AQUILA - All in One Endpoint Protection
Overview
Install the AQUILA Endpoint Agent (AEA) to start monitoring your device and strengthen your security posture. The AQUILA Endpoint Agent (AEA) helps you scan and monitor your endpoints for Endpoint Protection, Data Loss Prevention, and Vulnerability Detection, giving you continuous visibility and control over your environment.
How To Install
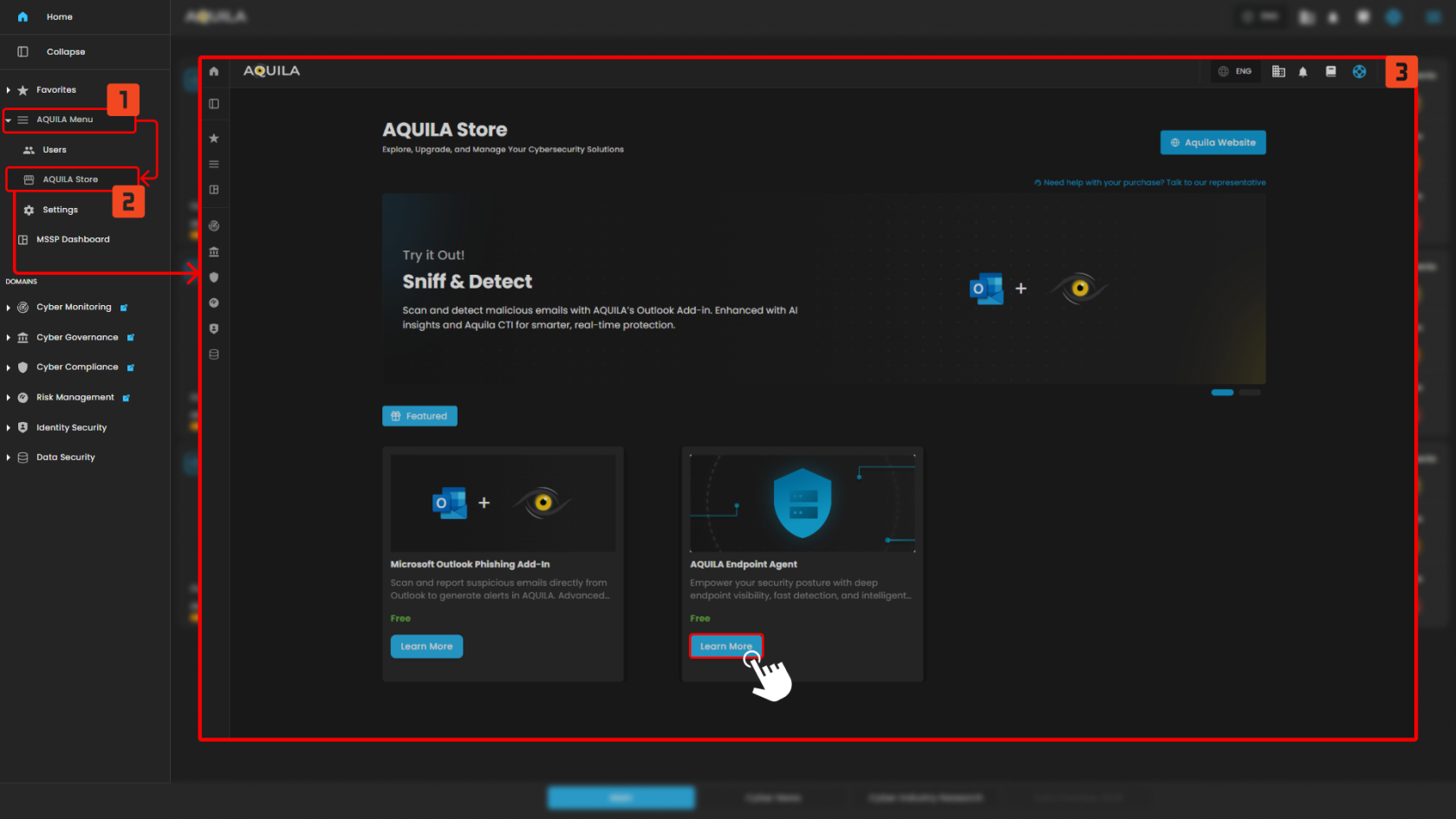
To install the AQUILA Endpoint Agent, access the AQUILA menu from the sidebar and select AQUILA Store. This action redirects you to the catalog listing for the AQUILA Endpoint Agent. Selecting Learn More opens the agent details page, which provides, system requirements, and publisher information.
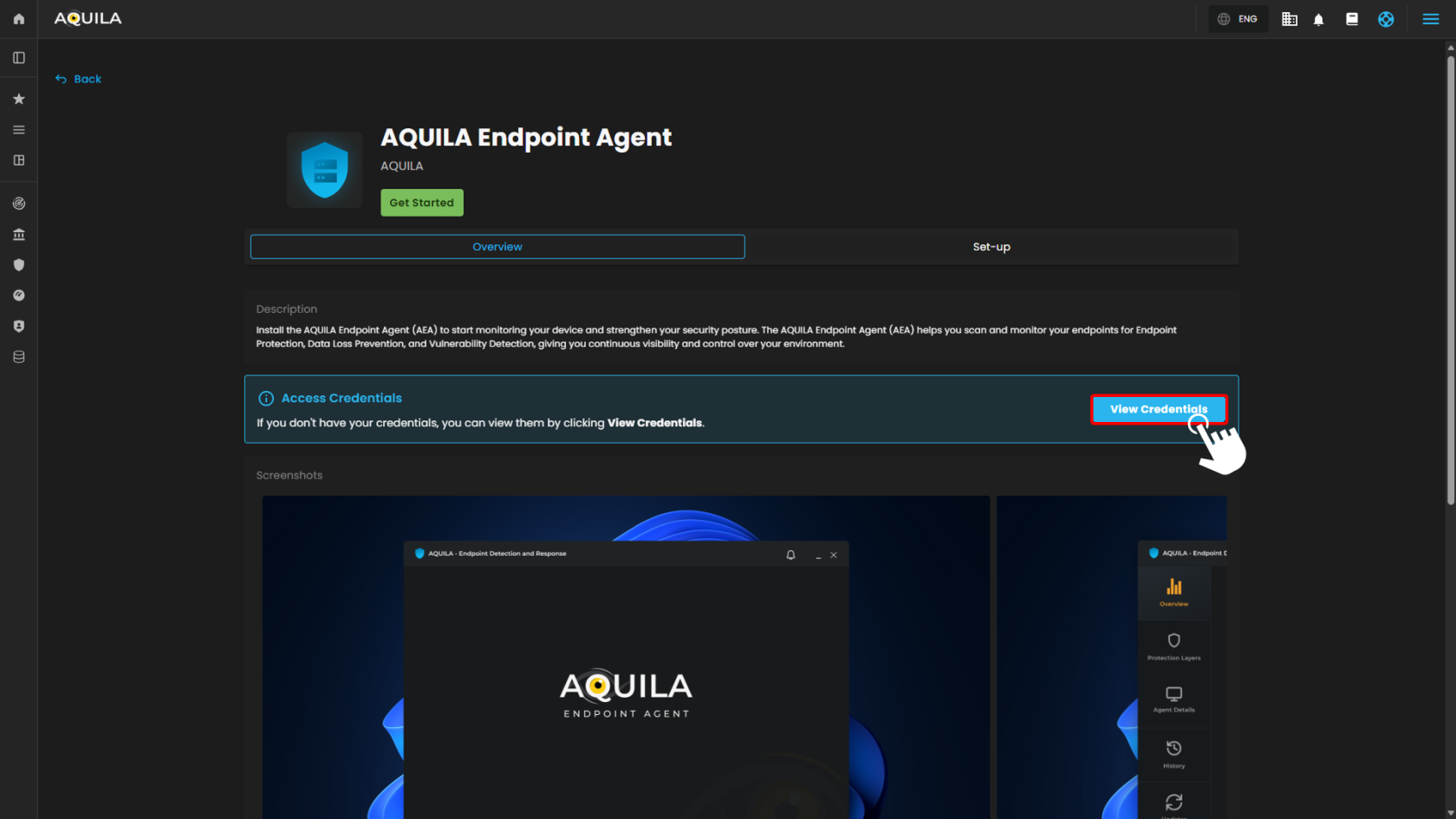
In this interface you can download the AQUILA Endpoint Agent by pressing the get started but before we proceed on that we must need the credentials first. To get the credentials press the view credentials in order to generate token, please copy those credentials and keep it in a safe note in order to proceed in the next step.
After saving the credentials let's proceed to the installation of the AQUILA Endpoint Agent.
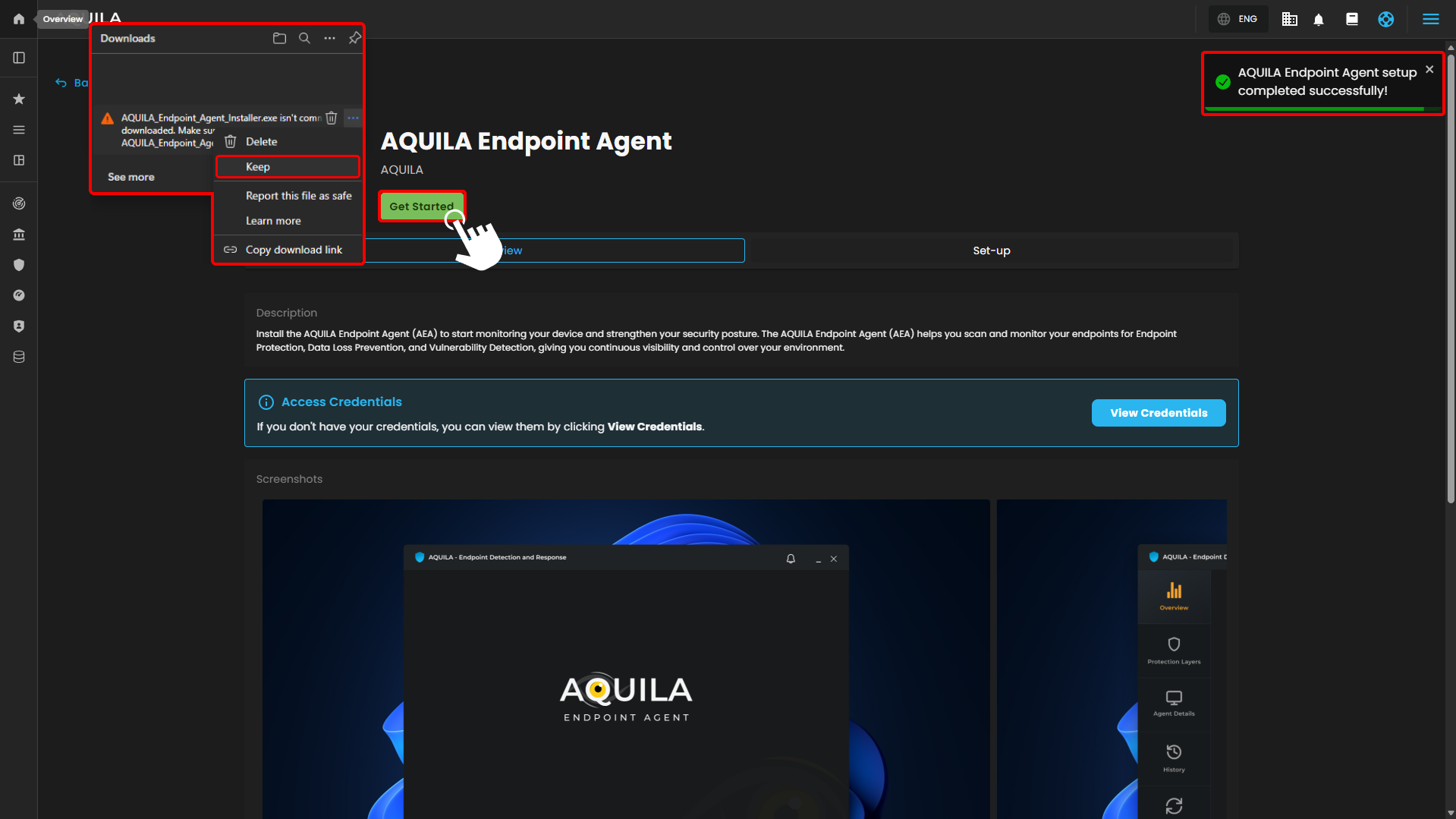
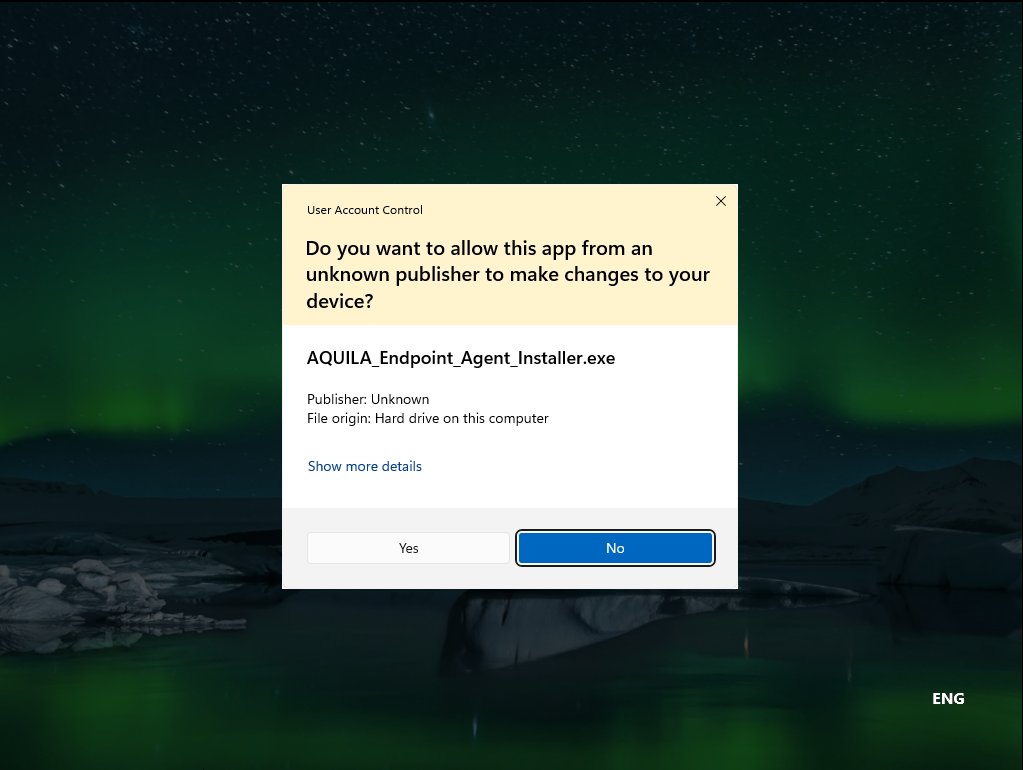
Press "Get Started" to download the AQUILA Endpoint Agent, please do not worry if AQUILA Endpoint Agent installer has that error saying "AQUILA_Endpoint_Agent_Installer.exe isn't commonly downloaded. Make sure you trust AQUILA_Endpoint_Agent_Installer.exe before you open it."
Security mechanisms such as Windows SmartScreen rely on reputation-based signals (download volume, age of the file, and digital signature prevalence). When a legitimate application is:
-
Newly released or recently updated
-
Downloaded by a limited number of users
-
Distributed privately or outside common marketplaces
-
Not yet widely recognized by SmartScreen
the system displays a cautionary message, even if the software is verified and secure.
This behavior is common for enterprise agents, internal tools, and controlled-distribution software. Make sure to keep the file in order to proceed in the installation thank you.
Installation Process
Allow this application to proceed in the installation
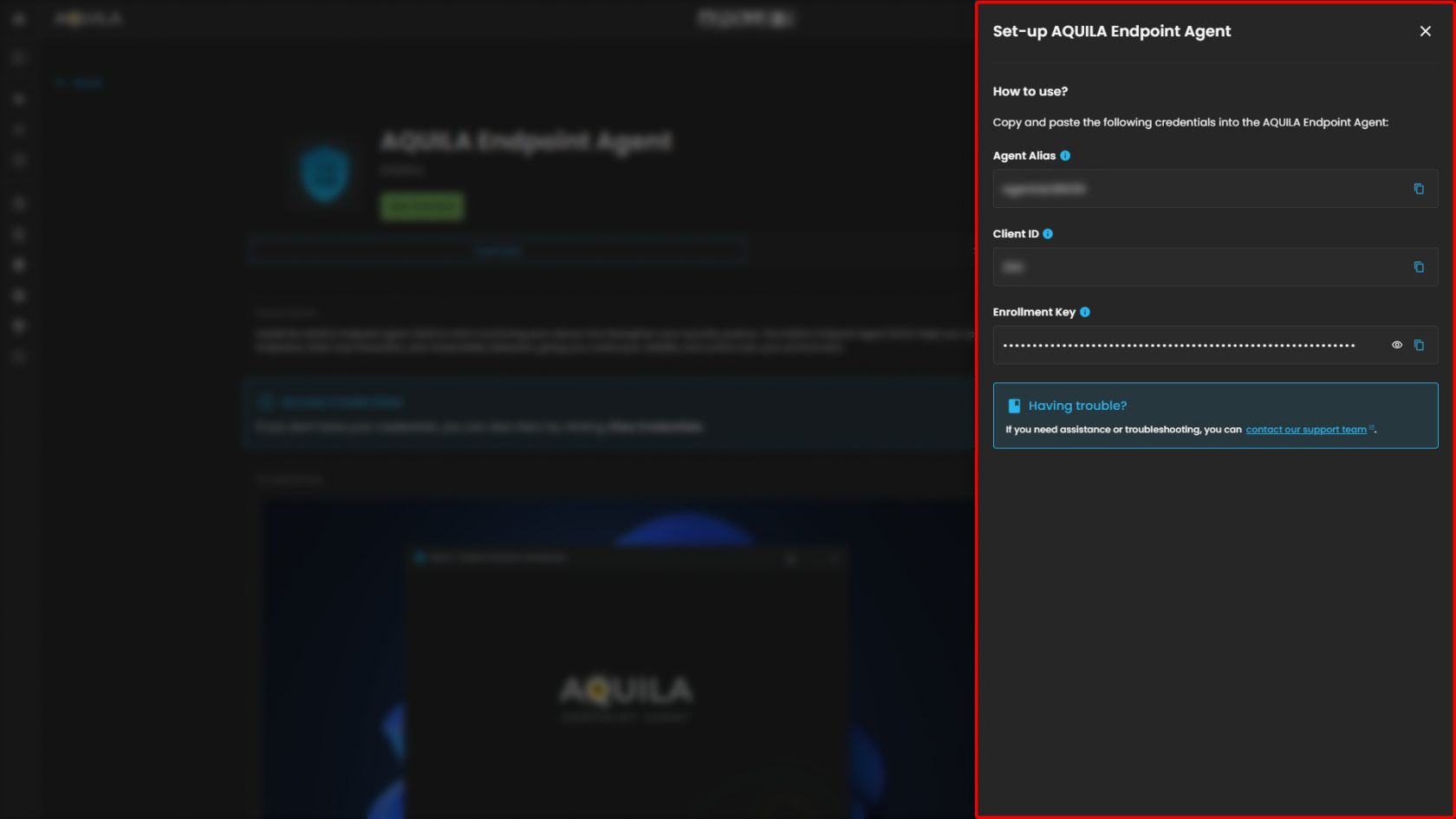
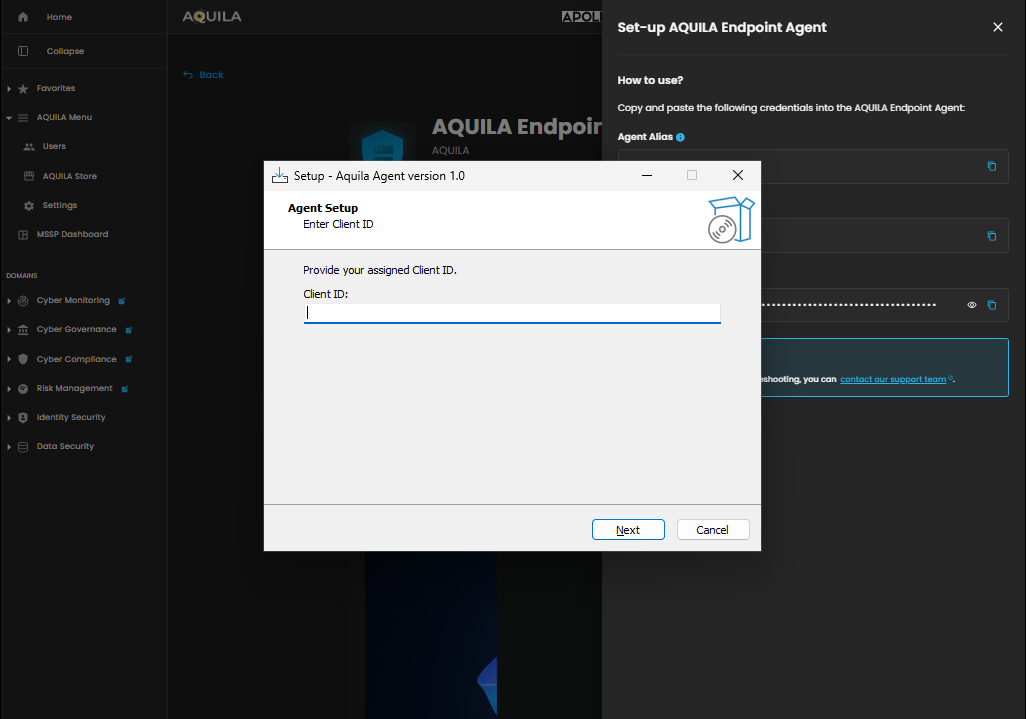
Input the Client ID:ID that was provided through the "view credentials":
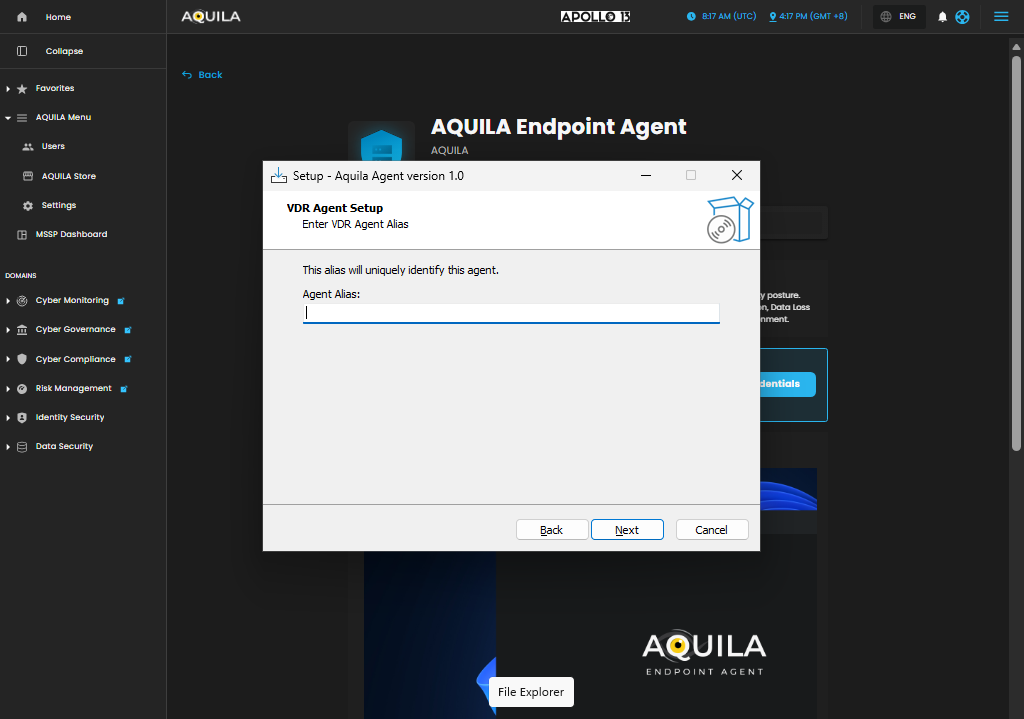
Input the Agent Alias that was provided through the "view credentials": :
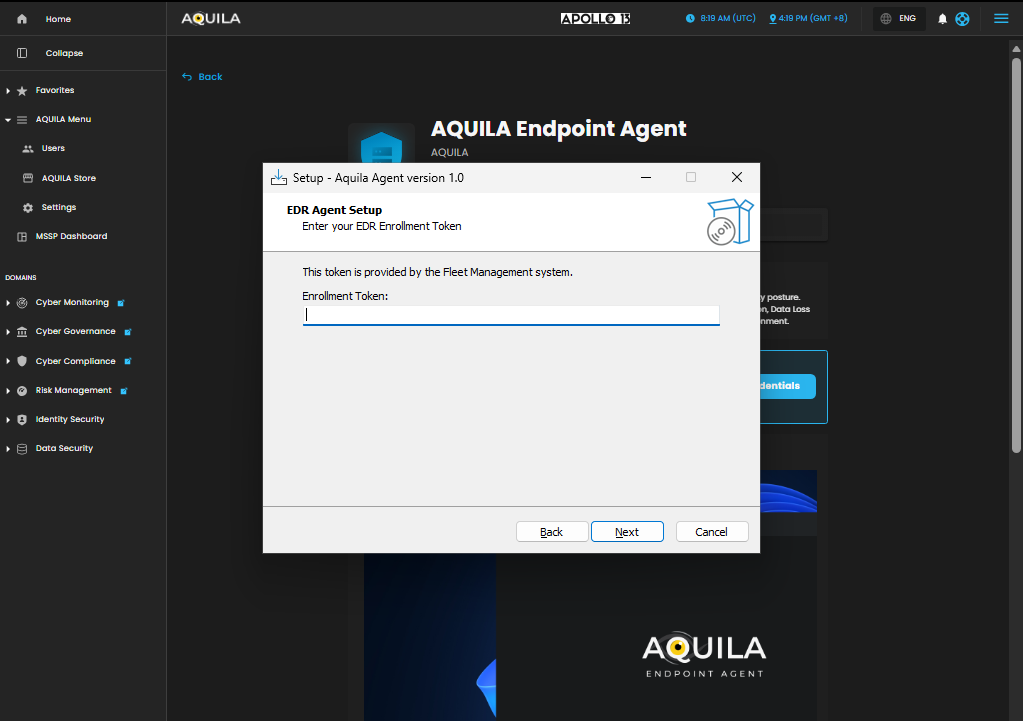
Input Enrollment Token that was provided through the "view credentials": :
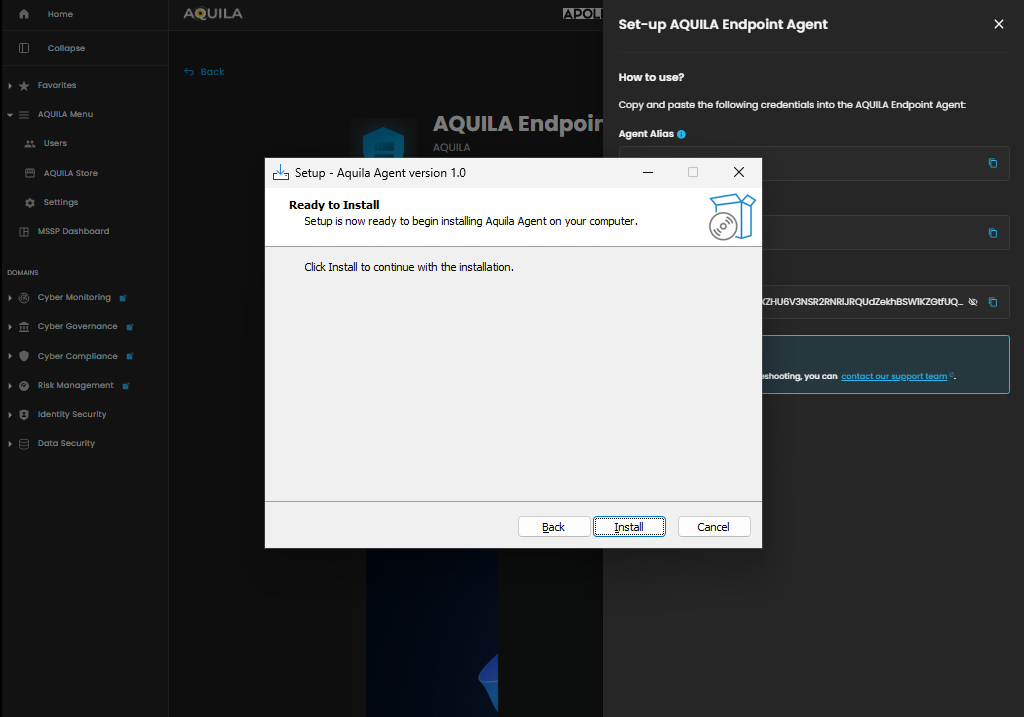
After inputting the Enrollment Token, press install to begin the installation of the AQUILA Endpoint Agent
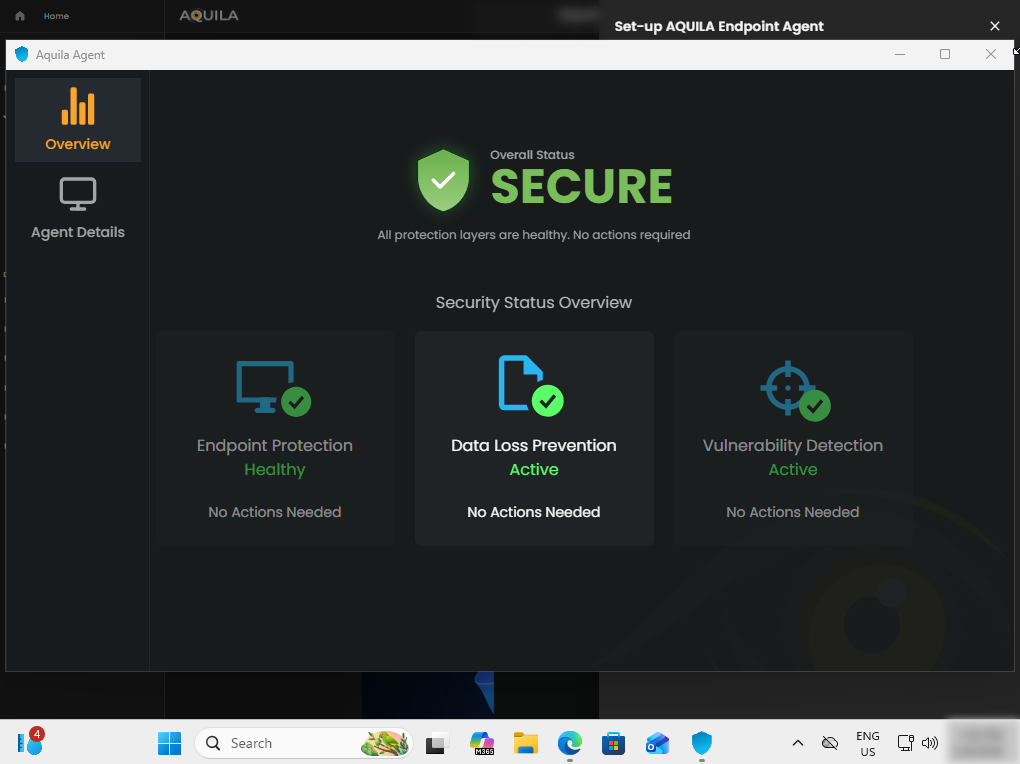
And now the installation is complete.
After the installation we can now proceed and see the scanned files through AQUILA website usdc.cytechint.io.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Note: The name of your Endpoint is using the name of your Personal Computer (PC).
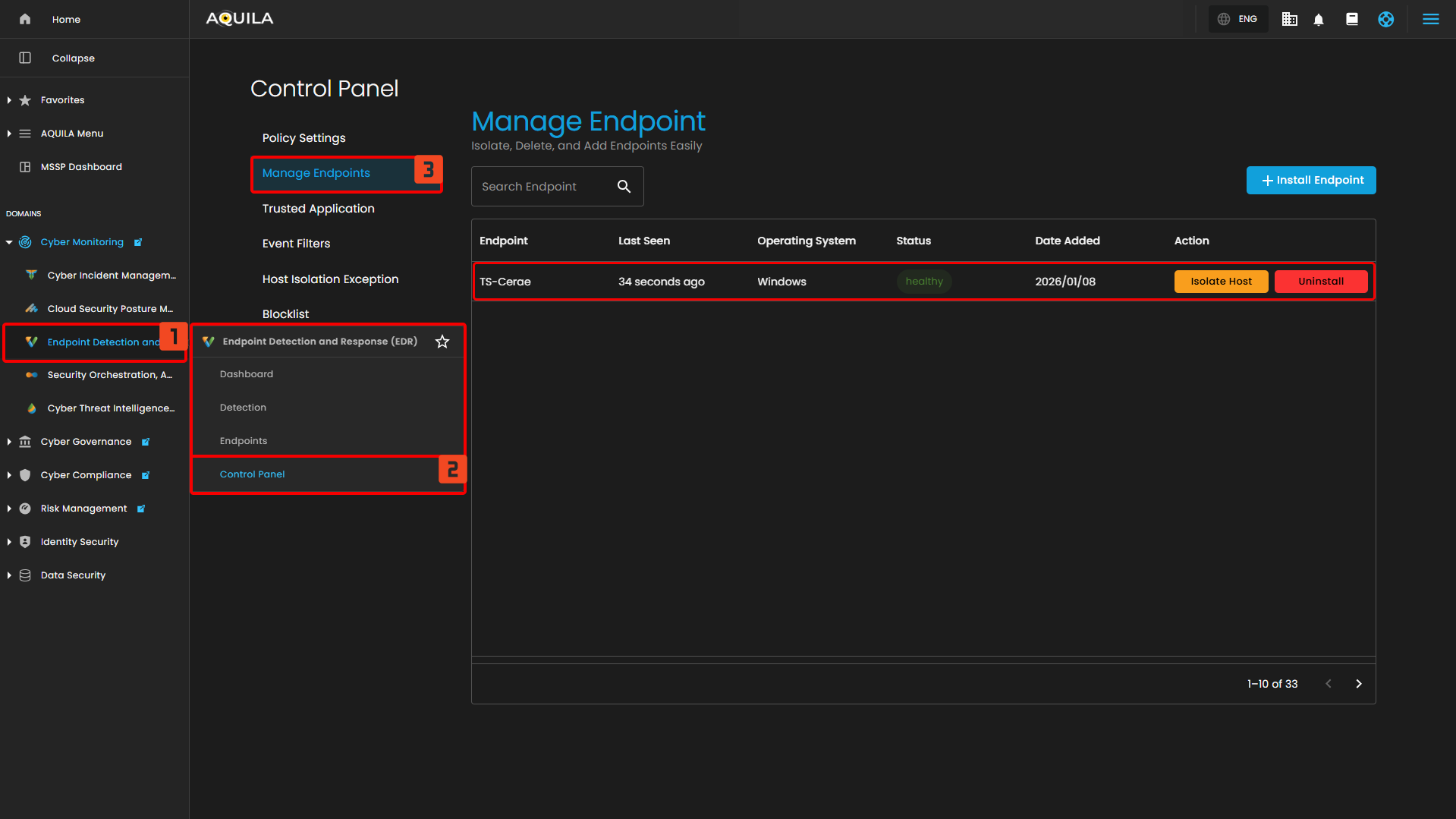
Or the client can access the endpoint in the "Control Panel" as well to isolate it or uninstall the Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) but be wary, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) is a separate application process of the AQUILA Agent Endpoint therefore do not uninstall the Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR). If the client decides to uninstall it, please contact support@cytechint.com to be assisted on the uninstallation for the AQUILA Agent Endpoint. Thank you.
Endpoint Detection and Response Capabilities
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) have multiple features to offer, let's summarize each of those features that could be helpful for monitoring multiple devices.
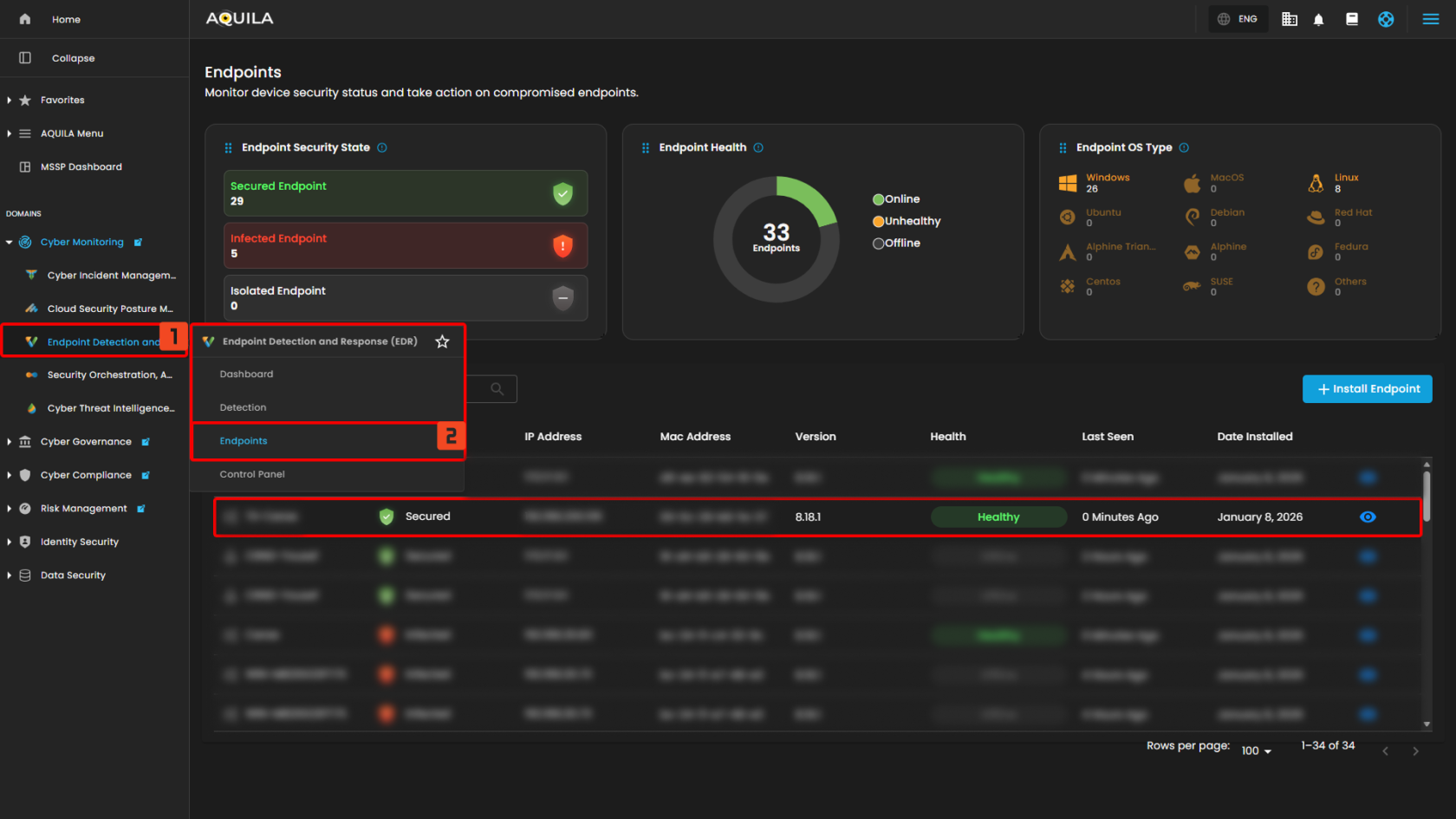
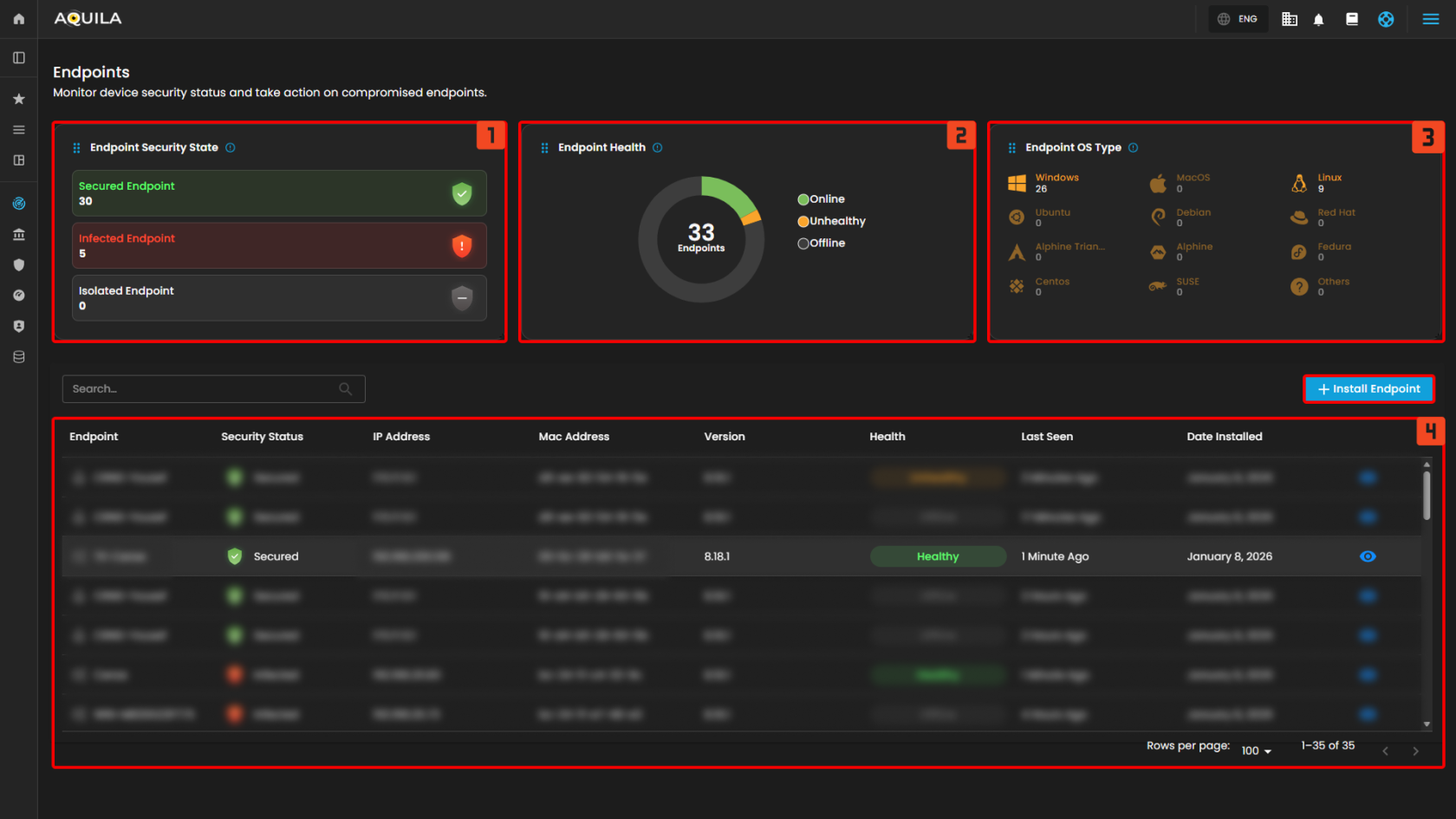
- Endpoint Security State - In this section, the client can identify which Endpoints are Secured, Infected, or Isolated. Which is helpful to identify which Endpoint needs remediation and needs to be isolated.
- Endpoint Health - In this chart, it shows how many Endpoints does the client have and how many are online, unhealthy, or offline.
- Endpoint OS Type - This section provides OS Types and how many Endpoints are installed in a specific Operating System.
- Endpoint List - This list provides information on each Endpoints. The client can also see further information by pressing the eye icon.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
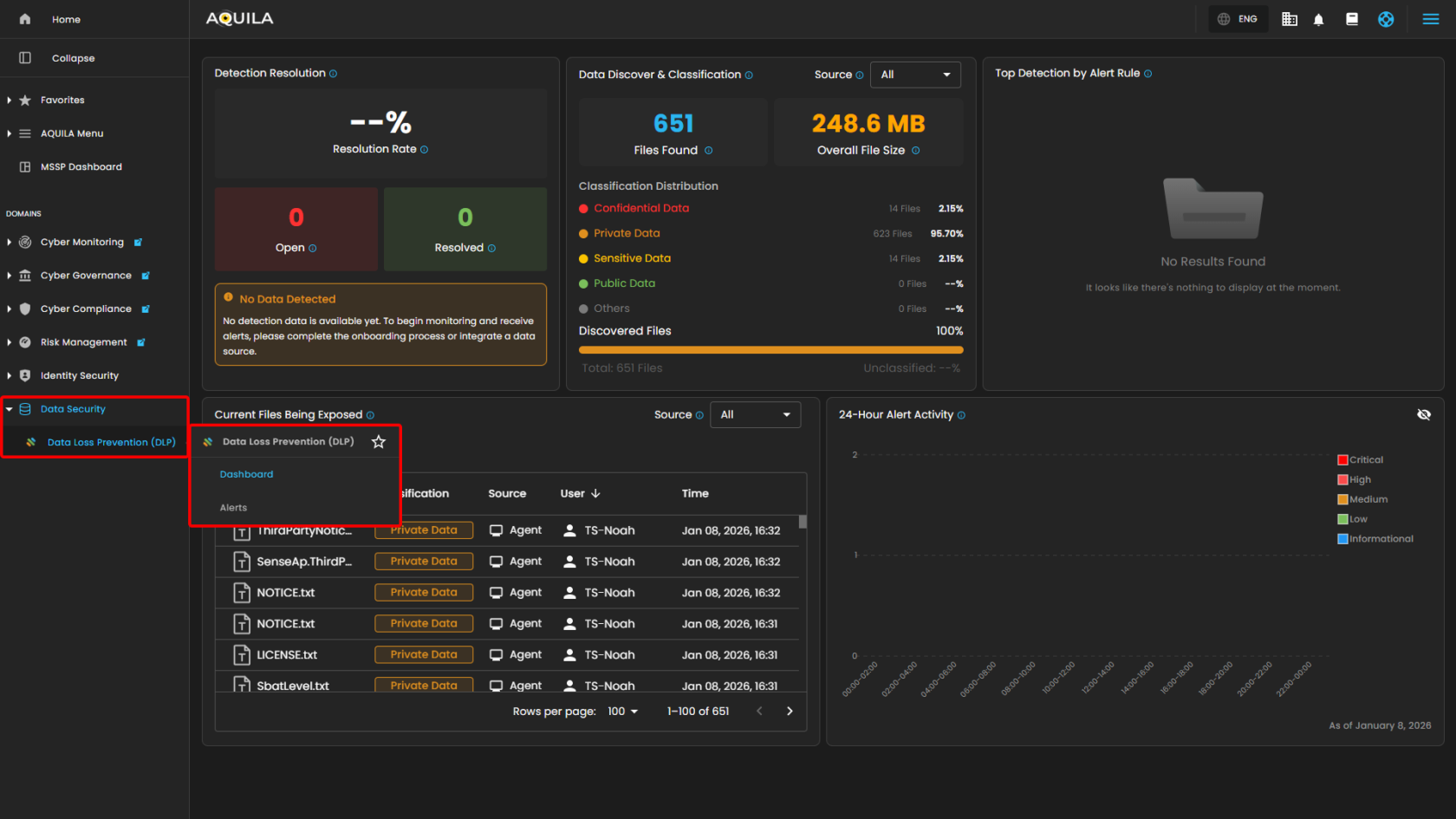
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) is a section where the client can check if the endpoint can detect Private Data, Confidential Data, or Sensitive Data,
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Capabilities
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) has plenty of features to identify and classify files and alert which are helpful for proper monitoring on data.
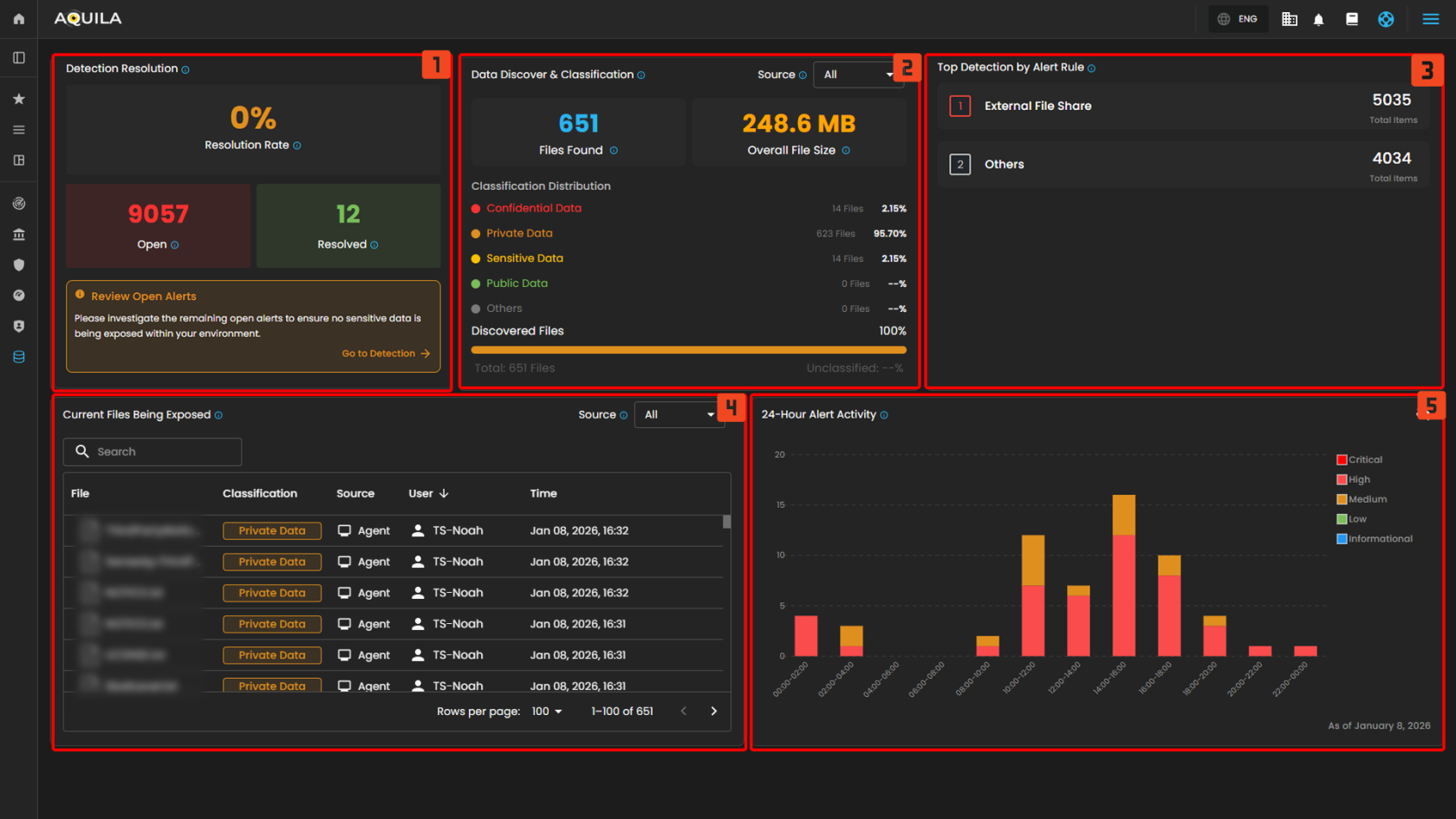
- Detection Resolution - Displays the current resolution rate of alerts generated by the DLP system. This includes how many alerts have been resolved versus those still open and require investigation.
- Data Discover & Classification - Summarizes the total number of files discovered, their combined size, and how they've been classified based on sensitivity levels.
- Top Detection by Alert Rule - Lists the top alert rules triggered by user or system behavior, indicating which policies are being violated most frequently.
- Current Files Being Exposed - Displays real-time visibility into sensitive or exposed files, including classification level, responsible user, and timestamp.
- 24-Hour Alert Activity - This chart displays the number of detections categorized by the type of data involved.
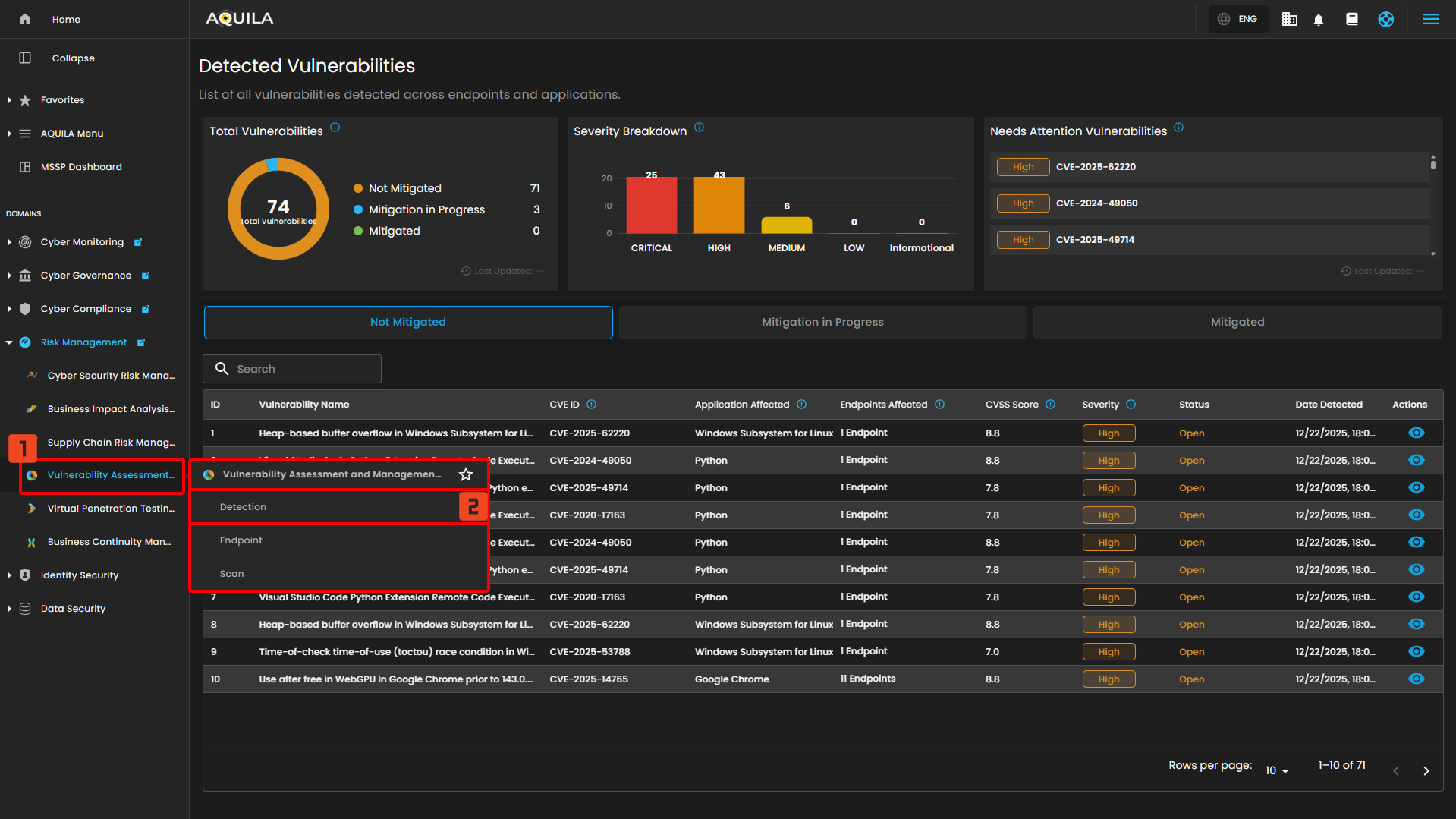
Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR)
Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR) is a section where clients can view detected vulnerabilities on their endpoints, including associated CVEs and the applications and endpoints affected by each vulnerability. Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR) can be navigated on the sidebar inside Risk Management.
Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR) Capabilities
Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR) provide multiple features to determine whether a vulnerability is currently in the process of mitigation or has already been mitigated. These vulnerabilities are based on a list of CVEs, which identify known security issues associated with vulnerable applications.
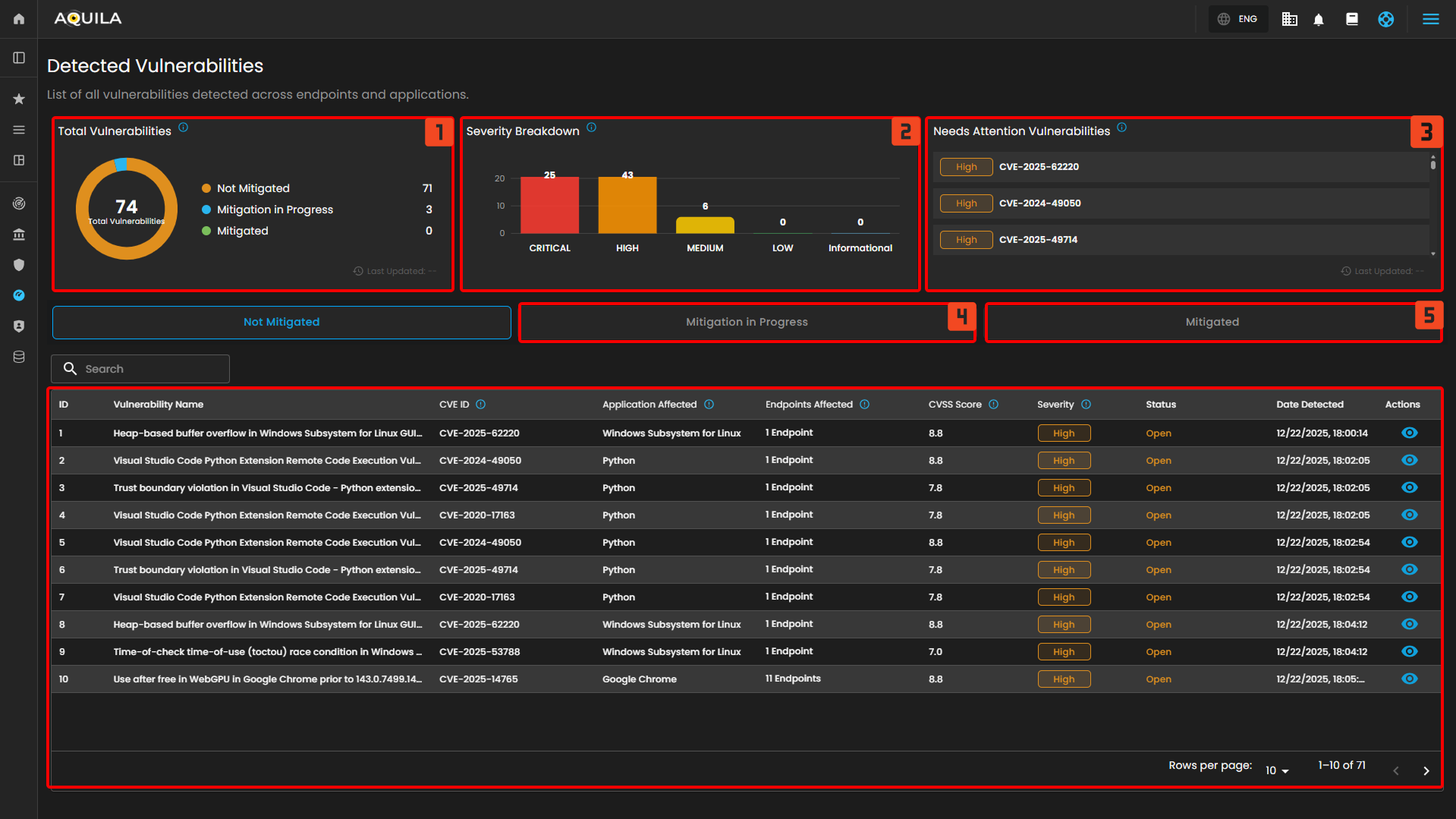
- Total Vulnerabilities - Displays the total number of detected vulnerabilities across all endpoints and their current mitigation status.
- Severity Breakdown - Shows the distribution of vulnerabilities based on their severity levels, helping prioritize remediation efforts.
- Needs Attention Vulnerabilities - Lists critical or high-severity vulnerabilities that require immediate review or action.
- Mitigated in Progress - List of the Vulnerabilities and Endpoints that are currently on process of mitigation.
- Mitigated - List of the Vulnerabilities that are mitigated
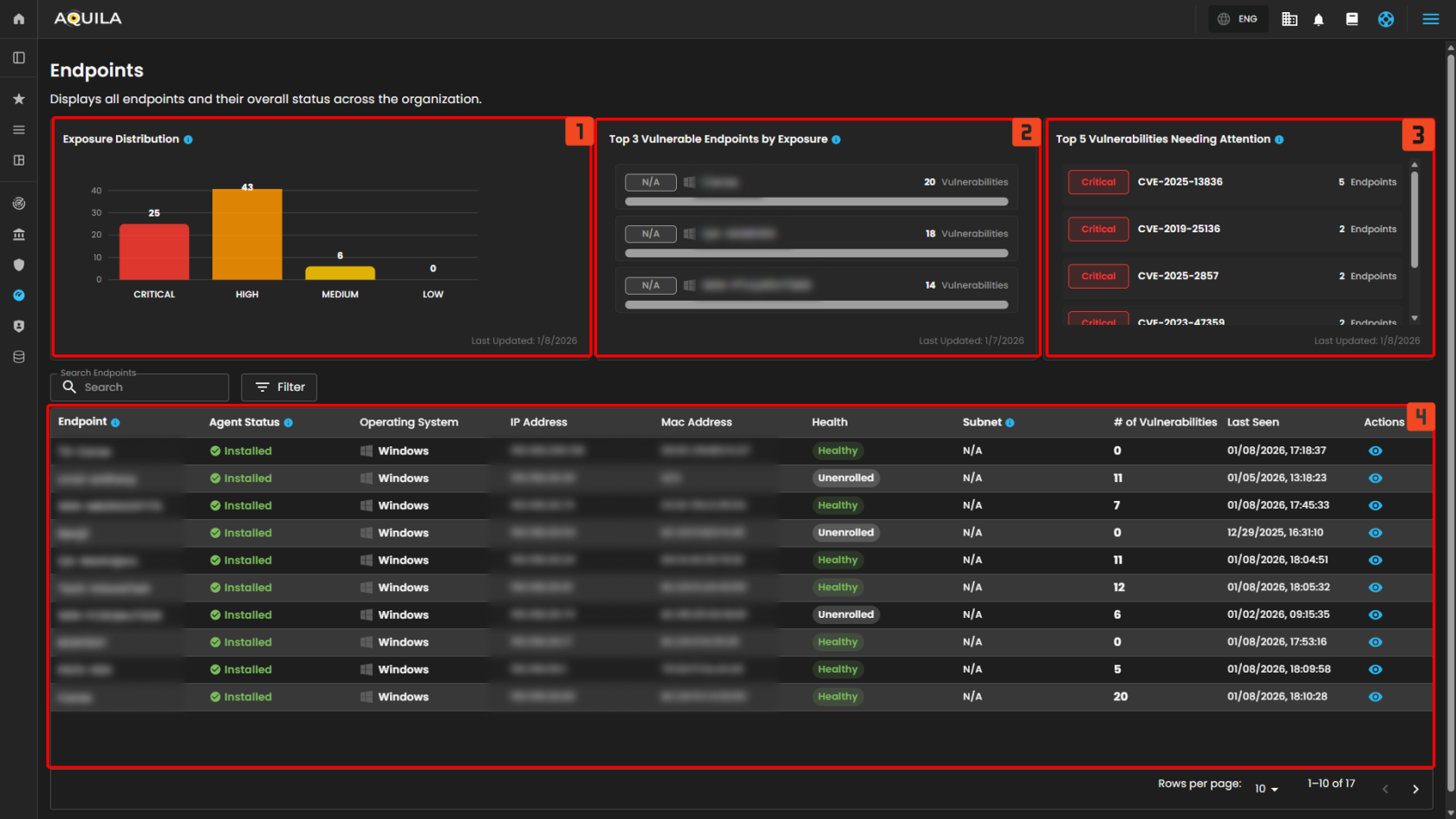
The client can also access the list of their endpoints and how many vulnerabilities are affected, this section can be found below the Detection.
- Exposure Distribution -Shows the number of endpoints based on their current exposure level (Critical, High, Medium, Low).
- Top 3 Vulnerable Endpoints by Exposure - Displays the three endpoints with the highest number of detected critical and high vulnerabilities, broken down by severity level.
- Top 5 Vulnerabilities Needing Attention - Lists the vulnerabilities that impact the most endpoints and require immediate action. Prioritizes Critical and High severity.
- Endpoint list - List of the Endpoints and # of vulnerabilities.
Core Capabilities
What does it do? The AEA provides three main security functions:
1. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
-
Checks your device for threats such as malware, suspicious behavior, or unauthorized changes.
-
Helps ensure your device is compliant with your company’s security rules.
-
Prevent complex attacks - Prevent malware (Windows, macOS, Linux) and ransomware (Windows) from executing, and stop advanced threats with malicious behavior (Windows, macOS, Linux), memory threat (Windows, macOS, Linux), and credential hardening (Windows) protections.
- Alert in high fidelity - Bolster team efficacy by detecting threats centrally and minimizing false positives via extensive corroboration.
- Detect threats in high fidelity - facilitates deep visibility by instrumenting the process, file, and network data in your environments with minimal data collection overhead.
- Triage and respond rapidly - Quickly analyze detailed data from across your hosts. Examine host-based activity with interactive visualizations. Invoke remote response actions across distributed endpoints. Extend investigation capabilities even further with the Osquery integration, fully integrated into Security workflows.
- Secure your cloud workloads - Stop threats targeting cloud workloads and cloud-native applications. Gain real-time visibility and control with a lightweight user-space agent, powered by eBPF. Automate the identification of cloud threats with detection rules and machine learning (ML). Achieve rapid time-to-value with MITRE ATT&CK-aligned detections.
- View terminal sessions - Give your security team a unique and powerful investigative tool for digital forensics and incident response (DFIR), reducing the mean time to respond (MTTR). Session view provides a time-ordered series of process executions in your Linux workloads in the form of a terminal shell, as well as the ability to replay the terminal session.
🛡️Protections Matrix
|
Protection Type |
OS Support |
Detect |
Prevent |
Description |
|
Malware |
Windows, macOS, Linux |
|
✅ |
Blocks known malicious executables and scripts at runtime. |
|
Ransomware |
Windows |
|
✅ |
Detects rapid file changes and unauthorized encryption activity. |
|
Memory Threats |
Windows, macOS, Linux |
|
✅ |
Prevents memory-based attacks like process injection or ROP chains. |
|
Malicious Behavior |
Windows, macOS, Linux |
|
✅ |
Stops suspicious techniques such as abnormal child processes or LOLBins. |
|
Credential Hardening |
Windows |
|
Enabled |
Protects credentials by preventing unauthorized LSASS access. |
📊Event Collection
|
Event Type |
Windows |
macOS |
Linux |
Description |
|
API |
✅ |
– |
Logs sensitive API calls that may indicate injection or system tampering. |
|
|
DLL & Driver Load |
✅ |
– |
Captures DLL/driver loading to detect unsigned or malicious code injection. |
|
|
DNS |
✅ |
– |
Records DNS queries/responses to spot C2, tunneling, or data exfiltration. |
|
|
File |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Monitors file creation, deletion, and modification to detect malware or ransomware. |
|
Network |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Logs connections, ports, and protocols to uncover C2 traffic or lateral movement. |
|
Process |
✅ |
✅ |
✅ |
Tracks process execution, parent/child relationships, and suspicious spawns. |
|
Registry |
✅ |
– |
– |
Detects persistence or tampering with critical Windows registry keys. |
|
Security |
✅ |
– |
– |
Captures login attempts, privilege changes, and policy modifications. |
⚙️Windows Antivirus Registration
- AQUILA EDR can register as the primary antivirus through Windows Security Center.
- Not supported on Windows Server (no Security Center available).
- Enabled to register AQUILA EDR as an official Antivirus solution for Windows OS. This will also disable Windows Defender.
- Current configuration: Sync with malware protection level. ✅
Event Categories – Detailed Reference
| Event Type | Description | Use Case | Example |
|
API Events |
Capture system-level API calls made by processes. These events show how applications interact with the OS, libraries, and security-sensitive functions. | Detect process injection, privilege escalation, exploitation attempts, or use of unusual APIs by non-standard processes. | A Microsoft Office process (WINWORD.EXE) invokes VirtualAllocEx and WriteProcessMemory to inject code into another process. |
| DLL & Driver Load Events | Record the loading of DLLs into user processes and drivers into the OS kernel. Includes path, signature status, and process context. | Detect unsigned or suspicious DLLs/drivers, DLL search order hijacking, and kernel-level rootkits. | An unsigned driver is loaded during system boot, or a legitimate app loads a DLL from a non-standard directory. |
| DNS Events | Log all DNS lookups and responses, showing which domains are queried and by which process. | Detect C2 callbacks, malware beaconing, DNS tunneling, and suspicious domain resolution. | A process repeatedly queries random subdomains of example[.]com, suggesting DGA (Domain Generation Algorithm) use. |
| File Events | Monitor file activity: creation, modification, deletion, renaming, and read access. Includes metadata like file path, hash, and process context. | Detect ransomware encryption, malware staging (dropping executables), tampering with sensitive files, or unauthorized access. | A process writes multiple .encrypted files in rapid succession in a user’s documents folder. |
| Network Events | Capture TCP/UDP connections, ports, IPs, protocols, and process responsible. | Detect outbound connections to malicious infrastructure, lateral movement inside a network, or data exfiltration attempts. | PowerShell initiates a connection to a known malicious IP over port 443 with unusual payload size. |
| Process Events | Record process lifecycle: creation, termination, parent-child relationships, command-line arguments, and integrity info. | Detect abnormal parent-child chains, privilege escalation, process hollowing/injection, and script-based attacks. | explorer.exe launches powershell.exe with a Base64-encoded command to download a payload. |
| Registry Events | Log modifications to Windows Registry, including key creation, deletion, and value changes. | Detect persistence mechanisms, system tampering, and security feature bypasses. | Malware creates HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\malware.exe for auto-start persistence. |
| Security Events | Record security-related activity: authentication attempts, user/group changes, privilege assignments, and policy alterations. | Detect brute force attacks, privilege abuse, unauthorized access, and security control disabling. | Multiple failed login attempts followed by a successful login with a privileged account. |
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
- Monitors how sensitive data is being used, shared, or transferred.
- Helps prevent accidental or intentional leaks of confidential information.
- Provide real-time visibility into data security by tracking potential risks and exposures.
- Monitor unresolved alerts to identify and address security issues promptly.
- Identify sensitive data that may be exposed and classify files accordingly (e.g., confidential, private, or public).
- Highlight trends in alert activity to spot and respond to critical incidents.
- Serve as a central tool for ensuring sensitive information remains secure and compliant with organizational policies.
🛡️Protections Matrix
| DLP Purpose | Description | DLP Detect |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Sensitive Data | Finds confidential or regulated information (PII, PHI, PCI, IP). | Recognizes sensitive data using patterns, keywords, regex, file classification, or ML. |
| Monitor Data Usage | Observes how data is accessed, edited, or transferred. | Flags unusual or risky user activities (e.g., mass copying or emailing). |
| Prevent Unauthorized Data Transfer | Ensures data doesn’t leave the organization improperly. | Detects attempts to send data via email, USB, cloud apps, or printing. |
| Protect Against Data Breaches | Reduces risk from insiders, malware, or accidents. | Alerts on anomalous access or large data movement. |
| Enforce Security Policies | Ensures compliance with regulations (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI). | Detects policy violations automatically. |
| Control Data Flow | Manages how data moves inside/outside the network. | Detects data movement patterns and unauthorized destinations. |
| Provide Visibility & Reporting | Offers logs and insights for audits/investigations. | Detects events and logs all data-related activities. |
3. Vulnerability Detection and Response (VDR)
- Scans the device for weaknesses, outdated software, or security gaps that hackers could exploit.
- Alerts administrators so they can fix issues before they become serious threats.
🛡️Protections Matrix
| Category / Purpose | Description | Detect |
|---|---|---|
| Identify System Weaknesses | Finds flaws in software, hardware, or configurations that attackers could exploit. | Scans for outdated software, missing patches, weak configurations, known CVEs. |
| Assess Security Posture | Evaluates how secure an environment is against threats. | Runs vulnerability assessments, baseline checks, and compliance scans. |
| Detect Misconfigurations | Finds incorrect or insecure setup of systems or applications. | Identifies open ports, weak permissions, default passwords, insecure protocols. |
| Find Network Vulnerabilities | Looks for weaknesses within network infrastructure. | Scans firewalls, routers, switches, exposed services, and network paths. |
| Identify Application Vulnerabilities | Locates flaws in web and software applications. | Detects OWASP Top 10 issues (XSS, SQL Injection, CSRF, etc.). |
| Detect Unauthorized Access Paths | Finds hidden or unintended ways attackers could enter the system. | Identifies backdoors, exposed APIs, weak authentication paths. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Ongoing observation for new or emerging vulnerabilities. | Uses automated scanning, SIEM alerts, threat intelligence feeds. |
| Risk Prioritization | Determines which vulnerabilities are most dangerous. | Rates vulnerabilities using CVSS scores and exploit likelihood. |
Why is it important?
- It gives your IT or security team continuous visibility into the health and security status of all devices.
- It allows them to control risks proactively, rather than waiting for something bad to happen.
- Overall, it strengthens the security posture of your organization by ensuring every device is properly monitored and protected.
Requirements
- Your device must have at least 1 CPU core running at 2 GHz or higher (2 cores recommended).
- Requires a minimum of 2 GB DDR4 RAM (3 GB recommended).
- Needs at least of 1.5 GB of available SSD storage space (2 GB recommended for optimal performance).
- Compatible with Windows OS.
- Requires a stable internet connection (minimum 5 Mbps) to connect with AQUILA services.