AQUILA - Salesforce Integration via JWT Authentication
Overview
With the OAuth 2.0 JWT bearer token flow, the client posts a JWT to the Salesforce OAuth token endpoint. Salesforce processes the JWT, which includes a digital signature, and issues an access token based on prior approval of the app.
Check "View Event Log Files" Permission
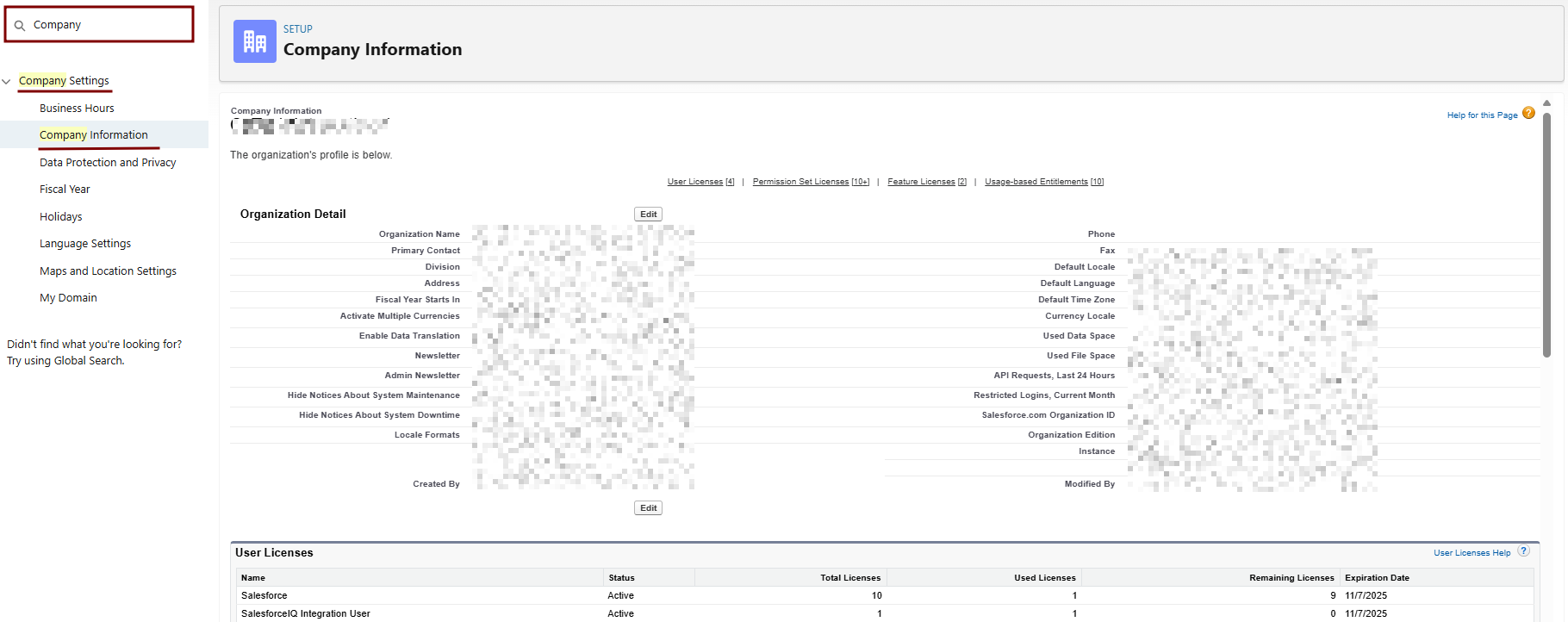
- Check Your Org's Event Monitoring License:
- Go to Setup > Quick Find > Installed Packages or Company Information (under Quick Find > Company Settings).
- Look for Event Log File Browser or Event Monitoring and enable it if it shows an option to do so.
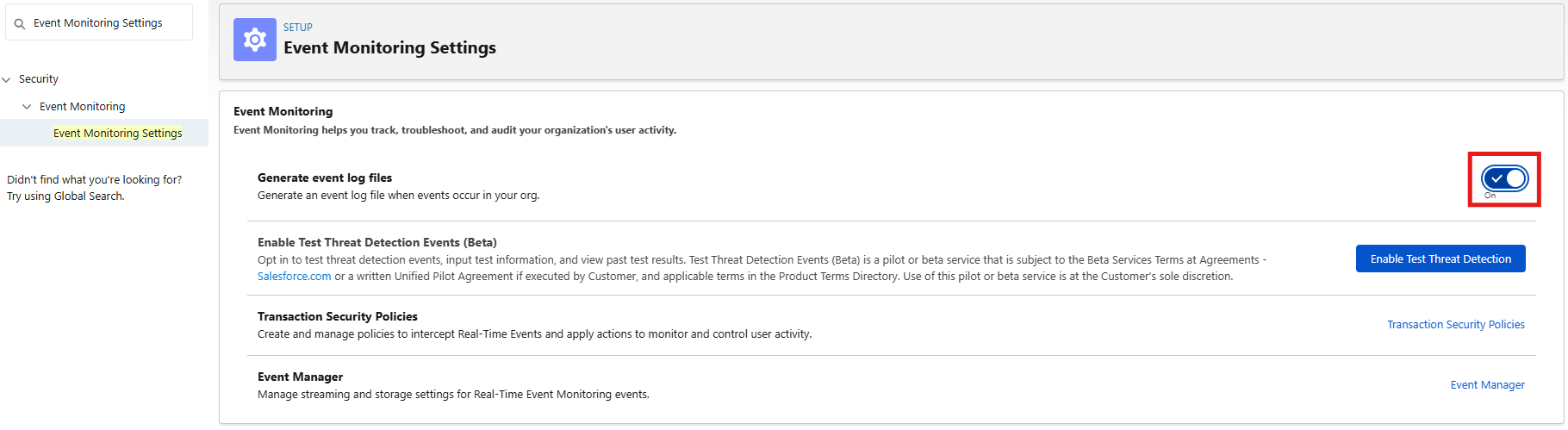
2. Enable Event Monitoring Features:
- Setup > Quick Find > Event Monitoring Settings (or search "Event Log File Browser").
- If the page loads: Check Enable Event Log File Browser > Save.
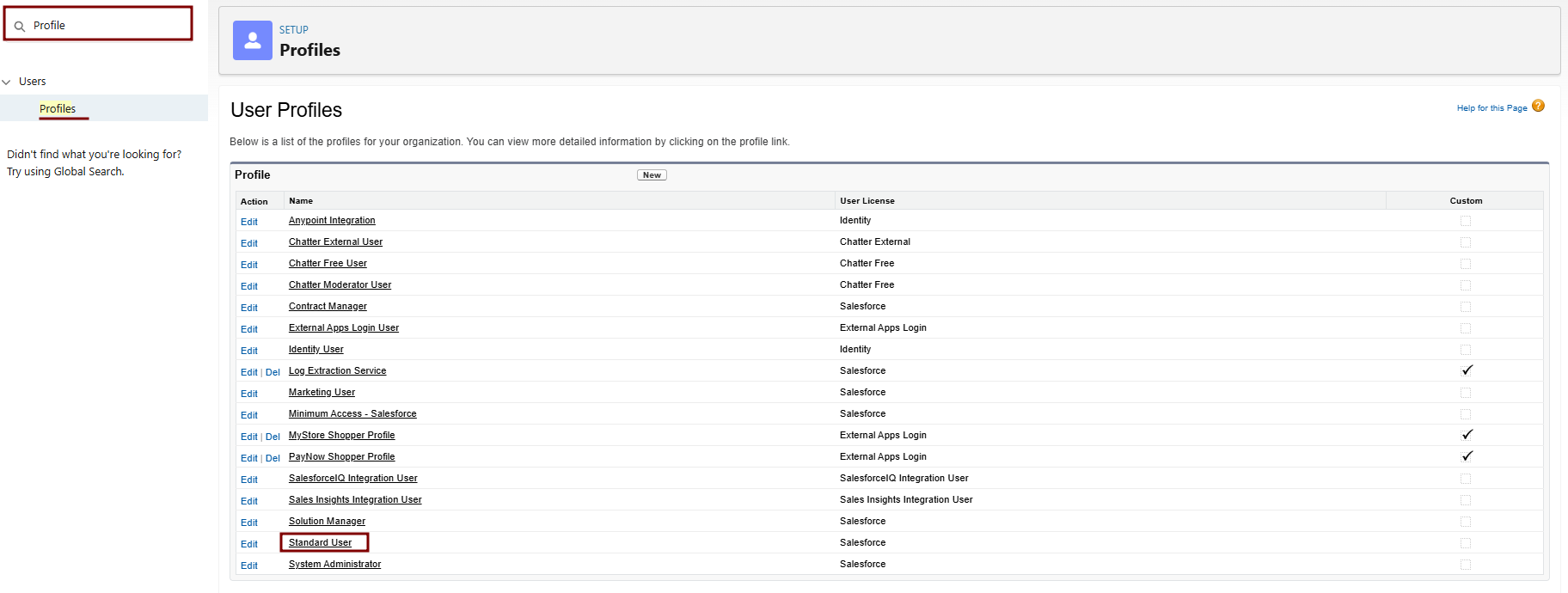
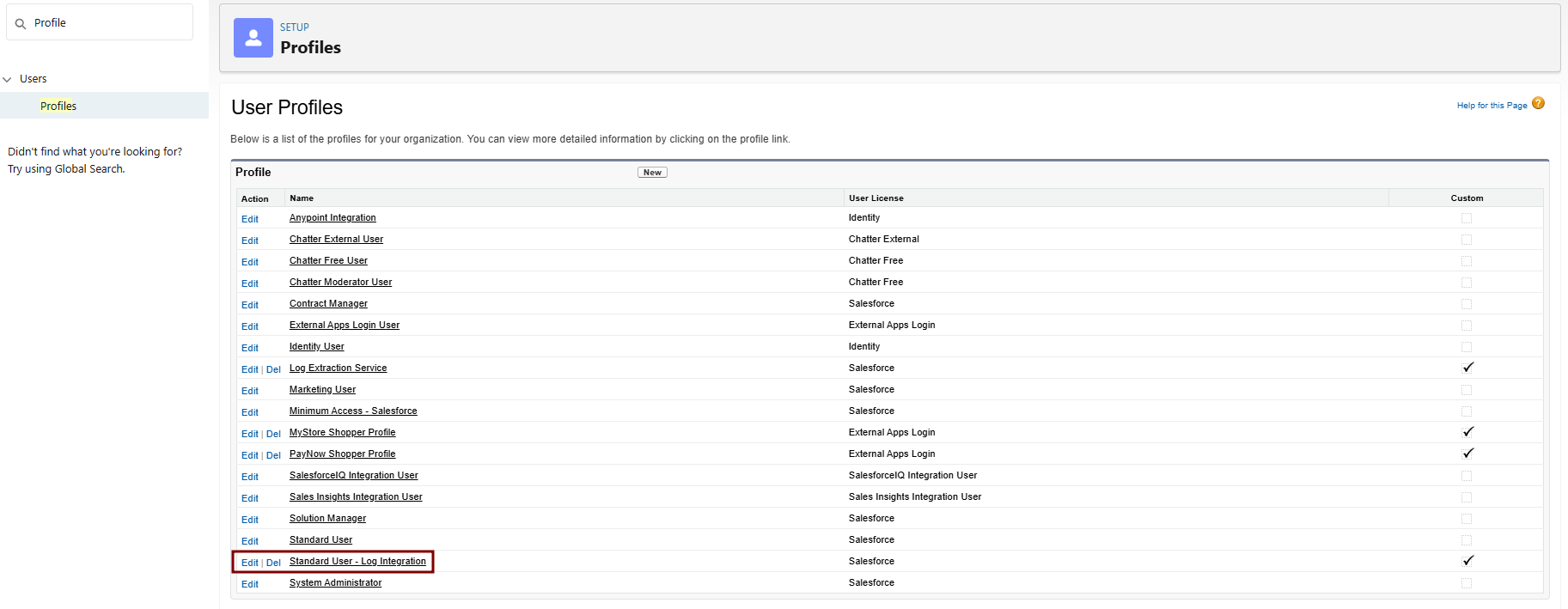
Clone and Modify the Profile
-
Log
CreateinatoJWTSalesforce
Setup:requires that a JWT is signed using RSA SHA256, which uses an uploaded certificate as the signing secret. Before using this authorization flow, make sure that you complete these steps.-
UploadGo to Setup (gear icon > Setup) as an
X509admin.Certificate
to a Java Key Store (JKS). The certificate size can’t exceed 4 KB. If it does, try using a DER encoded file to reduce the size. -
-
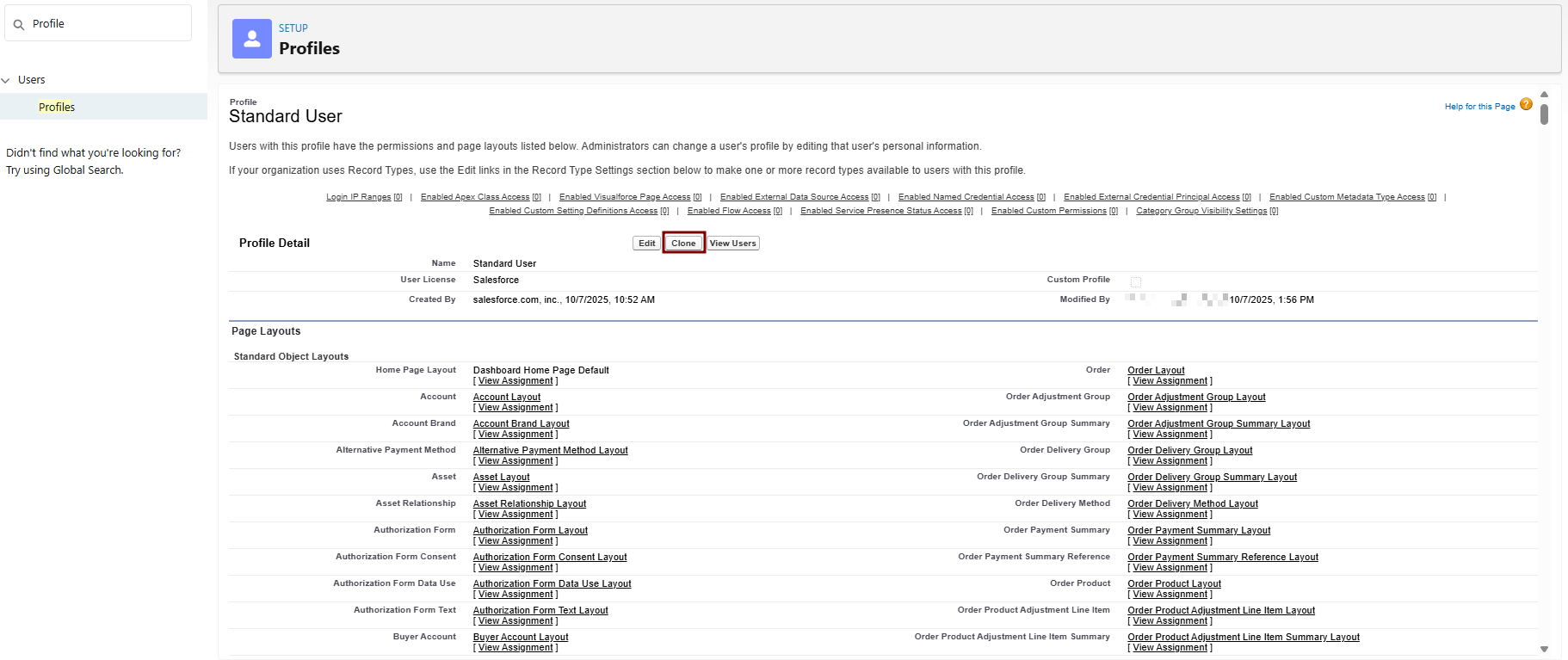
RegisterClone the
X509StandardCertificateUser Profile:-
Navigate to Setup > Quick Find > Profiles.
-
Find Standard User > Click Clone next to it.
-
Profile Information:
- Profile Name: e.g., "Standard User - Log Integration".
- Description: "Cloned for Elastic log integration with API and ELF access."
- User License: Salesforce Integration
-
Save. This creates a new custom profile based on Standard User.
-
3. Edit System Permissions in the connectedCloned app.Profile:
-
correspondsIn Profiles, find your new cloned profile > Click Edit > Go to the
privateSystemkeyPermissionsofsectionthe(orapp.useWhenQuicktheFindconnectedforapp"Systemis saved, the client_id and client_secret are generated and assigned to the app.Permissions"). -
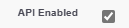
BuildEnable
antheappfollowingthatcheckboxesgenerates(theseaareJWT,the key changes from Standard User, whichis signedstarts withthethemX509disabledCertificate’sforprivate key. The associated connected app uses the certificate to verify the signature. The JWT must conform with the general format rules specified inhttps://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7519.security):
Note:Salesforce doesn’t require JWT ID (JTI) claims in your JWT bearer tokens. However, if you pass a JTI claim in your JWT bearer token, Salesforce validates that the JTI claim hasn’t been sent before. This validation prevents JWT replay attacks.
To create a valid JWT, take these steps.
1. Construct a JWT header with this format: {"alg":"RS256"}.
2. Base64url encode the JWT header as defined in http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4648#page-7. The result is similar to eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.
3. Construct a JSON Claims Set for the JWT with these parameters.
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
Allows REST/SOAP API calls for |
Check the
|
|
|
|
Grants read access to historical Event Log Files (ELF) like logins and |
Check the |
|
View All Data |
Disabled → Enabled |
Provides broader object read access if ELF queries fail due to restrictions. |
Check the |
Here’s
an-
exampleDo JSONNOT Claimenable Setunrelated forpermissions like "Modify All Data" or "Delete All Data" to maintain least-privilege.
-
Save the JWT.
profile.
Do JSONNOT Claimenable Setunrelated forpermissions like "Modify All Data" or "Delete All Data" to maintain least-privilege.
Save the JWT.
{"iss":
"3MVG99OxTyEMCQ3gNp2PjkqeZKxnmAiG1xV4oHh9AKL_rSK.BoSVPGZHQ
ukXnVjzRgSuQqGn75NL7yfkQcyy7",
"sub":
"aud": "https://login.salesforce.com",
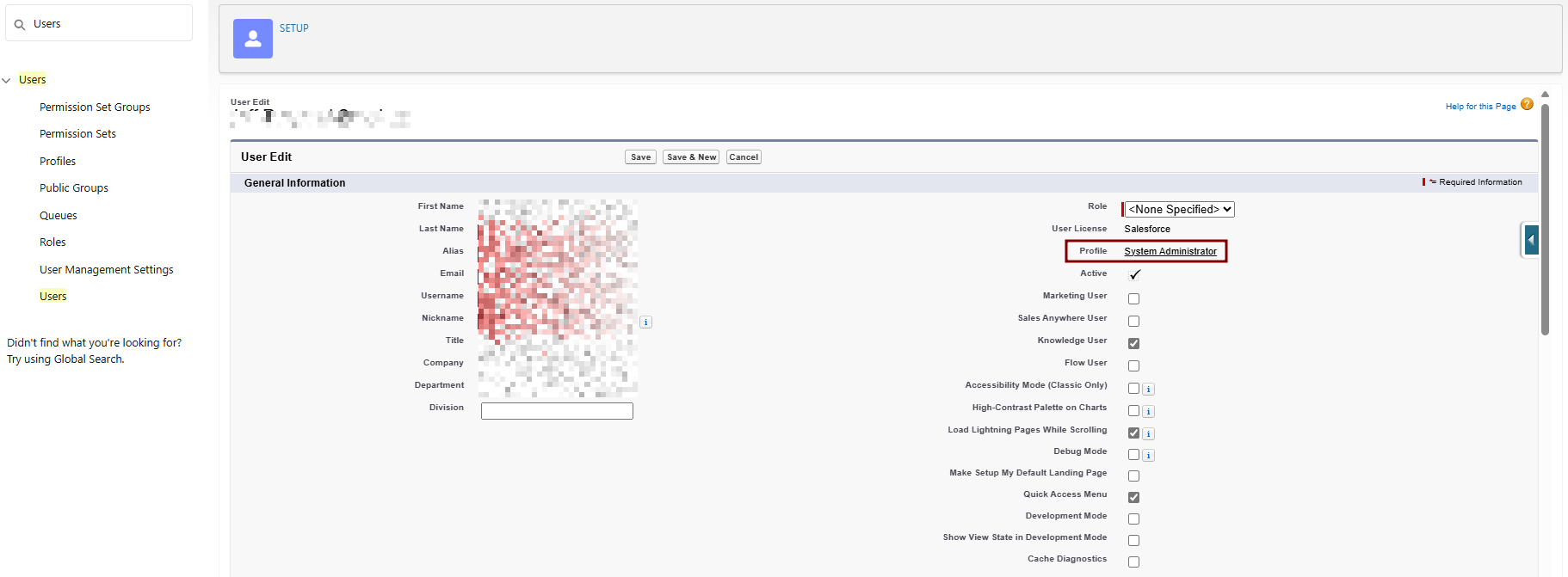
"exp": "1333685628"}4. Base64url encodeAssign the JWTCloned ClaimsProfile Setto withoutYour anyIntegration lineUser:
-
example:Setup
>eyJpc3MiOiAiM01WRzk5T3hUeUVNQ1EzZ05wMlBqa3FlWkt4bm1BaUcxeFY0b0hoOUFLTF9yU0su>Qm9TVlBHWkhRdWtYblZqelJnU3VRcUduNzVOTDd5ZmtRY3l5NyIsICJwcm4iOiAibXlAZW1haWwuQuickY29tIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwczovL2xvZ2luLnNhbGVzZm9yY2UuY29tIiwgImV4cCI6ICIxMzMzFindNjg1NjI4In0=Users > Select your integration user > Edit.
-
Profile: Select "Standard User - Log Integration".
-
Save.
5. CreateHandle aEvent stringMonitoring forPermissions the encoded JWT Header and the encoded JWT Claims Set(Not in thisProfile—Use format.Permission encoded_JWT_Header + "." + encoded_JWT_Claims_Set
Set):In this example, the encoded JWT Header is highlighted.
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiM01WRzk5T3hUeUVNQ1EzZ05wMlBqa3FlWkt4bm1BaUcxeFY0b0hoOUFLTF9yU0suQm9TVlBHWkhRdWtYblZqelJnU3VRcUduNzVOTDd5ZmtRY3l5NyIsICJwcm4iOiAibXlAZW1haWwuY29tIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwczovL2xvZ2luLnNhbGVzZm9yY2UuY29tIiwgImV4cCI6ICIxMzMzNjg1NjI4In0=
6. Download the X509 Certificate from the JKS.
7. Sign the resulting string using RSA SHA256.
8. Create a string of the string from this step in this format.
existing_string + "." + base64_encoded_signatureIn this example, the base64 encoded signature is highlighted.
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiAiM01WRzk5T3hUeUVNQ1EzZ05wMlBqa3FlWkt4bm1BaUcxeFY0b0hoOUFLTF9yU0su
Qm9TVlBHWkhRdWtYblZqelJnU3VRcUduNzVOTDd5ZmtRY3l5NyIsICJwcm4iOiAibXlAZW1haWwu
Y29tIiwgImF1ZCI6ICJodHRwczovL2xvZ2luLnNhbGVzZm9yY2UuY29tIiwgImV4cCI6ICIxMzMz
Njg1NjI4In0=.iYCthqWCQucwi35yFs-nWNgpF5NA_a46fXDTNIY8ACko6BaEtQ9E6h4Hn1l_pcwcK
I_GlmfUO2dJDg1A610t09TeoPagJsZDm_H83bsoZUoI8LpAA1s-2aj_Wbysqb1j4uDToz
480WtEbkwIv09sIeS_-QuWak2RXOl1Krnf72mpVGS4WWSULodgNzlKHHyjAMAHiBHIDNt
36y2L2Bh7M8TNWiKa_BNM6s1FNKDAwHEWQrNtAeReXgRy0MZgQY2rZtqT2FcDyjY3JVQb
En_CSjH2WV7ZlUwsKHqGfI7hzeEvVdfOjH9NuaJozxvhPF489IgW6cntPuT2V647JWi7ng
This Java code is a simple example of constructing a JWT bearer token.
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import java.io.*;
import java.security.*;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
public class JWTExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String header = "{\"alg\":\"RS256\"}";
String claimTemplate = "'{'\"iss\": \"{0}\", \"sub\": \"{1}\", \"aud\": \"{2}\", \"exp\": \"{3}\", \"jti\": \"{4}\"'}'";
try {
StringBuffer token = new StringBuffer();
//Encode the JWT Header and add it to our string to sign
token.append(Base64.encodeBase64URLSafeString(header.getBytes("UTF-8")));
//Separate with a period
token.append(".");
//Create the JWT Claims Object
String[] claimArray = new String[5];
claimArray[0] = "3MVG99OxTyEMCQ3gNp2PjkqeZKxnmAiG1xV4oHh9AKL_rSK.BoSVPGZHQukXnVjzRgSuQqGn75NL7yfkQcyy7";
claimArray[1] = "my@email.com";
claimArray[2] = "https://login.salesforce.com";
claimArray[3] = Long.toString( ( System.currentTimeMillis()/1000 ) + 300);
claimArray[4]=<JTI>
MessageFormat claims;
claims = new MessageFormat(claimTemplate);
String payload = claims.format(claimArray);
//Add the encoded claims object
token.append(Base64.encodeBase64URLSafeString(payload.getBytes("UTF-8")));
//Load the private key from a keystore
KeyStore keystore = KeyStore.getInstance("JKS");
keystore.load(new FileInputStream("./path/to/keystore.jks"), "keystorepassword".toCharArray());
PrivateKey privateKey = (PrivateKey) keystore.getKey("certalias", "privatekeypassword".toCharArray());
//Sign the JWT Header + "." + JWT Claims Object
Signature signature = Signature.getInstance("SHA256withRSA");
signature.initSign(privateKey);
signature.update(token.toString().getBytes("UTF-8"));
String signedPayload = Base64.encodeBase64URLSafeString(signature.sign());
//Separate with a period
token.append(".");
//Add the encoded signature
token.append(signedPayload);
System.out.println(token.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Request Access Token
To request an access token, the connected app posts a token request to the Salesforce instance’s token endpoint. It includes the JWT in the post.
This example shows a sample token request.
POST /services/oauth2/token HTTP/1.1
Host: login.example.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type= urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&
assertion=eyJpc3MiOiAiM01WRz...[omitted for brevity]...ZTImportant: When developing OAuth integrations, always pass sensitive information in the body of a POST request or in a request header. Don't use GET parameters in the URL query string to pass sensitive information. Sensitive information includes but isn't limited to usernames, passwords, OAuth tokens, client secrets, and any personally identifiable information. For more information on security best practices, see Storing Sensitive Data in the Secure Coding Guide.
Include these parameters in the post.
| PARAMETER | DESCRIPTION |
| grant_type | Use these values for the grant type: urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
| assertion |
The assertion is the entire JWT value. |
| format |
(Optional) Use to specify the expected return format. This parameter overrides the request’s header. These formats are supported.
|
Scope Parameter
You can’t specify scopes in a JWT bearer token flow. Scopes are issued according to the connected app’s Permitted Users policy or your org’s API Access Control settings, as shown in this table.
| SETTING |
RESULT |
| Permitted Users policy: All users may self-authorize | With a successful authorization, the scopes returned with the access token are derived from the scopes of prior approvals. |
| Permitted Users policy: Admin approved users are pre-authorized | Standard and custom scopes assigned to the connected app are returned with the access token. |
| API Access Control: Allowlist connected apps in your org |
Standard and custom scopes assigned to the connected app are returned with the access token. If you allowlist connected apps in your org and don’t receive the expected scopes, take these steps.
|
Salesforce Grants Access Token
The OAuth 2.0 JWT bearer and SAML assertion bearer flow requests look at all previous approvals for the user that include a refresh token. If Salesforce finds matching approvals, it combines the values of the approved scopes. Salesforce then issues an access token. If Salesforce doesn’t find previous approvals that included a refresh token or any available approved scopes, the request fails as unauthorized.
After a successful verification, the Salesforce instance sends a response to the connected app. A token response for the OAuth 2.0 JWT bearer token flow follows the same format as an authorization code flow, although a refresh token is never issued.
This example shows a response from Salesforce.
{"access_token":"00Dxx0000001gPL!AR8AQJXg5oj8jXSgxJfA0lBog.
39AsX.LVpxezPwuX5VAIrrbbHMuol7GQxnMeYMN7cj8EoWr78nt1u44zU31
IbYNNJguseu",
"scope":"web openid api id","instance_url":"
https://yourInstance.salesforce.com","id":"
https://yourInstance.salesforce.com
/id/00Dxx0000001gPLEAY/005xx000001SwiUAAS","token_type":"Bearer"}These parameters are in the body of the response.
| PARAMETER |
DESCRIPTION |
| access_token | OAuth token that a connected app uses to request access to a protected resource on behalf of the client application. Additional permissions in the form of scopes can accompany the access token. |
| token_type | A Bearer token type, which is used for all responses that include an access token. |
| scope | Scopes are issued according to the connected app’s Permitted Users policy or your org’s API Access Control settings. See Scope Parameter. |
| instance_url | A URL indicating the instance of the user’s org. For example: https://yourInstance.salesforce.com/. |
| id | An identity URL that can be used to identify the user and to query for more information about the user. See Identity URLs. |
| sfdc_site_url | If the user is a member of an Experience Cloud site, the site URL is provided. |
| sfdc_site_id | If the user is a member of an Experience Cloud site, the user’s site ID is provided. For Experience Cloud sites, this flow includes the "sfdc_site_id" value in the token endpoint. This site ID is potentially required in Connect REST API requests. |
Access Protected Data
After the connected app receives the access_token, it can pass it as a bearer token in the Authorization header request. This example shows a REST API call to Experience Cloud sites:
https://site.force.com/customers/services/data/v32.0/ -H
"Authorization: Bearer 00D50000000IehZ\!AQcAQH0dMHZfz972Szmpkb58urFRkgeBGsxL_QJWwYMfAbUeeG7c1E6 LYUfiDUkWe6H34r1AAwOR8B8fLEz6n04NPGRrq0FM"Required fields for JWT Authentication Integration:
-
JWT Authentication Audience URL
-
JWT Authentication Client Key Path
-
Username
-
Client ID
-
Instance URL
-
Token URL
Provide this required fields to CyTech Support.
Reference Link:
OAuth 2.0 JWT Bearer Flow for Server-to-Server Integration in Salesforce
If you need further assistance, kindly contact our support at support@cytechint.com for prompt assistance and guidance.