In what category does this vulnerability belong?” to classify identified vulnerabilities based on their nature or type.
The client can add, update, or modify vulnerabilities through the Edit section by pressing the Edit button below. Properly categorizing vulnerabilities enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess risk exposure more accurately, prioritize remediation efforts, and develop targeted strategies to mitigate potential threats.
Figure 23. Cyber Security Risk Management - Vulnerabilities
In this section, the client can add their identified vulnerabilities and specify the category to which each vulnerability belongs.
This allows the organization to classify weaknesses—such as technical, operational, or process-related vulnerabilities—so that the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform can better analyze risk exposure, prioritize mitigation measures, and develop targeted strategies to address potential threats.
Figure 23.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Vulnerabilities / Edit Section
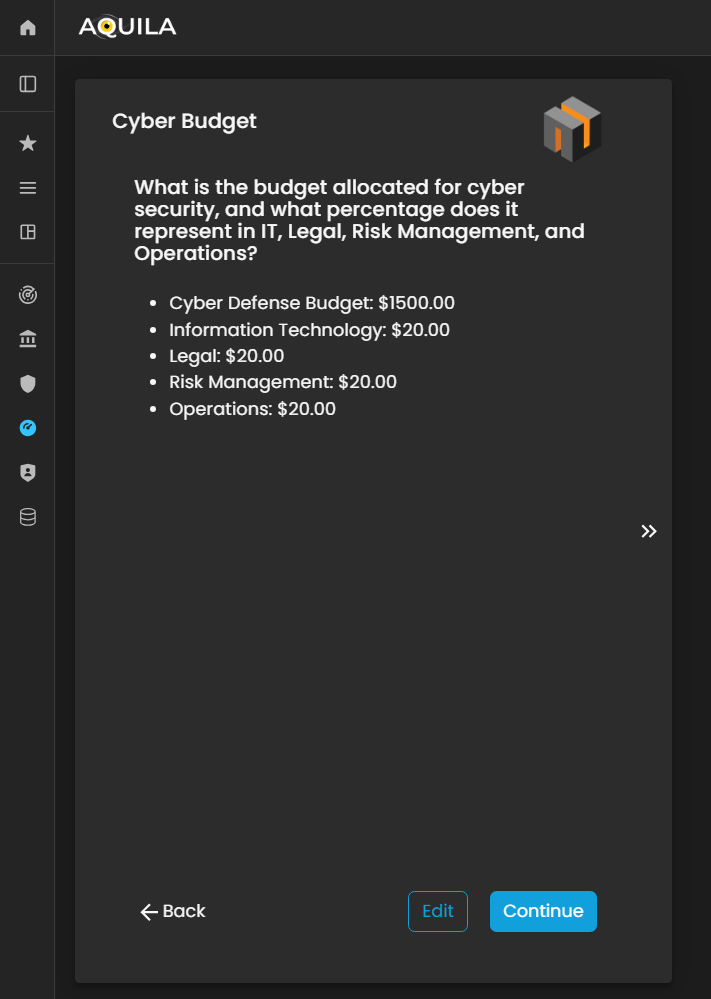
Cyber Budget
After completing the Vulnerabilities section, the client will proceed to the Cyber Budget module. This section asks the client to specify the budget allocated for responding to potential cyber incidents and to indicate what percentage of this budget is assigned to key departments such as IT, Legal, Risk Management, and Operations.
The client can add or update their Cyber Budget details through the Edit section by pressing the Edit button below. Accurately documenting budget allocations enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to evaluate the organization’s financial preparedness, assess resource distribution for cyber risk mitigation, and support strategic planning for incident response and recovery.
Figure 24. Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Budget
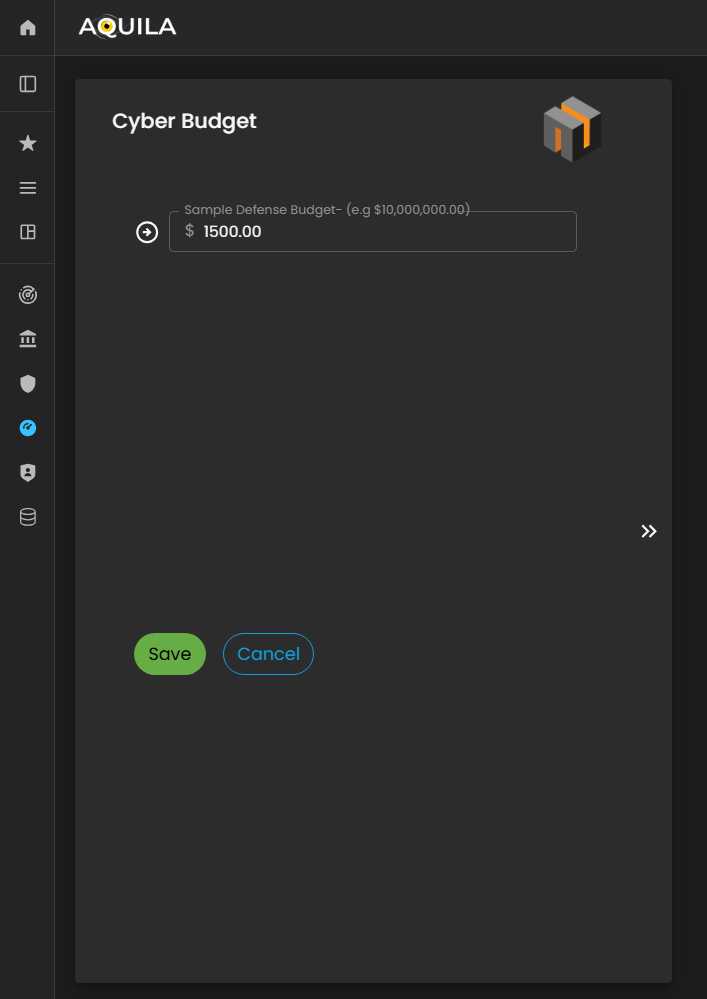
The client can input or update their Cyber Budget details through the Edit section by clicking the Edit button below.
This allows the client to specify the budget allocated for potential cyber incidents and assign percentages to departments such as IT, Legal, Risk Management, and Operations, ensuring the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform has accurate financial data for risk analysis and mitigation planning.
Figure 24.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Budget / Edit Section
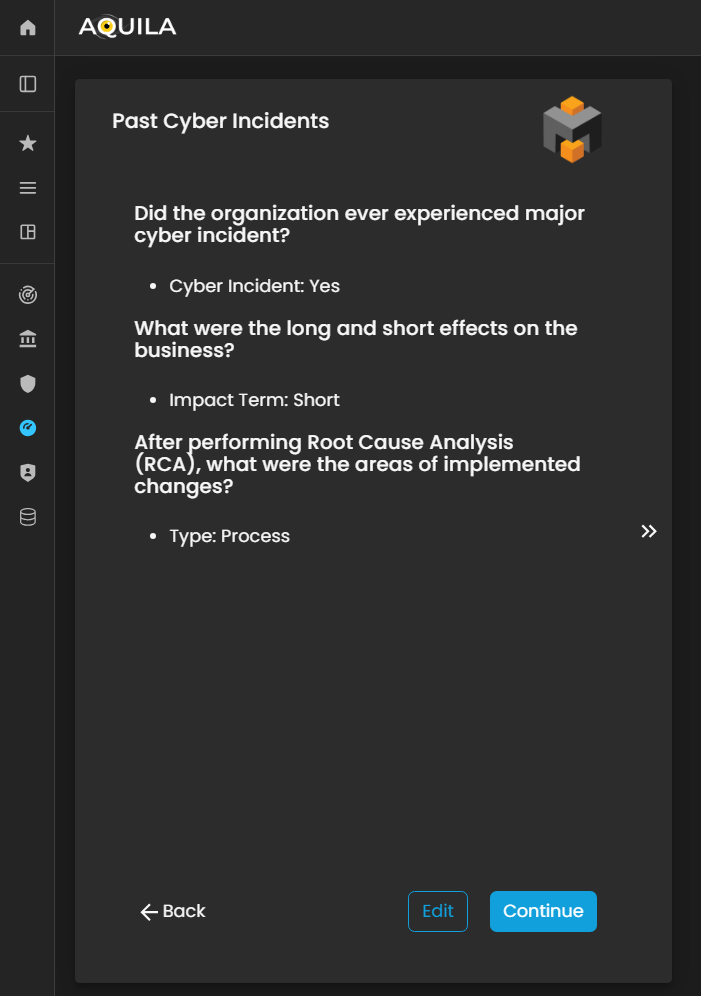
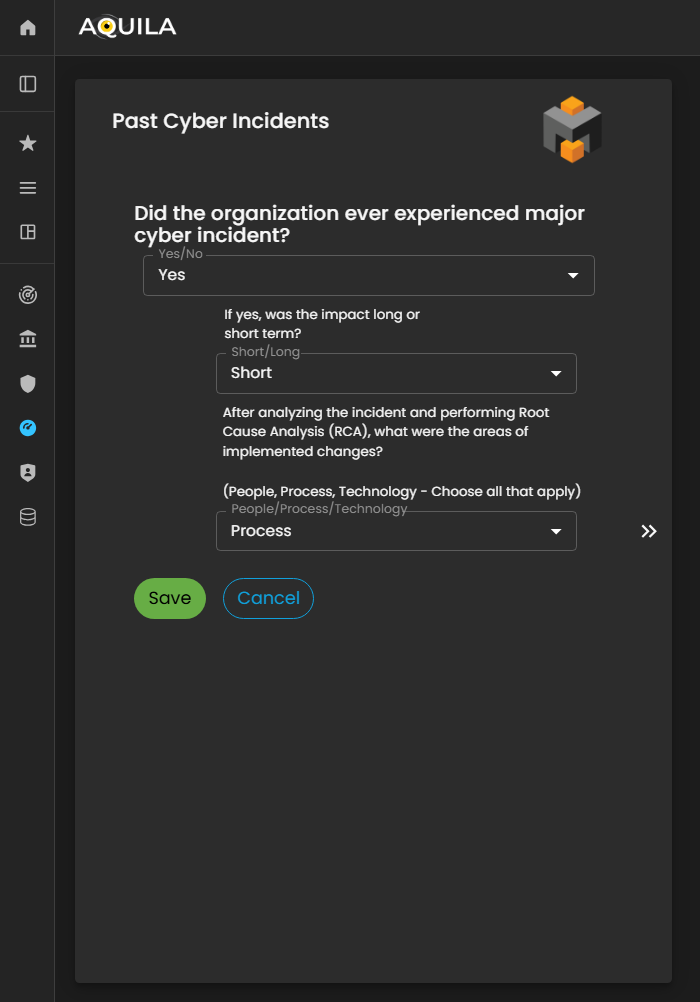
Past Cyber Incidents
In this section, the client will be asked questions regarding whether their organization has experienced past cyber incidents.
The client can modify or update their responses through the Edit section by pressing the Edit button. Providing accurate historical incident information enables the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess patterns of vulnerability, understand the organization’s prior risk exposure, and inform more effective cyber risk mitigation strategies.
Figure 25. Cyber Security Risk Management - Past Cyber Incident
In this section, the client can add details of Past Cyber Incidents their organization has experienced.
This allows the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to analyze historical incidents, identify recurring vulnerabilities or threat patterns, and provide insights for improving the organization’s cybersecurity posture and risk mitigation strategies.
Figure 25.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Past Cyber Incident / Edit Section
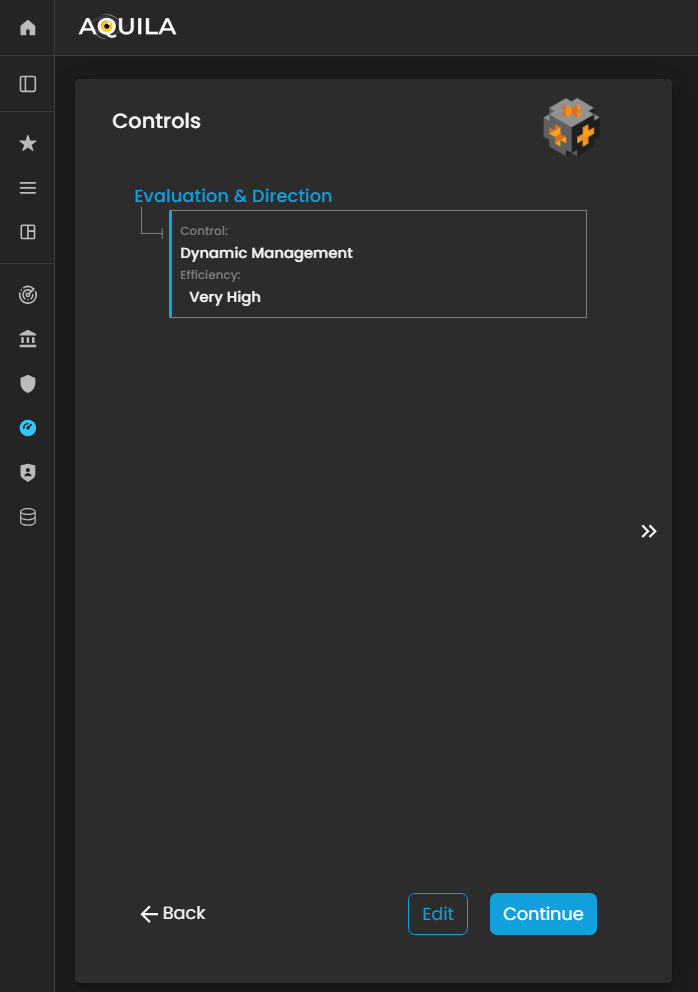
Controls
In this section, the client can add their existing controls and specify their efficiency or effectiveness in mitigating risks.
The client can input new controls or modify existing ones through the Edit section by pressing the Edit button. Accurately documenting controls and their efficiency allows the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to evaluate the organization’s current risk management measures, identify gaps, and recommend targeted improvements to strengthen overall cyber resilience.
Figure 26. Cyber Security Risk Management - Controls
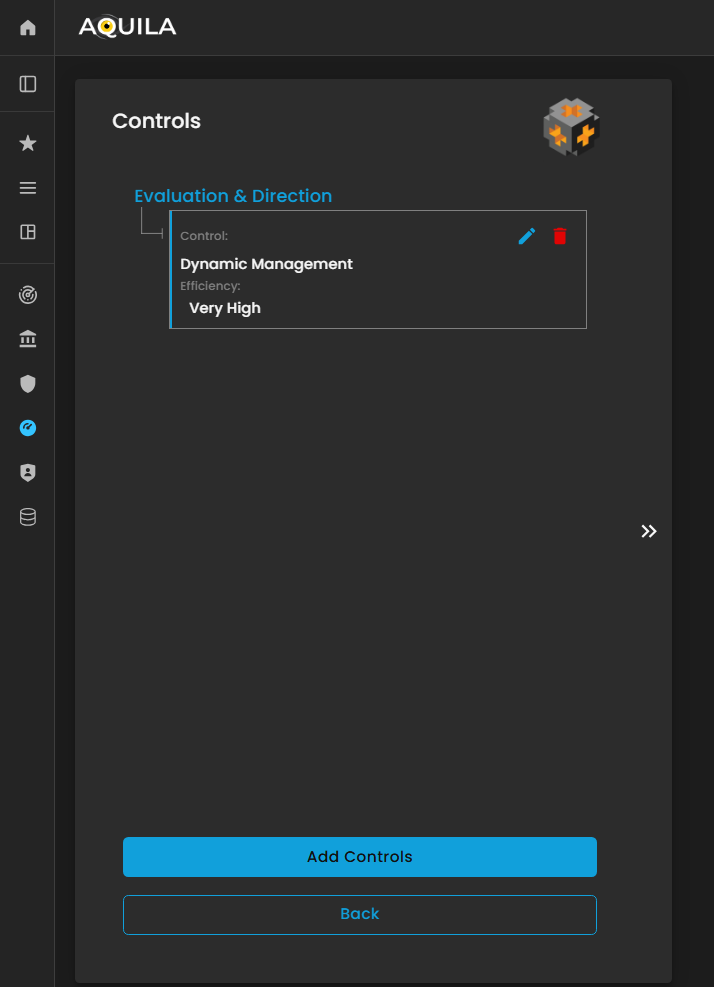
In the Edit Controls section, the client can add new controls, modify existing ones, or delete outdated or ineffective controls.
This functionality allows the client to maintain an up-to-date and accurate record of their risk mitigation measures, enabling the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to assess control effectiveness, identify gaps, and provide recommendations to enhance the organization’s overall cyber resilience.
Figure 26.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Controls / Edit Section
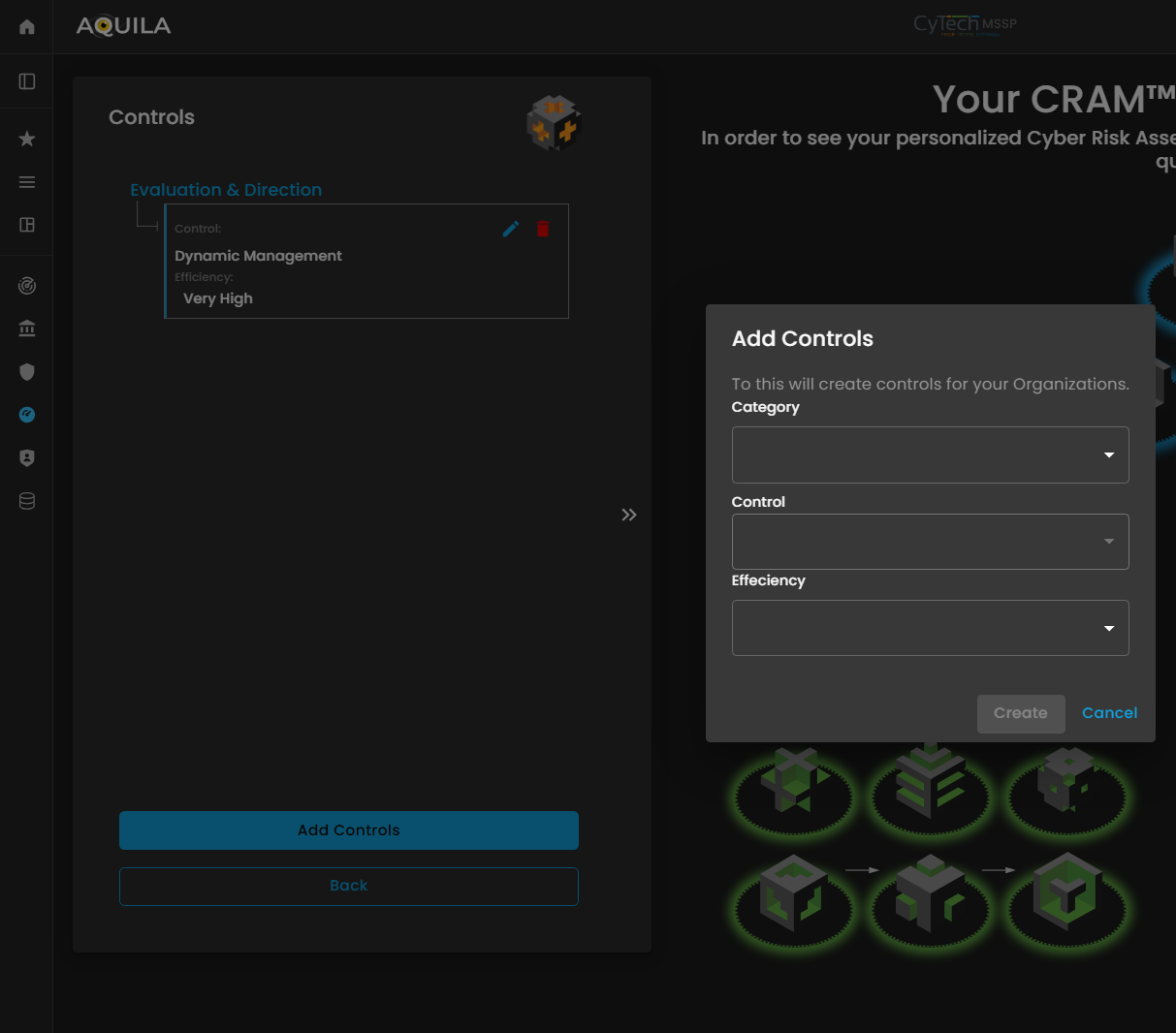
If the client chooses to add a control, a window will appear prompting them to specify:
-
Category – The type or classification of the control (e.g., technical, administrative, or physical).
-
Control – A description of the specific measure or safeguard implemented.
-
Efficiency – An assessment of how effective the control is in mitigating the associated risk.
Providing accurate information in this window allows the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) platform to evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls, identify gaps, and recommend improvements to strengthen the organization’s cyber risk posture.
Figure 26.2 Cyber Security Risk Management - Controls / Edit Section / Add Controls Section
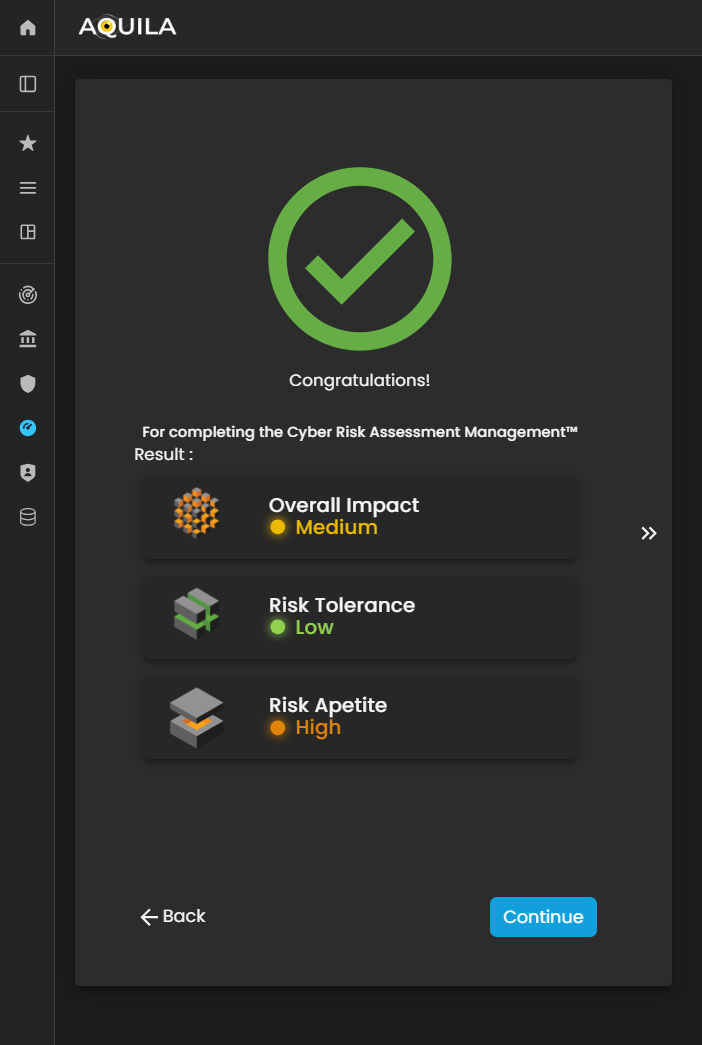
Results
After completing the Cyber Risk Assessment Management (CRAM) process, the client will receive a comprehensive assessment report detailing their organization’s cyber risk posture.
The results provide insights into identified threats, vulnerabilities, critical business functions, and the effectiveness of existing controls, as well as an evaluation of the organization’s risk tolerance, risk appetite, and preparedness for potential cyber incidents. This report enables the client to make informed decisions, prioritize risk mitigation efforts, and strengthen overall cyber resilience and business continuity.
Figure 27. Cyber Security Risk Management - Results
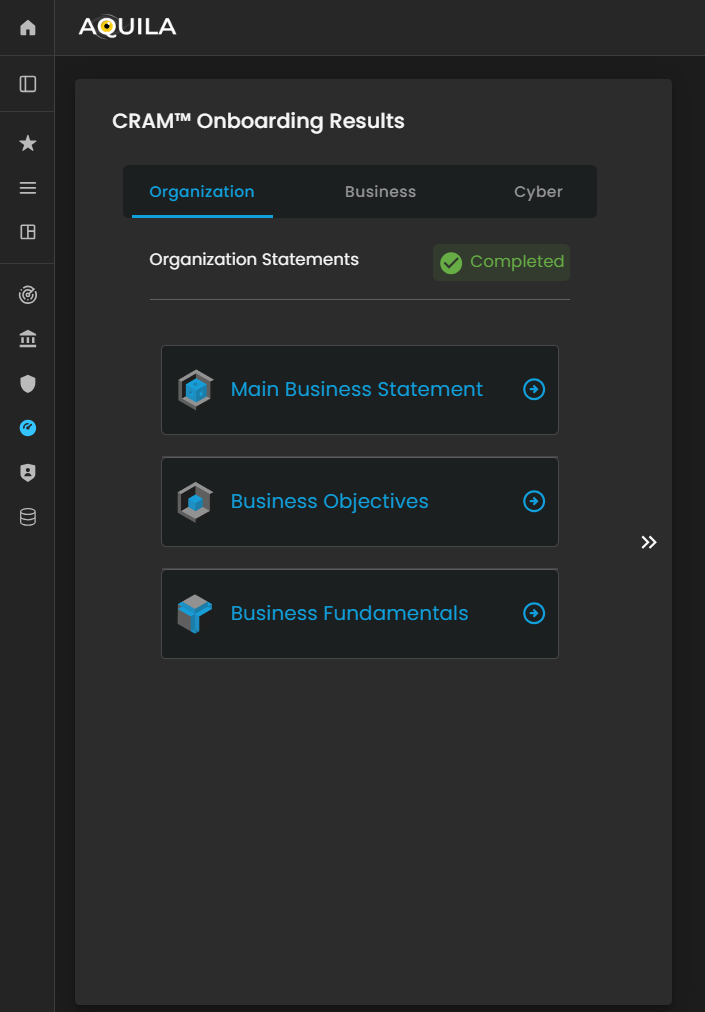
Figure 27.1 Cyber Security Risk Management - Organization Statements Results
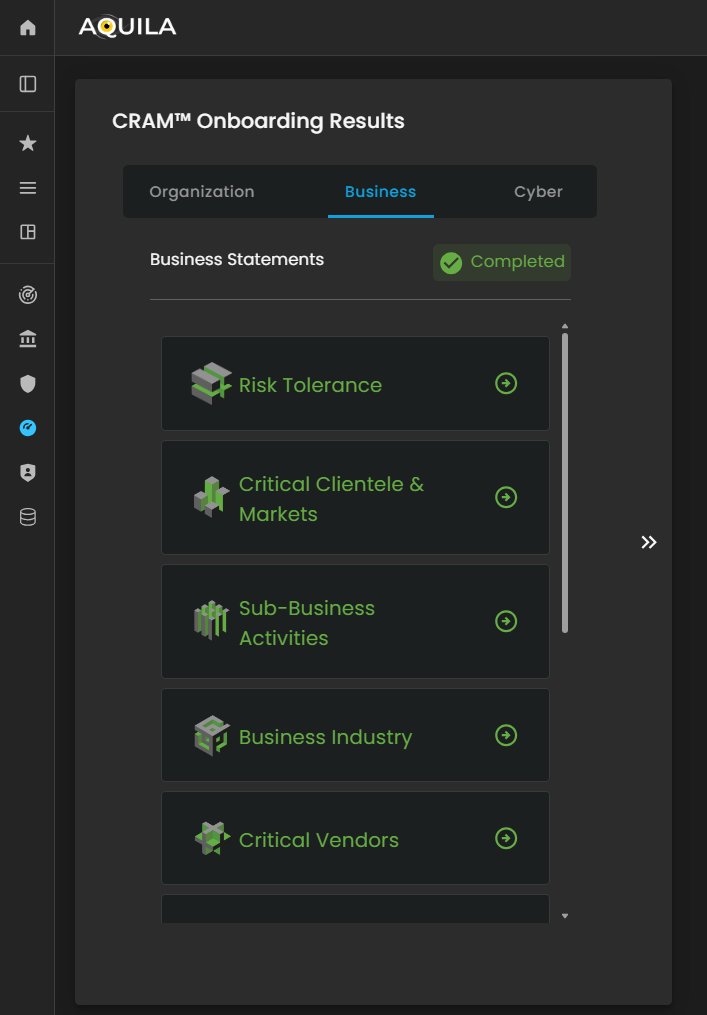
Figure 27.2 Cyber Security Risk Management - Business Statements Results
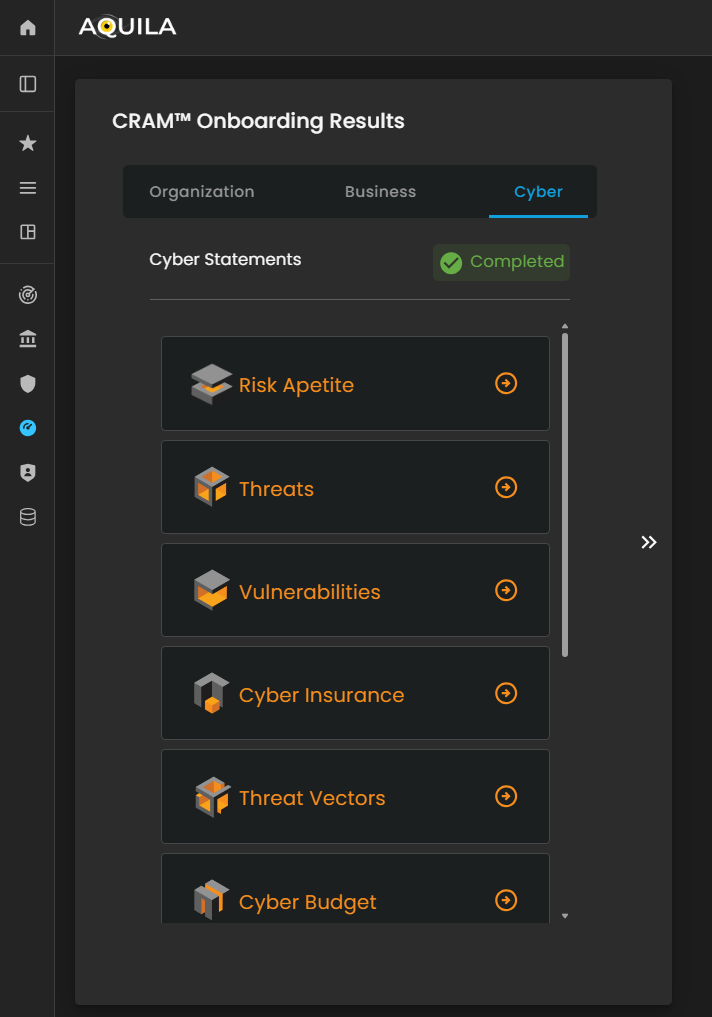
Figure 27.3 Cyber Security Risk Management - Cyber Statements Results